Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The first programming project involves extending the Java skeleton program that it is provided in the attached . zip file. That skeleton program displays a



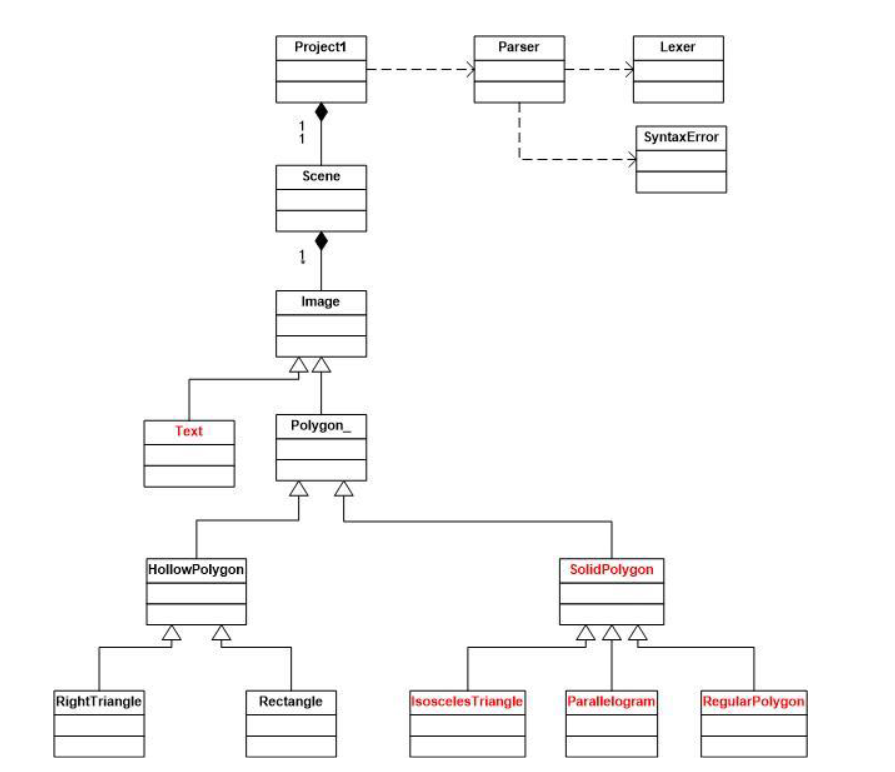


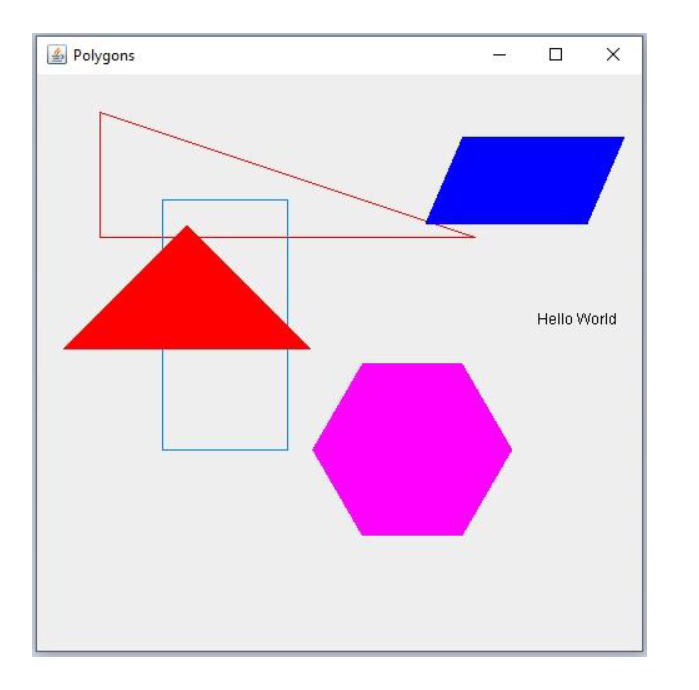
The first programming project involves extending the Java skeleton program that it is provided in the attached . zip file. That skeleton program displays a scene of graphic images contained in a scene definition file. The grammar for that scene definition file is shown below: Scene SCENE IDENTIFIER number_list images END ' ' images image images I image image right_triangle I rectangle right_triangle RIGHT TRIANGLE COLOR number_list AT number_list HEIGHT NUMBER WIDTH NUMBER ';' rectangle RECTANGLE COLOR number_list AT number_list HEIGHT NUMBER WIDTH NUMBER ';' number_list ' (' numbers ')' numbers NUMBER NUMBER ' '' numbers In the above grammar, terminal symbols are upper case names or character literals shown in blue and nonterminal symbols are lower case names shown in red. EBNF metacharacters are shown in black. Tokens can be separated by any number of spaces. Identifiers and keywords are strings of alphabetic characters. Both are case sensitive. Numbers are unsigned integers. That program reads in the scene definition file that defines the image objects in a scene and creates those objects, inserts them into the scene and displays that scene. You are to modify the program so that it will parse and display the additional images defined by the expanded grammar shown below with the additions to the grammar highlighted in yellow: scene SCENE IDENTIFIER number_list images END '.' images image images image image right triangle | rectangle | parallelogram | regular_polygon | isosceles | text right_triangle RIGHT_TRIANGLE COLOR number_list AT number_list HEIGHT NUMBER WIDTH NUMBER ';' rectangle RECTANGLE_ COLOR number_list AT number_list HEIGHT NUMBER WIDTH NUMBER ' ; ' parallelogram PARALLELOGRAM COLOR number_list AT number_list number_list OFFSET NUMBER ';' regular polygon REGULAR_POLYGON COLOR number_list AT number_list SIDES NUMBER RADIUS NUMBER ';' isosceles ISOSCELES COLOR number_list AT number_list HEIGHT NUMBER WIDTH NUMBER ';' text TEXT COLOR number_list AT number_list STRING ';' number_list ' (' numbers ')' regular polygon REGULAR POLYGON COLOR number_list AT number_list SIDES NUMBER RADIUS NUMBER ';' isosceles ISOSCELES COLOR number_list AT number_list HEIGHT NUMBER WIDTH NUMBER ';' text TEXT COLOR number_list AT number_list STRING '; ' number_list ' (' numbers ')'' numbers NUMBER I NUMBER ',' numbers The UML diagram for the whole project is