Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The first two pictures are info that may be needed, the third picture has the two problems, the chart for E and the question for

The first two pictures are info that may be needed, the third picture has the two problems, the chart for E and the question for F. Thank you
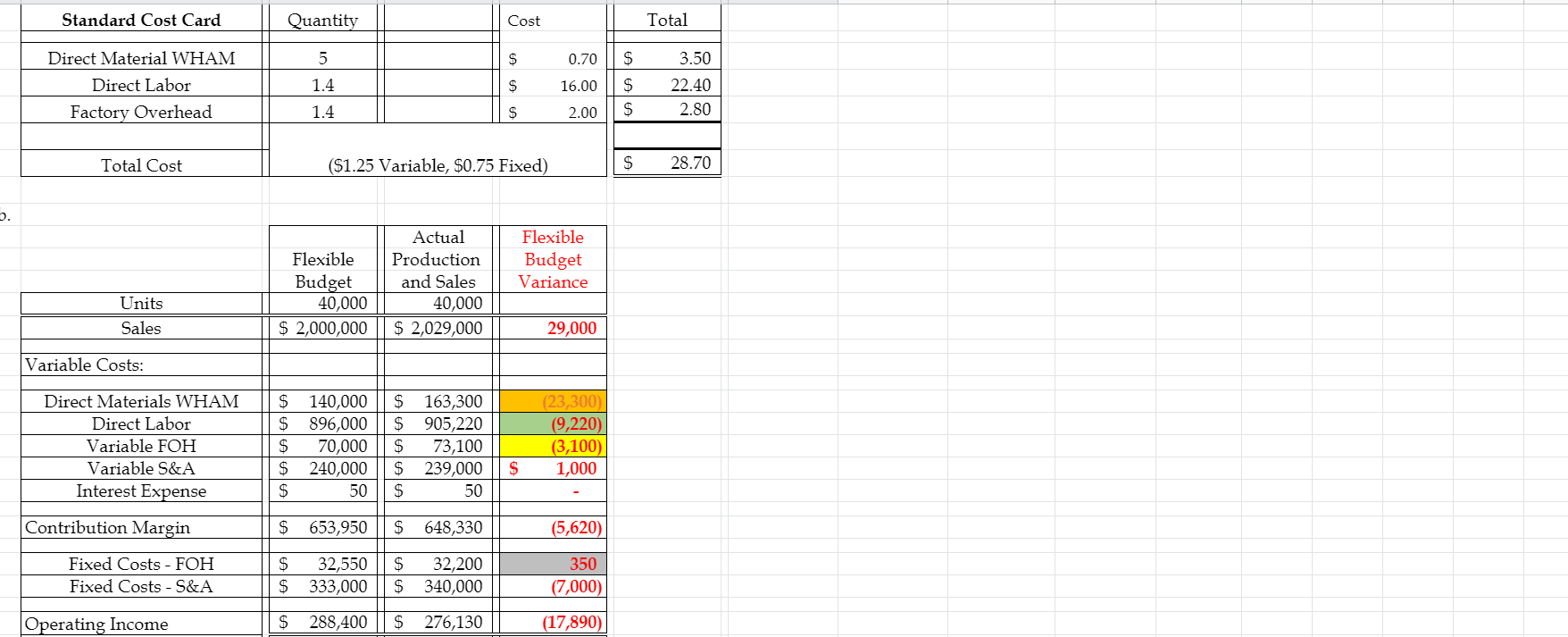
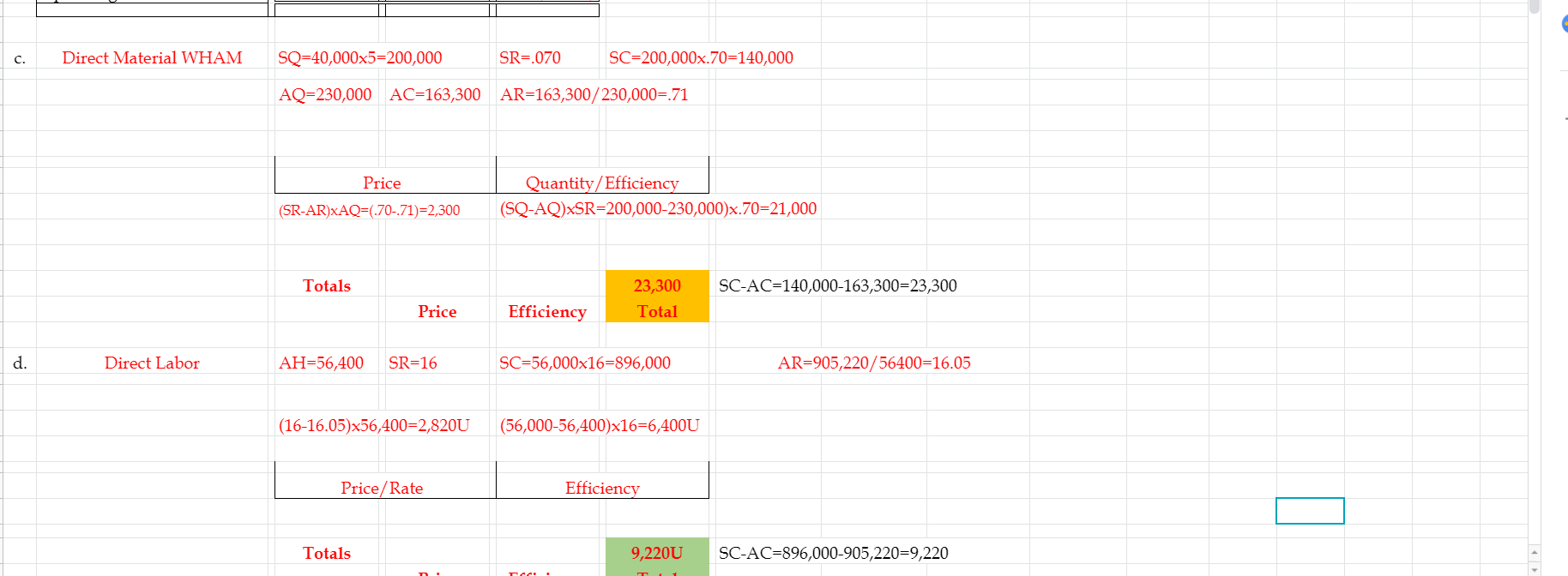
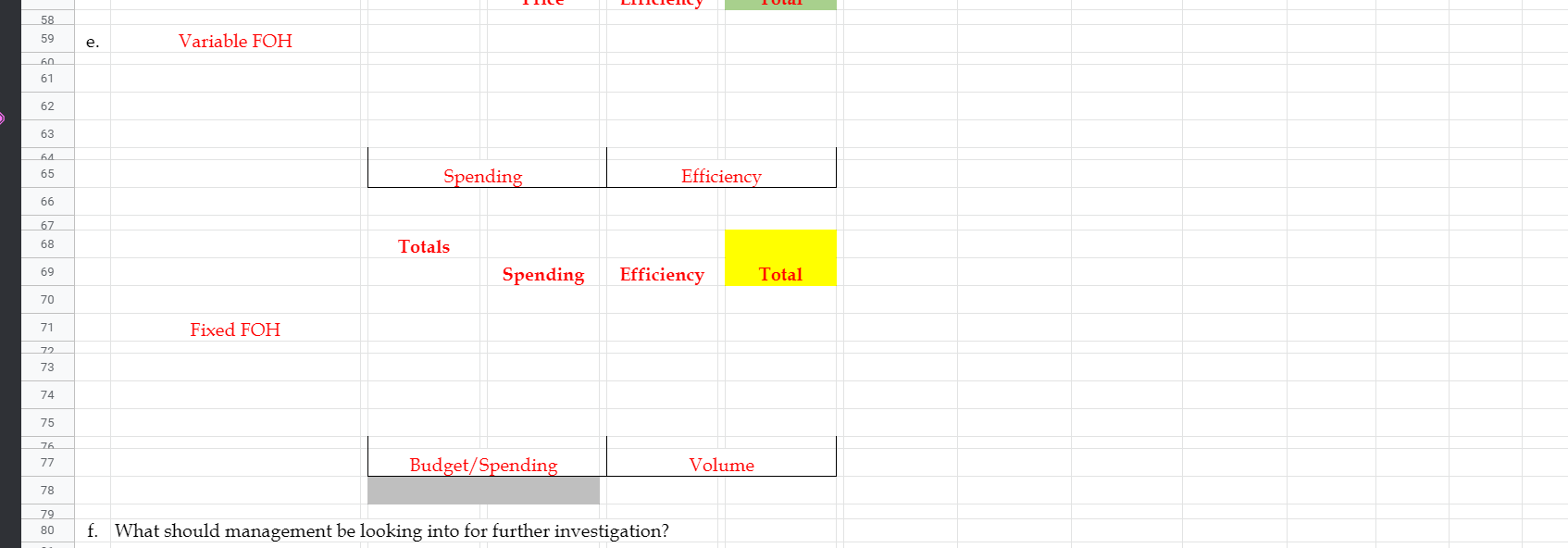
Vaughan Company had a fantastic sales 3rd Quarter! Management had wanted to wait until quarter end to do a post mortem of the annual results and do some investigations if necessary. Here is what actually happened: Total sales were $2,029,000 for 40,000 units. Management failed to be able to buy enough direct materials to produce the required units for ending inventory nor to keep the required direct materials on hand for ending inventory requirements due to a shortage of WHAM during the quarter. Total Production for 3rd quarter was 40,000 units. Vaughan uses LIFO inventory method. Regarding WHAM, Vaughan purchased and used 230,000 pounds at a total cost of $163,300. Vaughan used 56,400 DLH (direct labor hours) to make the 40,000 units at a total labor cost of $905,220. Actual Variable FOH was $73,100 and actual Fixed FOH was $32,200. Even though Production ended up being 40,000 units, the cash borrowings indicated by the static budget dictated that Vaughan borrow money ($2,000) on the last day of July and they did so. They also paid it back at the end of the September as budgeted. Selling and Administrative expenses totaled $579,000. $239,000 was variable and the rest was fixed. We have not covered S&A variances, but never the less, the difference between what actually occurred and what should have happened (the flexible