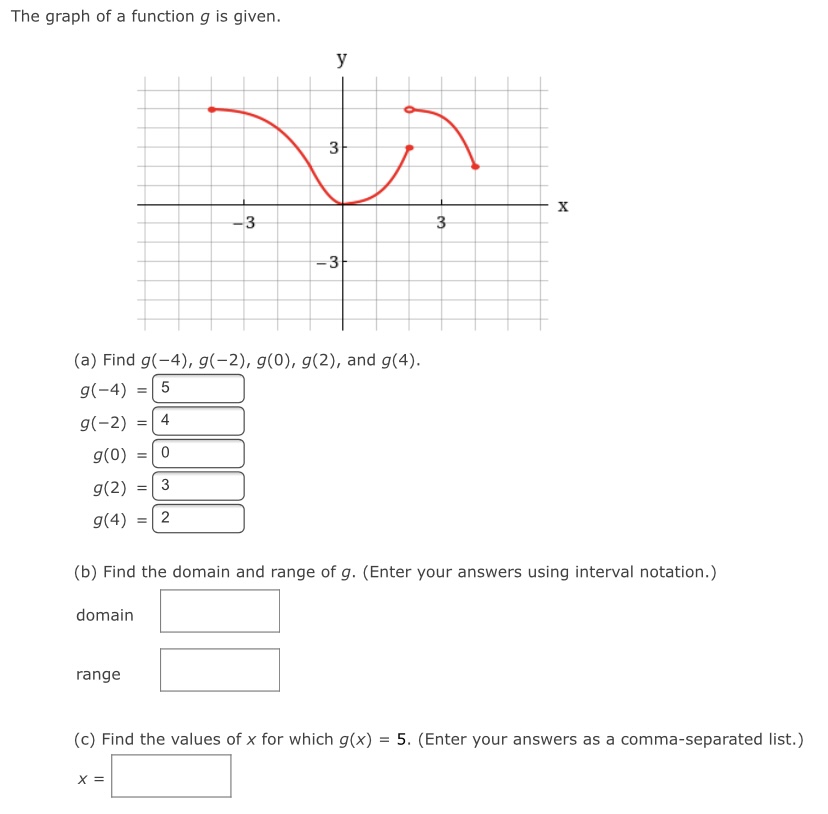
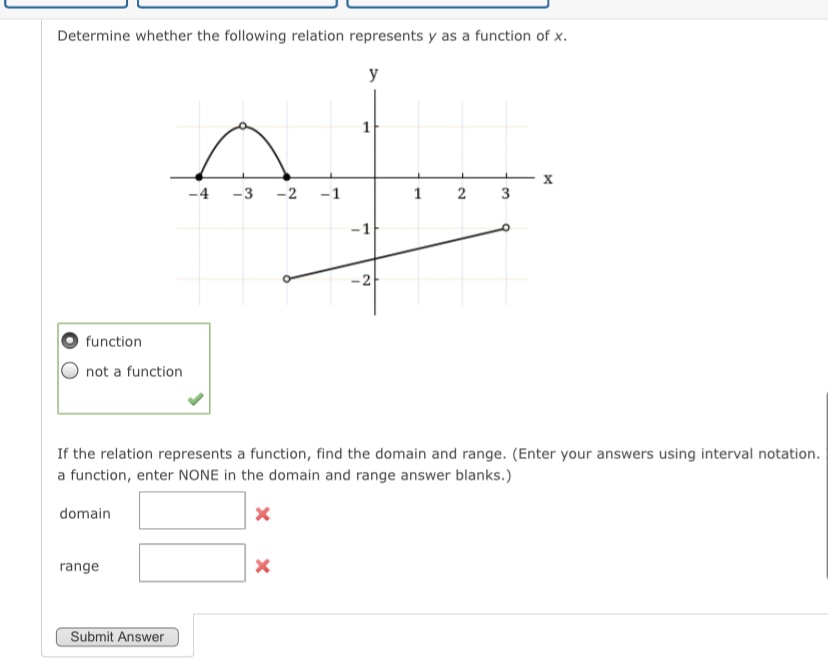
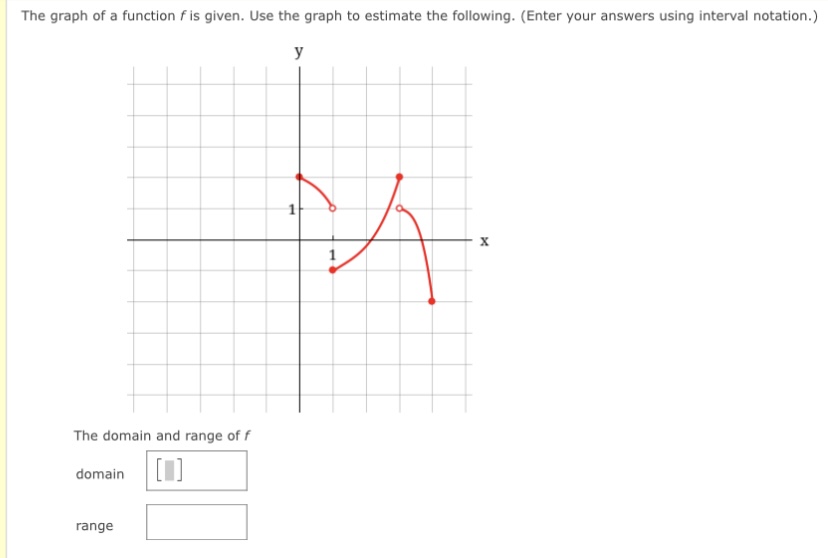
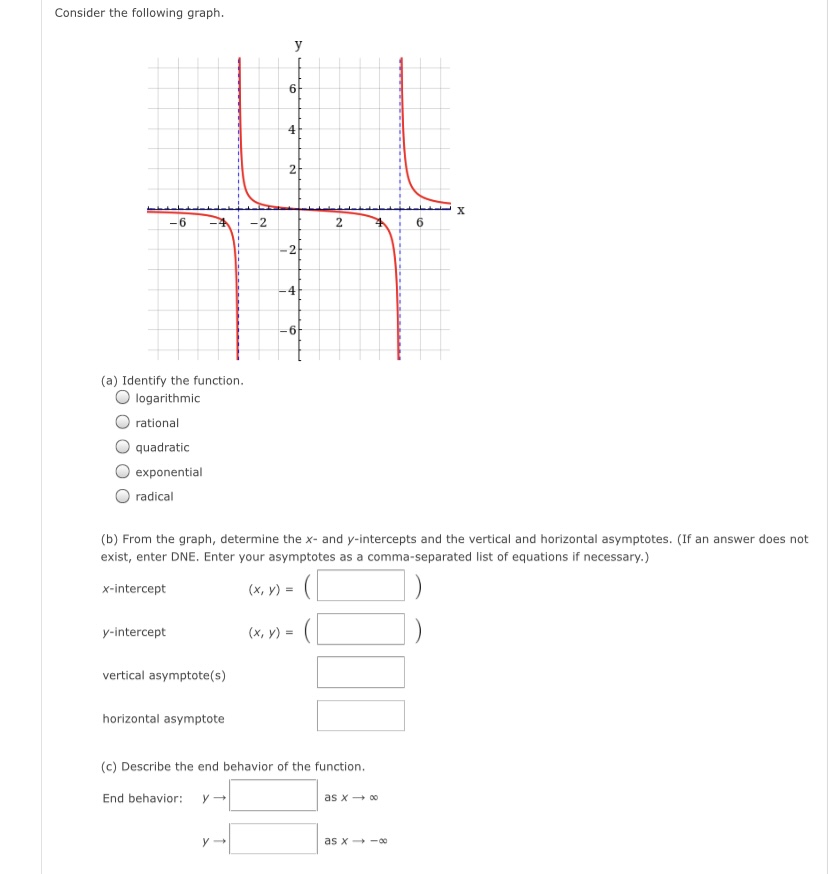
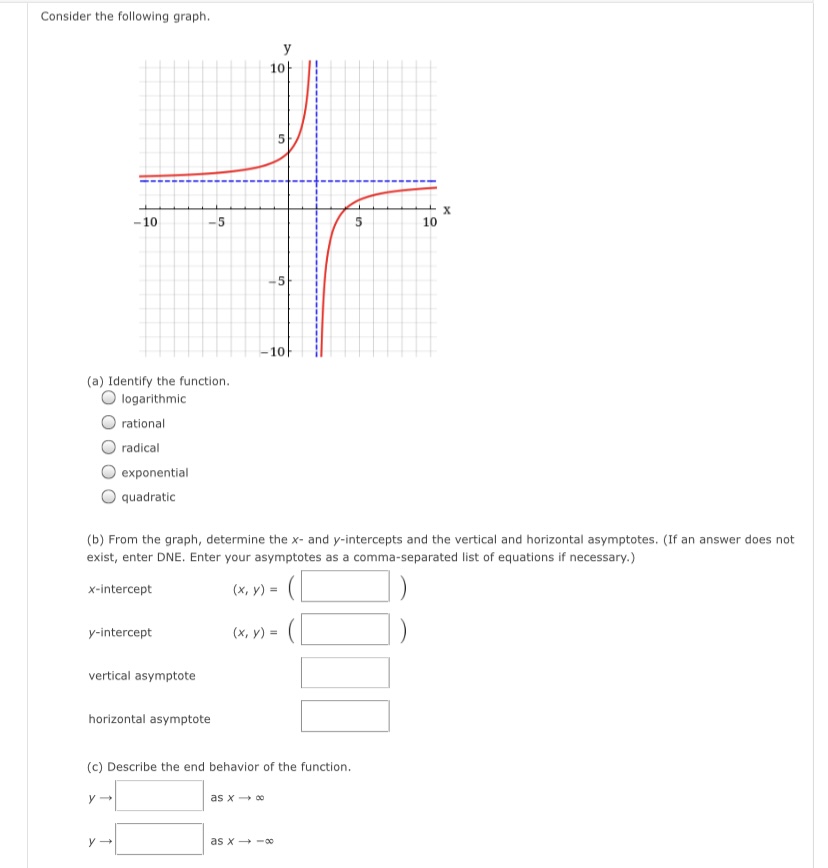
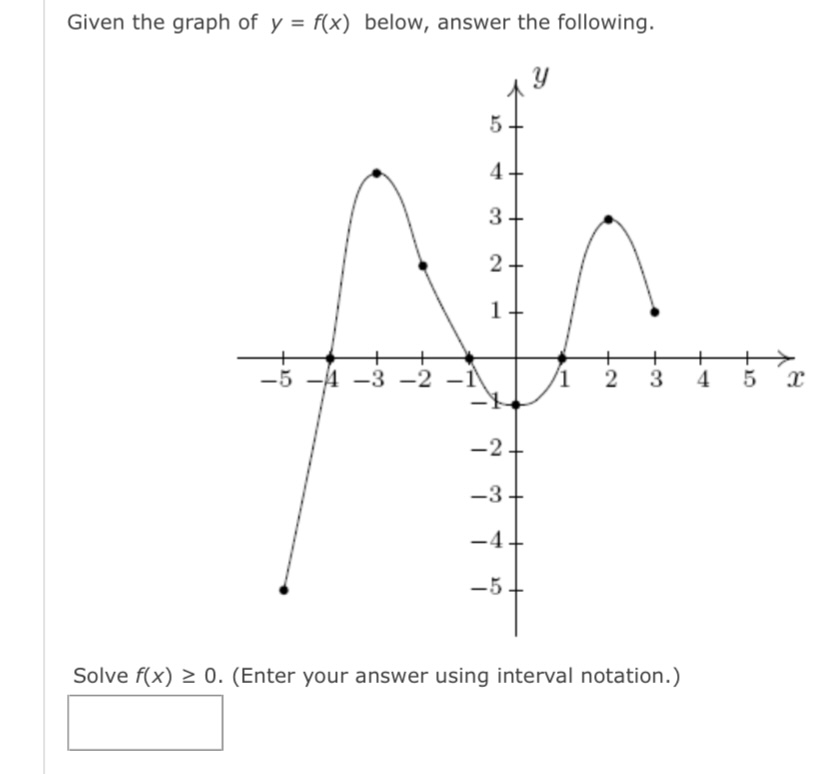
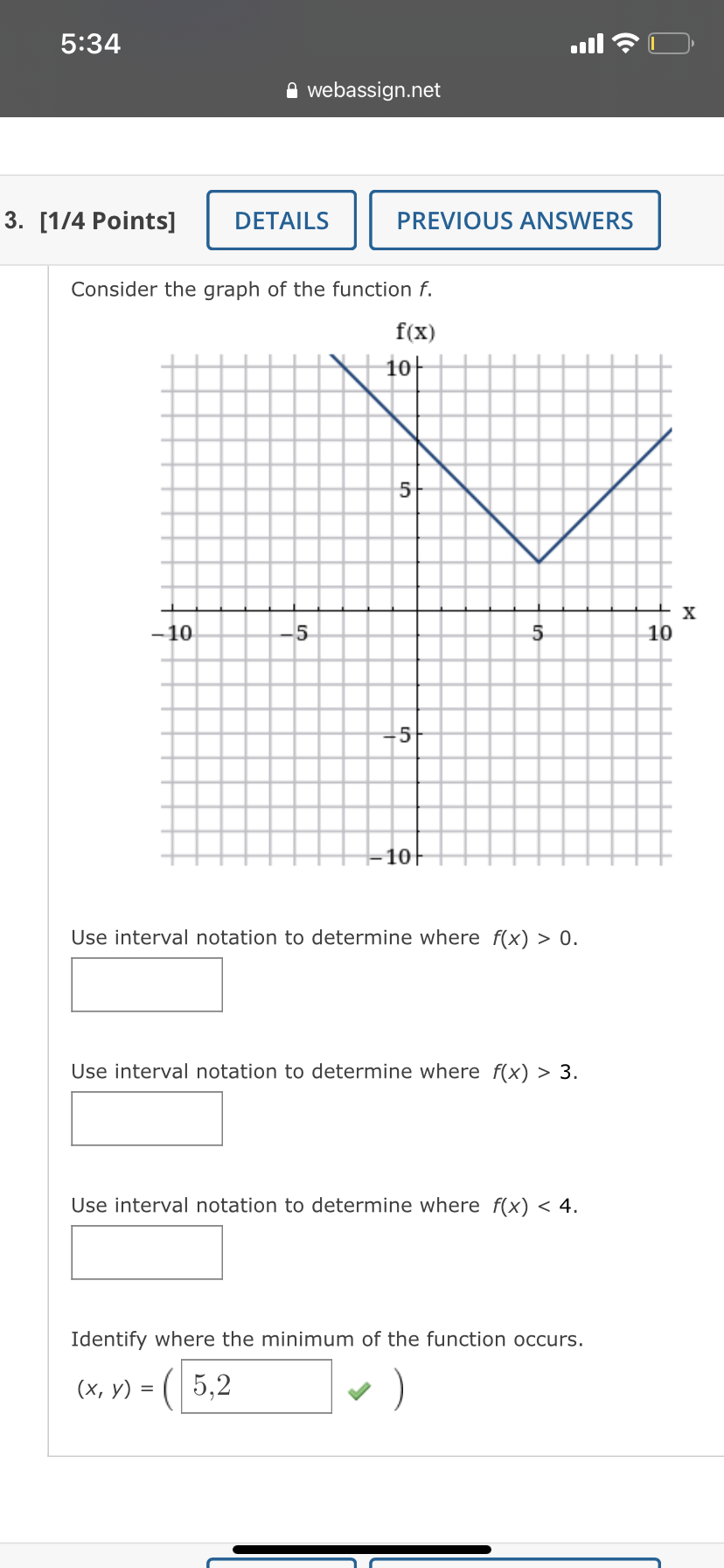
The graph of a function g is given. y 3 -3 3 X -3 (a) Find g(-4), g(-2), g(0), g(2), and g(4). g(-4) = 5 g(-2) = 4 g(0) = 0 g(2) = 3 g(4) = 2 (b) Find the domain and range of g. (Enter your answers using interval notation. ) domain range (c) Find the values of x for which g(x) = 5. