Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The following operator is often applied to an image I(x, y) in computer vision algorithms, to generate a related function h(x, y): where h(x,y)
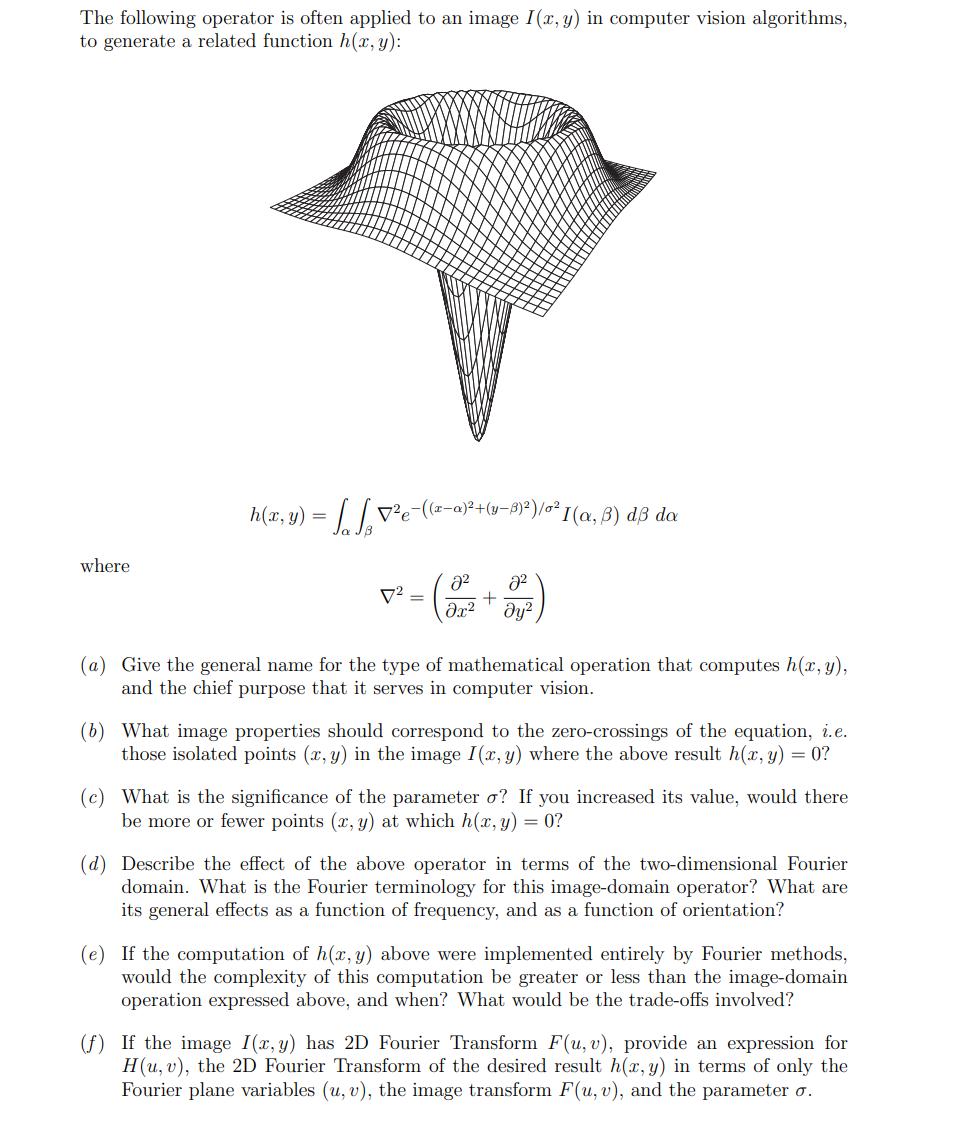
The following operator is often applied to an image I(x, y) in computer vision algorithms, to generate a related function h(x, y): where h(x,y) = | Ve-((z-a) +(y9)*)/z* I(a,B) dB da 8 8 + x y 7 = (a) Give the general name for the type of mathematical operation that computes h(x, y), and the chief purpose that it serves in computer vision. (b) What image properties should correspond to the zero-crossings of the equation, i.e. those isolated points (x, y) in the image I(x, y) where the above result h(x, y) = 0? (c) What is the significance of the parameter o? If you increased its value, would there be more or fewer points (x, y) at which h(x, y) = 0? (d) Describe the effect of the above operator in terms of the two-dimensional Fourier domain. What is the Fourier terminology for this image-domain operator? What are its general effects as a function of frequency, and as a function of orientation? (e) If the computation of h(x, y) above were implemented entirely by Fourier methods, would the complexity of this computation be greater or less than the image-domain operation expressed above, and when? What would be the trade-offs involved? (f) If the image I(x, y) has 2D Fourier Transform F(u, v), provide an expression for H(u, v), the 2D Fourier Transform of the desired result h(x, y) in terms of only the Fourier plane variables (u, v), the image transform F(u, v), and the parameter o.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