budget) can still be illuminating. (a) Prepare a standard cost card for a widget. (b) Prepare an flexible budget performance report comparing actual production/ sales to a flexible budget of such sales/ costs (Like #2 on the top of page 842 in our text) (c) Prepare the direct material variances (price and efficiency/quantity) for each material (d) Prepare the direct labor variances (price/rate and efficiency) (e) Prepare the Variable (spending & efficiency) and Fixed FOH (budget/spending & volume) variances. (refer to the appendix for the factory overhead variances) Standard Cost Card Quantity Cost Total 5 $ 0.70 $ Direct Material WHAM Direct Labor Factory Overhead 1.4 $ 16.00 $ 3.50 22.40 2.80 1.4 $ 2.00 $ Total Cost ($1.25 Variable, $0.75 Fixed) $ 28.70 Actual Production and Sales 40,000 $ 2,029,000 Flexible Budget Variance Flexible Budget 40,000 $ 2,000,000 Units Sales 29,000 Variable Costs: Direct Materials WHAM Direct Labor Variable FOH Variable S&A Interest Expense $ $ $ $ $ 140,000 896,000 70,000 240,000 50 S 163,300 $ 905,220 $ 73,100 S 239,000 $ 50 (23,300) (9,220) (3,100) 1,000 $ Contribution Margin $ 653,950 S 648,330 (5,620) Fixed Costs - FOH Fixed Costs - S&A $ $ 32,550 333,000 $ $ 32,200 340,000 350 (7,000) Operating Income $ 288,400 $ 276,130 (17,890) C. Direct Material WHAM SQ=40,000x5=200,000 SR=.070 SC=200,000x.70=140,000 AQ=230,000 AC=163,300 AR=163,300/230,000= 71 Price Quantity/Efficiency (SQ-AQ)XSR=200,000-230,000)x.70=21,000 (SR-AR)XAQ=0.70-.71)=2,300 Totals SC-AC=140,000-163,300=23,300 23,300 Total Price Efficiency d. Direct Labor AH=56,400 SR=16 SC=56,000x16=896,000 AR=905,220/56400=16.05 (16-16.05)x56,400=2,820U (56,000-56,400)x16=6,400U Price/Rate Efficiency Totals 9,2200 SC-AC=896,000-905,220=9,220 58 59 e. Variable FOH 60 61 62 63 64 65 