Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The following T-accounts represent September activity for Kelly Tools: Work-in-Process Inventory Materials Inventory Debit Credit Debit Credit Beginning Ending Balance 25,300 Balance 43,000 (9/38)
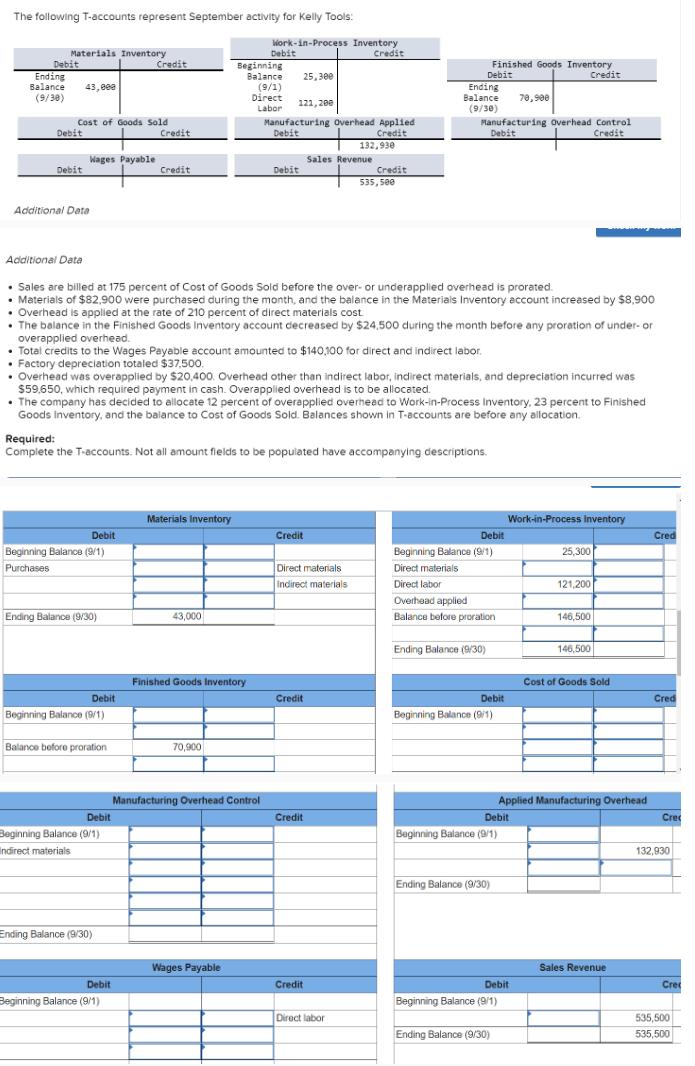
The following T-accounts represent September activity for Kelly Tools: Work-in-Process Inventory Materials Inventory Debit Credit Debit Credit Beginning Ending Balance 25,300 Balance 43,000 (9/38) (9/1) Direct 121,200 Labor Cost of Goods Sold Debit Credit Credit 132,930 Manufacturing Overhead Applied Debit Finished Goods Inventory Debit Ending Balance 70,900 Credit (9/30) Manufacturing Overhead Control Debit Credit Wages Payable Sales Revenue Debit Credit Debit Credit 535,500 Additional Data Additional Data Sales are billed at 175 percent of Cost of Goods Sold before the over- or underapplied overhead is prorated. Materials of $82,900 were purchased during the month, and the balance in the Materials Inventory account increased by $8,900 Overhead is applied at the rate of 210 percent of direct materials cost The balance in the Finished Goods Inventory account decreased by $24,500 during the month before any proration of under- or overapplied overhead. Total credits to the Wages Payable account amounted to $140,100 for direct and indirect labor. Factory depreciation totaled $37,500. Overhead was overapplied by $20,400. Overhead other than indirect labor, indirect materials, and depreciation incurred was $59,650, which required payment in cash. Overapplied overhead is to be allocated. The company has decided to allocate 12 percent of overapplied overhead to Work-in-Process Inventory, 23 percent to Finished Goods Inventory, and the balance to Cost of Goods Sold. Balances shown in T-accounts are before any allocation. Required: Complete the T-accounts. Not all amount fields to be populated have accompanying descriptions. Materials Inventory Debit Credit Beginning Balance (9/1) Purchases Work-in-Process Inventory Debit Cred 25,300 Beginning Balance (9/1) Direct materials Indirect materials Direct materials Direct labor 121,200 Overhead applied Ending Balance (9/30) 43,000 Balance before proration 146,500 Ending Balance (9/30) 146,500 Finished Goods Inventory Cost of Goods Sold Debit Credit Debit Cred Beginning Balance (9/1) Beginning Balance (9/1) Balance before proration 70,900 Debit Beginning Balance (9/1) Indirect materials Ending Balance (9/30) Manufacturing Overhead Control Applied Manufacturing Overhead Credit Debit Cre Beginning Balance (9/1) Wages Payable Debit Credit Beginning Balance (9/1) Ending Balance (9/30) 132,930 Sales Revenue Debit Cre Beginning Balance (9/1) Direct labor 535,500 Ending Balance (9/30) 535,500
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


