Question: The goal of this activity is to create a program that displays someone's name, age, and gendercalculating for age in minutes and centuries and determining
The goal of this activity is to create a program that displays someone's name, age, and gendercalculating for age in minutes and centuries and determining maximum heart rate based upon age and gender. By the end of this activity, you should be able to do the following:
Get user input using the Scanner class.
Create variables and concatenate variables with a string.
Use arithmetic operators to manipulate integer and double data types.
Use a basic if statement to determine which output is appropriate.
Run your program in a viewer canvas, including creating and saving the canvas file.
follow the instructions given. It is not as long as it appears. the instructions are just very detailed. Coded in Java. Thanks




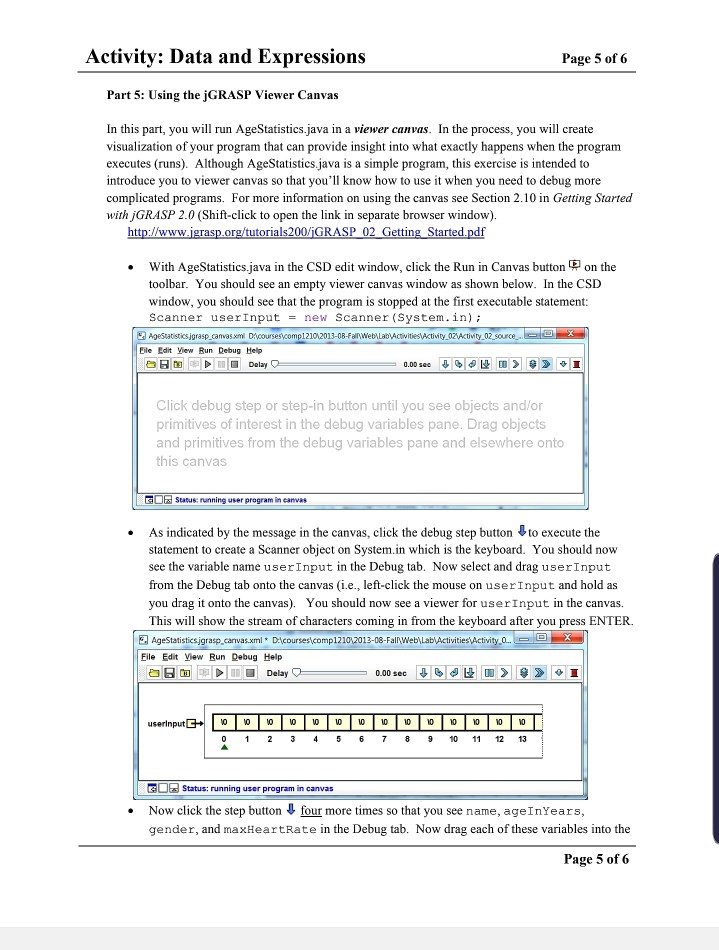
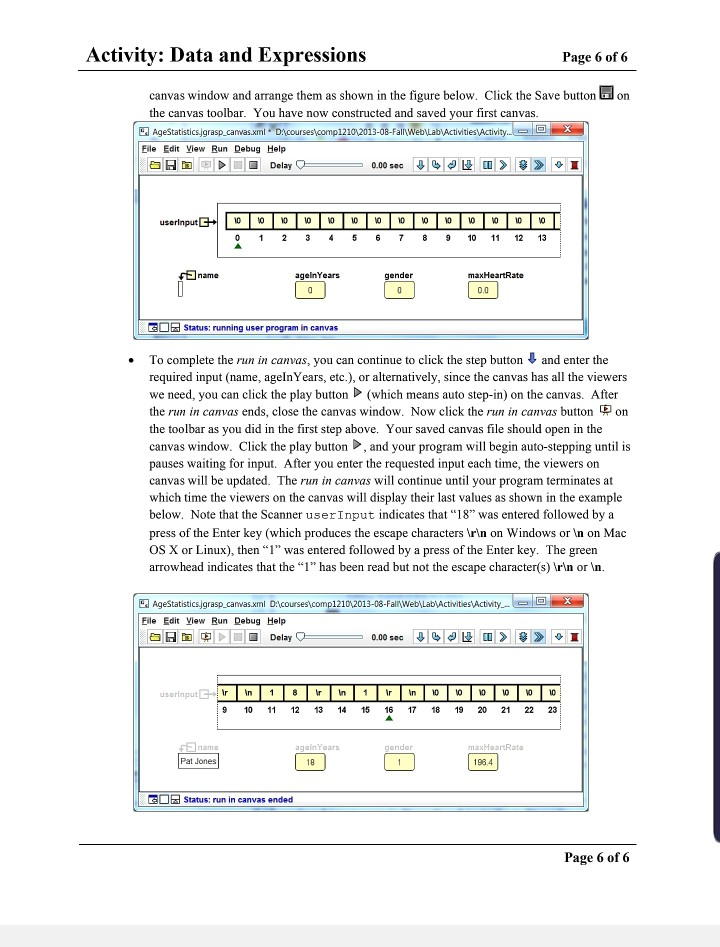
Activity: Data and Expressions Page 1 of 6 Terminology: string literal method parameter string concatenation escape sequence variable variable declaration variable initialization assignment statement assignment operator constant byte, short, int, long float, double char boolean character literal arithmetic operator operator precedence increment, decrement operators assignment conversion promotion casting delimiter Course Coding Standard Additions Follow the standards in the book when naming variables and constants Class names should begin with a capital letter, and method names and variables should start with a lower case. Both should use medial capitals (also called "camelCase". Examples: First Program, HelloWorld, main, number People, xAxis, result, finalResult o Local variables should be declared at the beginning of the method in which they are used. o Constants should be in all caps with words separated by an underscore. In addition to the type, a constant must be declared as static final (e.g., static final int MAX_NUMBER). Constants must be placed at the class level (e.g., before the first method in the class). Examples: MAX NUMBER, BASELINE, TAX_RATE Both variables and constants should have descriptive variable names. This convention is not enforced by Checkstyle; however, it will be graded by your Instructor/GTA in the projects. Example: Good 9: int numberjobs, numEmployees; Bad : int n, m; Activity: Data and Expressions Page 2 of 6 Goals: By the end of this activity you should be able to do the following: Get user input using the Scanner class Create variables and concatenate variables with a string >> Use arithmetic operators to manipulate integer and double data types Use a basic if statement to determine which output is appropriate > Run your program in a viewer canvas , including creating and saving the canvas file Program Description: The goal of this activity is to create a program that displays someone's name, age, and gender, along with calculations for age in minutes and centuries well as max heart rate based on age and gender. Directions: After you enter each segment of code below, be sure to compile and/or run your program. You should correct any errors prior to entering additional code. Part 1: Getting user's name and age Create the following class in GRASP and save it as AgeStatistics.java as soon as you have entered the skeleton code for the class. import java.util.Scanner; public class AgeStatistics { public static void main(String[] args) { Add Javadoc comments for the class and main method. Declare the following variables in the main method then compile your program: Scanner userInput = new Scanner(System.in); String name = ""; int ageInYears = olz int gender = 0; double maxHeartRate = 0; Prompt the user for their name: [Use the print method rather than the printin method.] //Prompt the user for their name: System.out.print("Enter your name: "); name = userInput.nextLine(); For this bold text, Prompt the user for their age: you have to come //Prompt the user for their age: up with the code on System.out.print("Enter your age in years: "); your own! ageInYears = userInput.nextInt(); Add lines to prompt for and input the user's gender after the previous code. Make sure that your program has the EXACT output as below. Page 2 of 6 Activity: Data and Expressions Page 3 of 6 ----GRASP exec: java -ea AgeStatistics Enter your name: Pat Enter your age in years: 71 Enter your gender (1 for female and 0 for male): 1 ----GRASP: operation complete. Part 2: Converting age First, calculate and print the age of the user in minutes (minutes = years * 525600). Note that the tab escape sequence is included in the print statement; tab character is set to three spaces in jGRASP. //convert age: System.out.println("\tYour age in minutes is - + ageInYears * 525600 + minutes."); Now calculate the age in centuries. You should be familiar with type conversion between numeric types. System.out.println("\tYour age in centuries is" + (double) ageInYears / 100 + centuries."); ----GRASP exec: java -ea AgeStatistics Enter your name: Pat Enter your age in years: 71 Enter your gender (1 for female and 0 for male): 1 Your age in minutes is 37317600 minutes. Your age in centuries is 0.71 centuries. ----GRASP: operation complete. Part 3: Max heart rate prompt Add the code to print max heart rate (note the print rather than println): // display max heart rate System.out.print("Your max heart rate is "); Add an if-else statement that will be used to assign maxHeartRate to the max heart rate calculation for male and female. The comments below are there to help you in the Part 4 where you will insert the code to do the calculations on the line after each comment. if (gender == 1) { //calculate female MHR else { //calculate male MHR Add one more print statement to print the max heart rate: System.out.println(maxHeartRate + beats per minute."); Page 3 of 6 Activity: Data and Expressions Page 4 of 6 Part 4: Max heart rate calculations On your own, complete the if-else statement by adding an assignment statement for female and another for male to assign the appropriate expression below to the variable maxHeartRate. The maximum heart rate is calculated as follows: O Max heart rate for females: 209 - (0.7 * age In Years) o Max heart rate for males: 214 - (0.8 + ageInYears) Test your program and make sure that the output is exactly as shown below. Your lab instructor may ask you to use a different set of values to test your program when you demo it for your activity grade. Output # 1: ----GRASP exec: java -ea AgeStatistics Enter your name: Lucy Enter your age in years: 25 Enter your gender (1 for female and 0 for male): 1 Your age in minutes is 13140000 minutes. Your age in centuries is 0.25 centuries. Your max heart rate is 191.5 beats per minute. ----GRASP: operation complete. Output # 2: ----GRASP exec: java -ea AgeStatistics Enter your name: Kao Enter your age in years: 19 Enter your gender (1 for female and 0 for male): 0 Your age in minutes is 9986400 minutes. Your age in centuries is 0.19 centuries. Your max heart rate is 198.8 beats per minute. ----GRASP: operation complete. Web-CAT - After you have completed Part 4, you should submit your AgeStatistics.java file to Web-CAT. This is the only file you will submit for this activity. Page 4 of 6 Activity: Data and Expressions Page 5 of 6 Part 5: Using the jGRASP Viewer Canvas In this part, you will run AgeStatistics.java in a viewer canvas. In the process, you will create visualization of your program that can provide insight into what exactly happens when the program executes (runs). Although AgeStatistics.java is a simple program, this exercise is intended to introduce you to viewer canvas so that you'll know how to use it when you need to