Spending Efficiency 66 67 68 Totals 69 Spending Efficiency Total 70 71 Fixed FOH 72 73 74 75 76 77 Budget/Spending Volume 78 79 80 f. What should management be looking into for further investigation? Vaughan Company had a fantastic sales 3rd Quarter! Management had wanted to wait until quarter end to do a post mortem of the annual results and do some investigations if necessary. Here is what actually happened: Total sales were $2,029,000 for 40,000 units. Management failed to be able to buy enough direct materials to produce the required units for ending inventory nor to keep the required direct materials on hand for ending inventory requirements due to a shortage of WHAM during the quarter. Total Production for 3rd quarter was 40,000 units. Vaughan uses LIFO inventory method. Regarding WHAM, Vaughan purchased and used 230,000 pounds at a total cost of $163,300. Vaughan used 56,400 DLH (direct labor hours) to make the 40,000 units at a total labor cost of $905,220. Actual Variable FOH was $73,100 and actual Fixed FOH was $32,200. Even though Production ended up being 40,000 units, the cash borrowings indicated by the static budget dictated that Vaughan borrow money ($2,000) on the last day of July and they did so. They also paid it back at the end of the September as budgeted. Selling and Administrative expenses totaled $579,000. $239,000 was variable and the rest was fixed. We have not covered S&A variances, but never the less, the difference between what actually occurred and what should have happened (the flexible budget) can still be illuminating. (a) Prepare a standard cost card for a widget. (b) Prepare an flexible budget performance report comparing actual production/ sales to a flexible budget of such sales/ costs (Like #2 on the top of page 842 in our