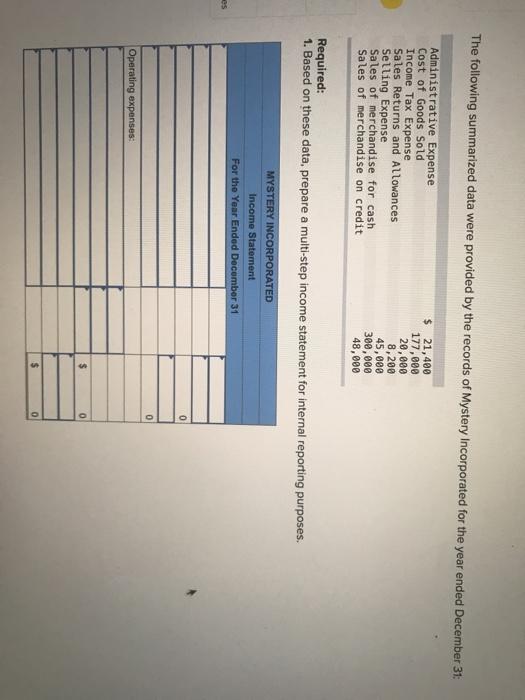
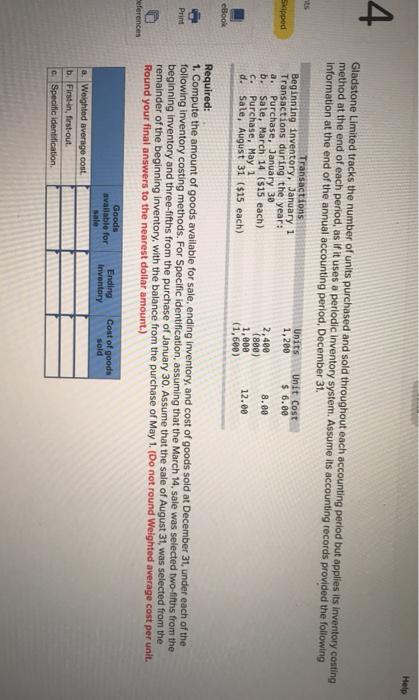
The following summarized data were provided by the records of Mystery Incorporated for the year ended December 31: Administrative Expense Cost of Goods Sold Income Tax Expense Sales Returns and Allowances Selling Expense Sales of merchandise for cash Sales of merchandise on credit $ 21,400 177,000 20,000 8,200 45,000 300,000 48,000 Required: 1. Based on these data, prepare a multi-step income statement for internal reporting purposes. MYSTERY INCORPORATED Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31 es 0 0 Operating expenses: $ 0 $ 0 2 10 points 2-a. What was the amount of gross profit? Skipped Gross profil eBook Print 2-b. What was the gross profit percentage? Gross profit percentage References % 2-c. Which of the following(s) is true? (Select all that apply.) The gross profit percentage is the average amount of gross profit eamed on each dollar of not purchase. The gross profit is cost of goods sold minus net sales revenue. The gross profit is net sales revenue minus cost of goods sold The gross profit percentage is the average amount of gross profit eamed on each daltar of net sales "ences 3. Did the gross profit percentage in the current year improve, or decline, relative to the 46 percent gross prolt percentage in the price year? There is in the gross profit percentage when compared to do in pred Help 4 Gladstone Limited tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each period, as if it uses a periodic Inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following Information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31. Transactions Units Unit Cost Beginning inventory, January 1 1,200 $ 6.00 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase, January 30 2,400 8.89 b. Sale, March 14 ($15 each) (880) Purchase, May 1 1,000 12.00 d. Sale, August 31 ($15 each) (1,600) Skipped C. eBook Print Required: 1. Compute the amount of goods available for sale, ending inventory, and cost of goods sold at December 31, under each of the following inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assuming that the March 14, sale was selected two-fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the sale of August 31, was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1. (Do not round Weighted average cost per unit. Round your final answers to the nearest dollar amount.) Seferences Goods available for Ending Inventory Cost of goods sold a. Weighted average cost. b. First-in, first-out Specific identification oped Fook 2-a. Of the three methods, which will result in the highest gross profit? rint Weighted average cost First-in, first-out erences Specific identification 2-b. Of the three methods, which will result in the lowest income taxes? Weighted average cost First-in, first-out Specific identification