Question
The following hypothetical machine is from Chapter 1 of our textbook: In the following problem sets, we will use this expanded set of list of
The following hypothetical machine is from Chapter 1 of our textbook:
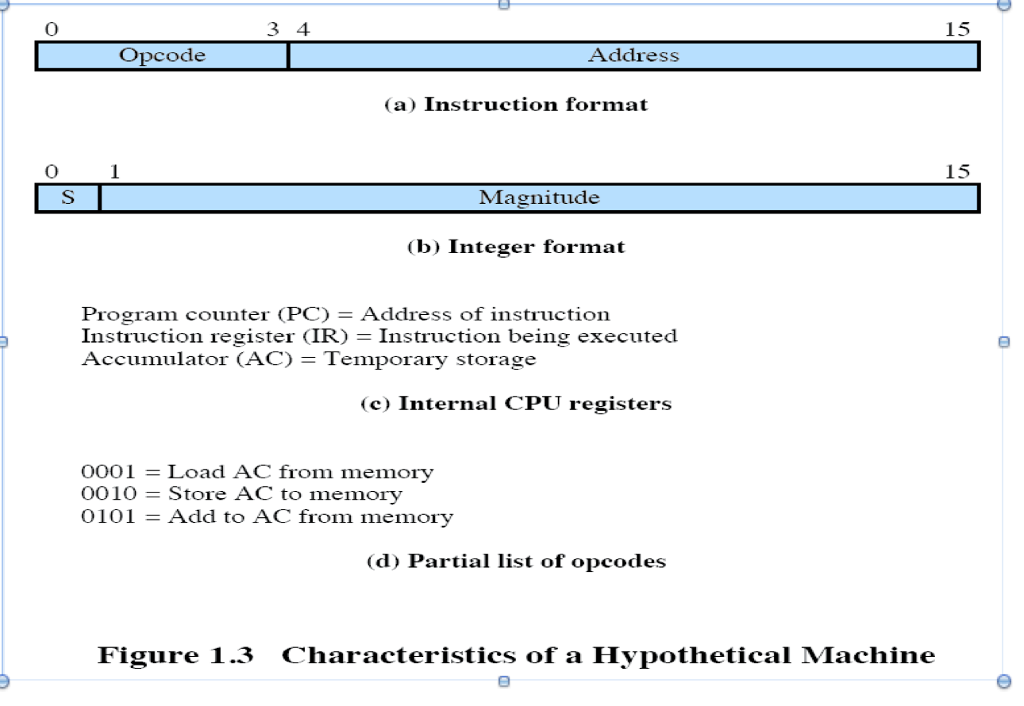
In the following problem sets, we will use this expanded set of list of opcodes for our hypothetical machine:
0001 = Load AC from memory
0010 = Store AC to memory
0011 = Jump to address
0100 = Subtract memory from AC (result in AC)
0101 = Add to AC from memory (result in AC)
Perform program fetch/execute cycles for the following initial memory and program states. NOTE: one of the problems uses the Jump to address instruction to implement a loop. You do not need to simulate more than the 4 fetch/execute cycles for this problem, even though the program in principle would execute forever.
| Fetch stage | Execute stage |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 1 |
Step 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 3 |
Step 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 5 |
Step 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Step 7 |
Step | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