debug more complicated programs. For more information on using the canvas see Section 2.10 in Getting Started with GRASP 2.0 (Shift-click to open the link in separate browser window) http://www.jgrasp.org/tutorials 200/GRASP 02 Getting Started.pdf With AgeStatistics.java in the CSD edit window, click the Run in Canvas button on the toolbar. You should see an empty viewer canvas window as shown below. In the CSD window, you should see that the program is stopped at the first executable statement: Scanner userInput = new Scanner(System.in); AgeStatistics jorasp_canvas mi Discourses compl21012013-08-Fall WebLab Activities Activity OZ Activity 02 source Eile Edit View Run Debug Help OBD Delay Click debug step or step-in button until you see objects and/or primitives of interest in the debug variables pane. Drag objects and primitives from the debug variables pane and elsewhere onto this canvas a Status: running user program in canvas As indicated by the message in the canvas, click the debug step button to execute the statement to create a Scanner object on System.in which is the keyboard. You should now see the variable name userInput in the Debug tab. Now select and drag userInput from the Debug tab onto the canvas (i.e., left-click the mouse on userInput and hold as you drag it onto the canvas). You should now see a viewer for user input in the canvas. This will show the stream of characters coming in from the keyboard after you press ENTER. AgeStatisticsjgrasp canvas.xml. De courses comp121042013-08-Fall Web\Lab Activities Activity... D e File Edit View Run Debug Help Delay userinput 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 GOR Status: running user program in canvas Now click the step button four more times so that you see name, ageInYears, gender, and maxHeartRate in the Debug tab. Now drag each of these variables into the Page 5 of 6 Activity: Data and Expressions Page 6 of 6 on canvas window and arrange them as shown in the figure below. Click the Save button the canvas toolbar. You have now constructed and saved your first canvas. AgeStatistics grasp canvas.xml DAcourses comp121042013-08-Fall Web\Lab Activities Activity.. Eile Edit View Run Debug Help D OO Delay 0 0 .00 sec J > > userInputE | | | | | - |*|*|*|*|*|*|*|*| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 name agein Years maxHeartRate gender 10 0 0.0 GO Status: running user program in canvas To complete the run in canvas, you can continue to click the step button and enter the required input (name, ageIn Years, etc.), or alternatively, since the canvas has all the viewers we need, you can click the play button (which means auto step-in) on the canvas. After the run in canvas ends, close the canvas window. Now click the run in canvas button on the toolbar as you did in the first step above. Your saved canvas file should open in the canvas window. Click the play button and your program will begin auto-stepping until is pauses waiting for input. After you enter the requested input each time, the viewers on canvas will be updated. The run in canvas will continue until your program terminates at which time the viewers on the canvas will display their last values as shown in the example below. Note that the Scanner userInput indicates that "18" was entered followed by a press of the Enter key (which produces the escape characters on Windows or in on Mac OS X or Linux), then "1" was entered followed by a press of the Enter key. The green arrowhead indicates that the "1" has been read but not the escape character(s) or In. e AgeStatistics.jgrasp_canvas.xml D:\courses comp121012013-08-Fall\Web\Lab Activities Activity. D Eile Edit View Run Debug Help ADOO Delay 0 0 .00 sec JL > > I in 1 10 1 14 in 17 100 000 19 20 21 22 23 9 11 12 13 15 16 18 al Status: run in canvas ended Page 6 of 6
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