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list.) X =Determine whether the following relation represents y as a function of x. X -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 -1 -2 function O not a function If the relation represents a function, find the domain and range. (Enter your answers using interval notation. a function, enter NONE in the domain and range answer blanks.) domain X range X Submit AnswerThe graph of a function f is given. Use the graph to estimate the following. (Enter your answers using interval notation.) X The domain and range of f domain rangeConsider the following graph. 4 N -6 -2 2 6 -2- -4 (a) Identify the function. O logarithmic O rational O quadratic O exponential O radical (b) From the graph, determine the x- and y-intercepts and the vertical and horizontal asymptotes. (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE. Enter your asymptotes as a comma-separated list of equations if necessary.) x-intercept (x, y) = ( y-intercept (x, y ) = vertical asymptote(s) horizontal asymptote (c) Describe the end behavior of the function. End behavior: as x -+ 00 as x -* -60Consider the following graph. 10/ -10 -5 5 10 45 -10 (a) Identify the function. O logarithmic O rational O radical O exponential O quadratic (b) From the graph, determine the x- and y-intercepts and the vertical and horizontal asymptotes. (If an answer does not exist, enter DNE. Enter your asymptotes as a comma-separated list of equations if necessary.) x-intercept (x, y) = y-intercept ( x, y ) = vertical asymptote horizontal asymptote (c) Describe the end behavior of the function. as x -0 as x - -0Given the graph of y = for) below, answer the following. Solve for) a 0. (Enter your answer using interval notation.) S ii webassignhet 3. [1/4 Points] DETAILS PREVIOUS ANSWERS Consider the graph of the function f. fix) Use interval notation to determine where f(x) > 0. U Use interval notation to determine where f(x) > 3. U Use interval notation to determine where f(x)