Question
The Lab Problem We are going to work on making our own data structures using a C++ struct . Specifically, we are going to create
The Lab Problem
We are going to work on making our own data structures using a C++ struct. Specifically, we are going to create both data members and member functions. We are going to make a 2D MathVector struct. Keep it straight, these are the mathematical entitles called Vectors (a geometric entity with direction and magnitude).
Some Background
So if you dont remember, here is a little background on two-dimensional vectors. A vector is basically an arrow that has a magnitude (a length) and a direction (an angle with respect to typically the x axis). It usually is represented as an x,y pair, where the origin of the vector is assumed to be at 0,0 and the head of the vector is as the listed x,y pair.
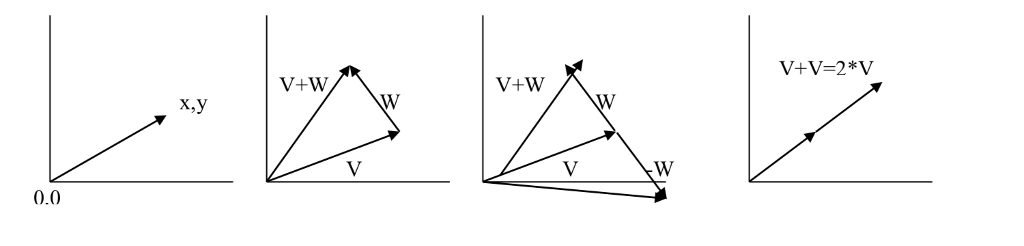
A Vector V+W V-W V*2
Here are some of the operations you can perform on your new MathVector struct.
--------- MathVector addition. If V1 is (x,y) and V2 is (a,b), the V+W is a new MathVector with
the values (x+a, y+b)
--------- MathVector multiplication by a scalar integer type. If V1 is (x,y), then V*n is (x*n,y*n),
returning a new MathVector
--------- MathVector multiplication with another MathVector. There are two possibilities, dot
product or cross product. Well do dot product. If V=(x,y) and W=(a,b), then V*W = x*a + y*b, a scalar.
Thus the dot product returns a scalar type long, not a MathVector.
-------- MathVector magnitude. The magnitude based on the Pythagorean theorem. For V=(x,y), the
magnitude is sqrt(x^2 + y^2).
Tasks
Make a MathVector struct. Data members are:
-------- long x
-------- long y
Constructors:
-------- default constructor
-------- two args, each a long, constructor: first arg is the x value, the second is the y value. No defaults.
Member Functions:
---------- MathVector add(const MathVector&). Single arg a const ref to MathVector. Adds two MathVectors as described. Returns a new MathVector.
---------- MathVector mult(long). Multiplies a single MathVector element by a long as described. Returns a new MathVector.
----------- long mult(const MathVector&). Single arg a const ref to MathVector . Multiplies the two MathVectors as a dot product, yielding a long as described above.
----------- double magnitude() No args. Calculate the magnitude of the MathVector as described. Returns a double.
Make the following regular function (not a member):
----------- string vec_to_str(const MathVector &v). No args, returns a string representation
of the MathVector in the format: "x:y"
We provide lab09_vector.h you write lab09_vector.cpp. Make your own lab09_main.cpp
that is in the lab directory and run and test your work
lab09_vector.h
#ifndef VECTOR_H #define VECTOR_H #includeusing std::string; struct MathVector{ // data members, default public long x=0; long y=0; // 2 constructors // =default uses default values of data members (above). // no other work required. You're welcome! MathVector()=default; // you must write MathVector(long, long); // 4 function members you must write MathVector add (const MathVector&); MathVector mult(long); long mult(const MathVector&); double magnitude(); }; // a function! You must write string vec_to_str(const MathVector&); #endif
V+W x,y 0.0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


