Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The following is a comprehensive hedging problem. Answer parts (a)-(g). < Suppose today is January 2 and BSK, Inc. is a US firm that
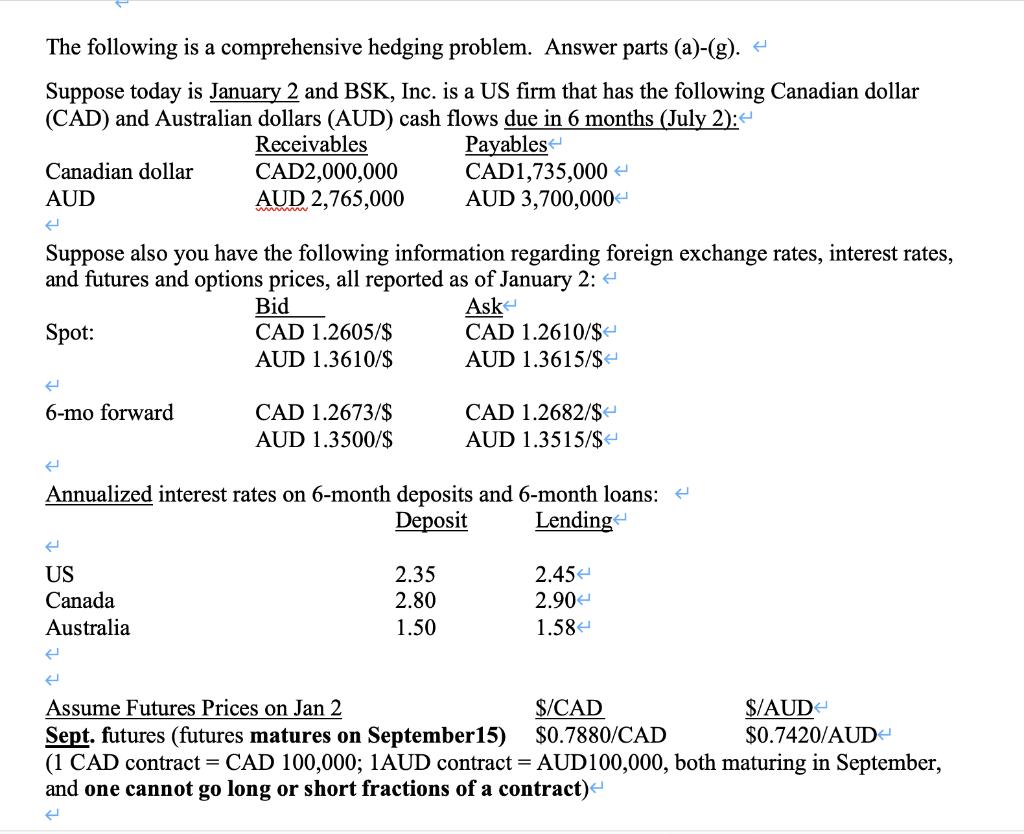


The following is a comprehensive hedging problem. Answer parts (a)-(g). < Suppose today is January 2 and BSK, Inc. is a US firm that has the following Canadian dollar (CAD) and Australian dollars (AUD) cash flows due in 6 months (July 2): < Receivables Payables CAD2,000,000 CAD1,735,000 < AUD 3,700,000 AUD 2,765,000 Canadian dollar AUD Suppose also you have the following information regarding foreign exchange rates, interest rates, and futures and options prices, all reported as of January 2: < Ask Spot: CAD 1.2610/$ < AUD 1.3615/$ < 6-mo forward Bid CAD 1.2605/$ AUD 1.3610/$ ( US Canada Australia CAD 1.2673/$ AUD 1.3500/$ Annualized interest rates on 6-month deposits and 6-month loans: < Deposit Lending CAD 1.2682/$ AUD 1.3515/$ < 2.35 2.80 1.50 2.45 < 2.90 1.58 Assume Futures Prices on Jan 2 $/CAD $/AUD $0.7420/AUD Sept. futures (futures matures on September 15) $0.7880/CAD (1 CAD contract = CAD 100,000; 1AUD contract = AUD100,000, both maturing in September, and one cannot go long or short fractions of a contract) ( Options market prices on Jan. 2. (Note: Quotes below are in US cents/1FX on Sept. Contracts): Sept option on CAD w/ 80 strike Sept option on AUD w/74 strike (Suppose 1 CAD options contract = CAD50,000; 1AUD options contract = 50,000 AUD, and assume one cannot buy fractions of the options contracts) J a) What is the firm's net exposure in each currency? How would currency correlations (in general) affect your assessment of the firm's total exposure to exchange risk? e b) Suppose BSK, Inc. wishes to hedge its net foreign exchange rate exposure in each currency with forward hedges (that is, regardless of your answer to (a), it plans on hedging its net exposure in CAD and AUD separately). What will the firm pay or receive (number of $) for CAD and AUD 6 months from Jan.2 (i.e. on July 2) if it hedges its risks in the forward market? Call Prem 1.17 1.14 c) Suppose instead the firm considers hedging its net foreign exchange exposures in each currency with money market hedges. What will the firm pay or receive (number of $) for CAD and AUD 6 months from Jan.2 (i.e. on July 2) if it hedges its risks using money market hedges (given the data provided in the problem)? < H ( d) Suppose the firm decides to hedge its foreign exchange risks using futures market hedges. Suppose also the firm opens positions in the futures market on January 2 at the prices quoted at the beginning of the problem (at the Jan. 2 prices shown above). < (i) E Put Prem 1.45 1.90 E (ii) How would the firm hedge its risk in the futures market? (ie, how many contracts, would it go long or short?) < Suppose on July 2 (6 months from Jan.2), the spot exchange rates and the September futures prices are as follows: Ask CAD 1.2690/$ < AUD 1.3523/$ Bid Spot: CAD 1.2682/$ AUD 1.3508/$ September futures prices on July 2: < Canadian dollar Sept. futures prices: $0.7835/CAD < Australian dollar Sept. futures prices:$0.7438/AUD < Suppose that the September futures contracts mature on September 15. Assume, however, the firm decides to close out its futures positions on July 2 since its foreign exchange receivables and payables come due on that date. What will the firm pay or receive (number of $) for CAD and AUD six months from now (on July 2) given that it hedged its positions using futures market? ] e) Suppose now the firm wishes to hedge its foreign exchange risk using foreign exchange options. (i) E (ii) What kind of options should the firm purchase to hedge its risk (i.e. calls or puts)? How many contracts should the firm purchase? < Assume on January 2 the firm buys options at the prices quoted at the beginning of the problem. Suppose the spot rates on July 2 turn out to be the same as in part (d) above: < Bid Spot: CAD 1.2682/$ AUD 1.3508/$ Ask CAD 1.2690/$ < AUD 1.3523/$ < Given these spot rates, on July 2 will the firm exercise the options it had purchased? What will the firm pay or receive (number of $) for CAD and AUD 6 months from Jan.2 (i.e. on July 2) given it hedged its risk in the options market (consider all costs)? < ( f) Suppose the firm is considering using currency collars (also called a 'range forward' contract) to hedge its CAD & AUD positions. How would a currency collar be implemented for the CAD position in this problem? For the AUD position in this problem? (note: simply state how you would construct, no calculations involved here) g) Compare the four hedges considered above--What are some advantages/disadvantages each? Of the choices in (b)-(e), which type of hedge would the firm likely choose and why? h) Suppose the net payables or receivables in the CAD & AUD are expected to be maintained for years into the future. What does this imply for BSK's operating (also called economic exposure) to foreign exchange risk? What actions could BSK take to reduce its operating exposure to exchange risk over the longer term?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a The firms net exposure in each currency is CAD Receivables of CAD2000000 Payables of CAD1735000 CA...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


