Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The model below describes a situation where is a pool of 10 customers who each may or may not make a purchase. The probability
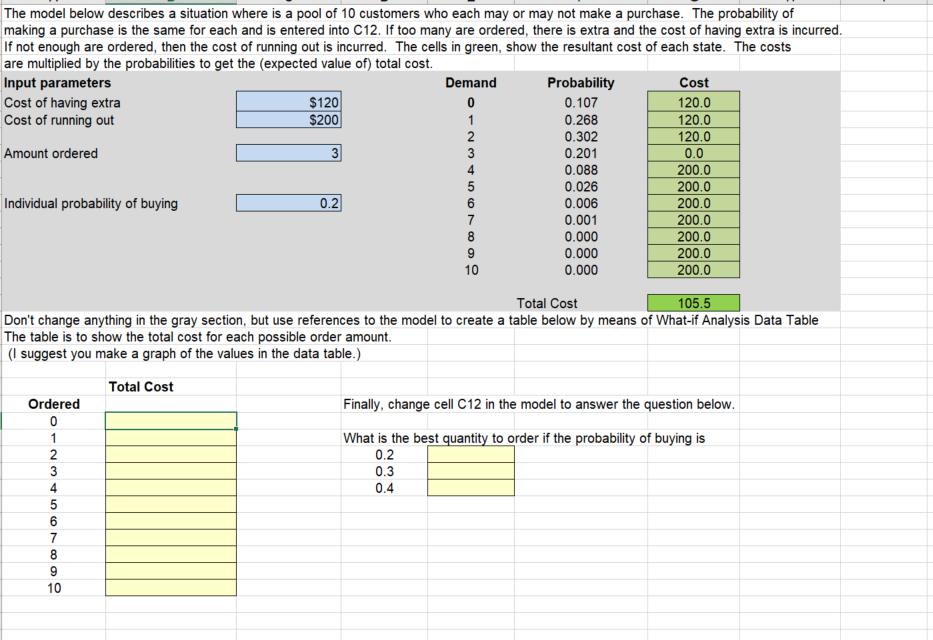
The model below describes a situation where is a pool of 10 customers who each may or may not make a purchase. The probability of making a purchase is the same for each and is entered into C12. If too many are ordered, there is extra and the cost of having extra is incurred. If not enough are ordered, then the cost of running out is incurred. The cells in green, show the resultant cost of each state. The costs are multiplied by the probabilities to get the (expected value of) total cost. Input parameters Cost of having extra Cost of running out Amount ordered Individual probability of buying 0.2 Demand Probability Cost $120 $200 3 072345678 0.107 120.0 1 0.268 120.0 0.302 120.0 0.201 0.0 0.088 200.0 0.026 200.0 0.006 200.0 0.001 200.0 0.000 200.0 9 10 0.000 200.0 0.000 200.0 Total Cost 105.5 Don't change anything in the gray section, but use references to the model to create a table below by means of What-if Analysis Data Table The table is to show the total cost for each possible order amount. (I suggest you make a graph of the values in the data table.) Total Cost Ordered 01234567820 Finally, change cell C12 in the model to answer the question below. What is the best quantity to order if the probability of buying is 0.2 0.3 0.4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