text) (c) Prepare the direct material variances (price and efficiency/quantity) for each material (d) Prepare the direct labor variances (price/rate and efficiency) (e) Prepare the Variable (spending & efficiency) and Fixed FOH (budget/spending & volume) variances. (refer to the appendix for the factory overhead variances) Standard Cost Card Quantity Cost Total 5 $ 0.70 $ Direct Material WHAM Direct Labor Factory Overhead 1.4 $ 16.00 $ 3.50 22.40 2.80 1.4 $ 2.00 $ Total Cost ($1.25 Variable, $0.75 Fixed) $ 28.70 Actual Production and Sales 40,000 $ 2,029,000 Flexible Budget Variance Flexible Budget 40,000 $ 2,000,000 Units Sales 29,000 Variable Costs: Direct Materials WHAM Direct Labor Variable FOH Variable S&A Interest Expense $ $ $ $ $ 140,000 896,000 70,000 240,000 50 S 163,300 $ 905,220 $ 73,100 S 239,000 $ 50 (23,300) (9,220) (3,100) 1,000 $ Contribution Margin $ 653,950 S 648,330 (5,620) Fixed Costs - FOH Fixed Costs - S&A $ $ 32,550 333,000 $ $ 32,200 340,000 350 (7,000) Operating Income $ 288,400 $ 276,130 (17,890) C. Direct Material WHAM SQ=40,000x5=200,000 SR=.070 SC=200,000x.70=140,000 AQ=230,000 AC=163,300 AR=163,300/230,000= 71 Price Quantity/Efficiency (SQ-AQ)XSR=200,000-230,000)x.70=21,000 (SR-AR)XAQ=0.70-.71)=2,300 Totals SC-AC=140,000-163,300=23,300 23,300 Total Price Efficiency d. Direct Labor AH=56,400 SR=16 SC=56,000x16=896,000 AR=905,220/56400=16.05 (16-16.05)x56,400=2,820U (56,000-56,400)x16=6,400U Price/Rate Efficiency Totals 9,2200 SC-AC=896,000-905,220=9,220 58 59 e. Variable FOH 60 61 62 63 64 65 Spending Efficiency 66 67 68 Totals 69 Spending Efficiency Total 70 71 Fixed FOH 72 73 74 75 76 77 Budget/Spending Volume 78 79 80 f. What should management be looking into for further investigationStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


