Question
The following two reactions occur in the ethylene oxide production process: A stream containing equimolar amounts of ethylene and oxygen is joined by a recycle
The following two reactions occur in the ethylene oxide production process:
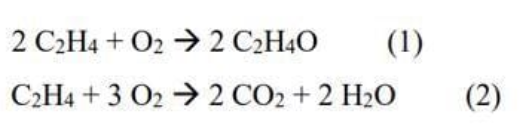
A stream containing equimolar amounts of ethylene and oxygen is joined by a recycle stream containing pure ethylene, and the combined stream is fed to the reactor. The single-pass conversion of ethylene in the reactor and the single-pass ethylene oxide yield based on ethylene consumption are defined as Xsp (mol C2H4 react /mol C2H4 fed) and Ysp (mol C2H40 formed/mol C2H4 react). The reactor effluent goes through a multiple-unit separation process that has three outlet streams. The first stream is pure ethylene oxide leaving the reactor. The second stream contains the remaining oxygen, ethylene and the products formed according to the 2nd reaction (take 100% yield). The third stream, which is the loopback stream, contains only the remaining unreacted ethylene. Take the fresh feed current of 100 mol/s. Take the fresh feed current of 100 mol/s. Consider XSP = 0.20 to YSP = 0.90 for reaction 1 and the separation process as a single unit. Use the loopback flow rate as a shear current variable (ie, assume a loopback flow rate entering the loopback-fresh feed mixing point), solve the system equilibrium equations to recalculate the loopback flowrate at the outlet of the separation and return the default and recalculated values to the same Find the default value.
C2H4+3O22CO2+2HStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