shown below: The classes shown in black are included in the skeleton project. You must complete the project by writing those classes shown in red and modifying the Parser class so that it will parse the expanded grammar. Below is a description of each of the five classes that you must write: The Text class must contain a constructor that is supplied the color that defines the text color, a point that specifies the text location and a string containing the text to be displayed. It must also contain a draw function because it is extends the abstract class Image. The draw function must draw the text using the method drawstring in Graphics class. The Solidpolygon class must contain a constructor that is passed the number of vertices in the polygon and its color. It must define the method drawPolygon because it is extends the abstract class Polygon.. It should call the fillpolygon method of the Graphics class to draw a solid polygon. The Isoscelestriangle class must have a constructor that is supplied the color of the triangle, a point that specifies the location of the top vertex, and the height and width of the triangle. It must allocate the arrays of x and y coordinates that defines the triangle and it must compute their values. The Parallelogram class must have a constructor that is supplied the color of the parallelogram, two points that specifies the location of the upper left and lower right vertices in addition to an x offset value that specifies the x distance between the upper and lower left vertices. It must allocate the arrays of x and y coordinates that defines the parallelogram and it must compute their values. The Regularpolygon class must contain a constructor that is supplied the color of the polygon, the number of sides, a point that specifies the location of its center, and the radius, which defines the distance between the center and each of the vertices. It must allocate the arrays of x and y coordinates that defines the regular polygon and it must compute their values. Below is a sample of a scene definition file that would provide input to the program: Scene Polygons (500, 500) Rightriangle Color (255, 0, 0) at (50,30) Height 100 Width 300; Rectangle Color (0,128,255) at (100,100) Height 200 Width 100; Isosceles Color (255, 0, 0) at (120, 120) Height 100 Width 200; Parallelogram Color (0, 0, 255) at (340,50)(440,120) offset 30; Regularpolygon Color (255, 0, 255) at (300, 300) Sides 6 Radius 80; Text Color (0, 0, 0) at (400, 200) "Hello World"; End. Shown below is the scene that should be produced when the program is provided with the above scene definition. Polygons
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


