Question
The five equations that make up the dynamic AD-AS model are a) Derive the long-run equilibrium for the dynamic AD-AS model. Assume there are no
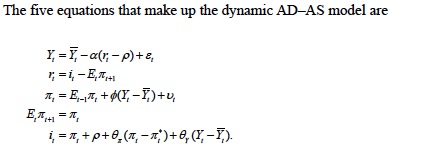

The five equations that make up the dynamic AD-AS model are
a) Derive the long-run equilibrium for the dynamic AD-AS model. Assume there
are no shocks to demand or supply (?" = ?" = 0) and inflation has stabilized
(?" = ?"#$). Be sure to show each step you follow.
b) If the central bank decides to reduce the target inflation rate from 5% to 2%.
Using a graph of the dynamic AD-AS model, show the effect of this change.
What happens to the nominal interest rate immediately after the policy change
and in the long run? Explain.
c) Suppose that there is a shock to aggregate supply (for example, a sudden
increase in the oil price), which causes ?" rise to 1 percent for one period and
subsequently returns to zero. Using a graph of the dynamic AD-AS model,
show the effect of this change on output and inflation rate. What happens to
the nominal interest rate immediately after the policy change and in the long
run?
d) Assume that the central bank decides to increase the response of interest rate
to inflation (by increasing ?%), how does this change in policy alter the
response of the economy to a supply shock you discussed in part c)? Give an
economic explanation.
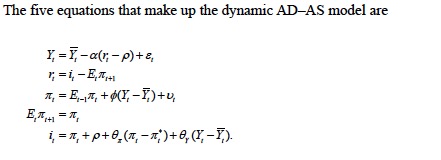

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


