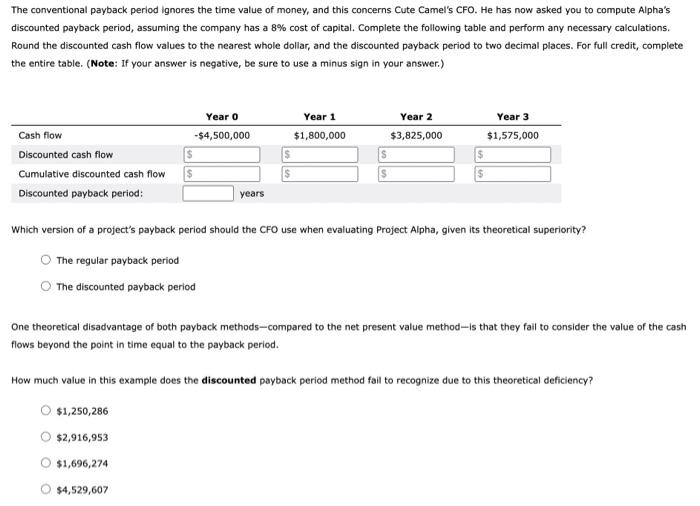
The payback method helps firms establish and identify a maximum acceptable payback period that helps in their capital budgeting decisions. Consider the case of Cute Camel Woodcraft Company: Cute Camel Woodcraft Company is a small firm, and several of its managers are worried about how soon the firm will be able to recover its initial investment from Project Alpha's expected future cash flows. To answer this question, Cute Camel's CFO has asked that you compute the project's payback period using the following expected net cash flows and assuming that the cash flows are received evenly throughout each year. Complete the following table and compute the project's conventional payback period. For full credit, complete the entire table. (Note: Round the conventional payback period to two decimal places. If your answer is negative, be sure to use a minus sign in your answer.) Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Expected cash flow -$4,500,000 $1,800,000 $3,825,000 $1,575,000 Cumulative cash flow Conventional payback period: years $ The conventional payback period ignores the time value of money, and this concerns Cute Camel's CFO. He has now asked you to compute Alpha's discounted payback period, assuming the company has a 8% cost of capital. Complete the following table and perform any necessary calculations. Round the discounted cash flow values to the nearest whole dollar, and the discounted payback period to two decimal places. For full credit, complete the entire table. (Note: If your answer is negative, be sure to use a minus sign in your answer.) Year 1 Year 0 -$4,500,000 Year 2 $3,825,000 Year 3 $1,575,000 Cash flow $1,800,000 Discounted cash flow $ S $ Cumulative discounted cash flow $ $ Discounted payback period: years Which version of a project's payback period should the CFO use when evaluating Project Alpha, given its theoretical superiority? The regular payback period The discounted payback period One theoretical disadvantage of both payback methods-compared to the net present value method-is that they fail to consider the value of the cash flows beyond the point in time equal to the payback period. How much value in this example does the discounted payback period method fail to recognize due to this theoretical deficiency? $1,250,286 $2,916,953 $1,696,274 O $4,529,607