Question
The Plant loadings for the following process schematic are as follows Anoxic basin-5 1 MG, or 4.8 hours. Aerobic basin (large) 1 MG, or 4.8
The Plant loadings for the following process schematic are as follows
Anoxic basin-5 1 MG, or 4.8 hours.
Aerobic basin (large) 1 MG, or 4.8 hours.
Aerobic basin (small; 1 and 2) 0.55 MG, or 1.9 hours.
Aerobic basin (small 3) 0.34 MG, or 1.2 hours.
Total hydraulic retention time 11.5 hours.
Internal recirculation rate 8000 to 12,000 gallon per minute (gpm), or four times the influent flow rate.
Secondary clarifier 6.7 hours, or 412 gallons per day per square foot (gpd/ft2).
Denitrification filter, hydraulic loading rate 3 pgm/ft2.
Plant influent and effluent average results are shown in the following table.
Performance data
Reliability data for total removal of total phosphorus show that removal is good, with the effluent total phosphorus (TP) averaging 0.26 mg/L and a medium coefficient of variation (Cv) of 62%.
Reliability data for ammonia nitrogen removal show that removal of ammonia nitrogen is very good, with a mean effluent of 0.44 mg/L and a very low Cv of 12%. Reliability data for removal of total nitrogen (TN) show that between the anoxic portion of the activated sludge system and the denitrification filter, the plant gives outstanding TN removal, with effluent TN of 2.14 mg/L and a Cv of 1%.
Reliability factors
The plant achieves a phosphorus mean concentration of 0.26 mg/L with a Cv of 62% without any chemical addition and a TN concentration of 2.14 mg/L with a Cv of only 16%. In terms of wastewater characteristics, the BOD to TP ratio is high, with an average value of 55.1.
The BOD to TN ratio is high at 10, when 5 or greater would be recommended. The plant uses a plug-flow, activated sludge process with anoxic and aerobic basins in series. This was a retrofit design that the plant personnel implemented.
Some unique features of this process are an anoxic basin with a long detention time, followed by a two-stage aerobic stage in series and, at the same time, the flexibility of operating parallel trains, such as during high-flow periods. The base mode of operation includes a long detention time at the anoxic basin (1 MG in basin 5), followed by an equal-size first aerobic basin (1 MG, basin 4 or 6) and then a smaller basin (either basin 3 or basins 1and 2 combined).
The internal recirculation from aerobic zone to the anoxic zone in the head area is up to four times the influent flow rate.
A unique operational strategy developed at the plant calls for a low return activated sludge (RAS) flow rate and a deep sludge blanket in the clarifiers. The clarifiers are operated with 3 to 4 feet of blanket, while RAS is maintained at only 10 to 25% of the flow rate. In addition, the controlling parameter is mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS), ranging between 1700 mg/L in summer and 2400 mg/L in winter. There is no separate tank for volatile fatty acid generation.
This practice provides a full nitrification and a significant degree of denitrification in the retrofitted activated sludge (AS) process. The average nitrate-nitrogen in the secondary effluent is 4 to 8 mg/L, leaving the denitrification filter to polish the effluent.
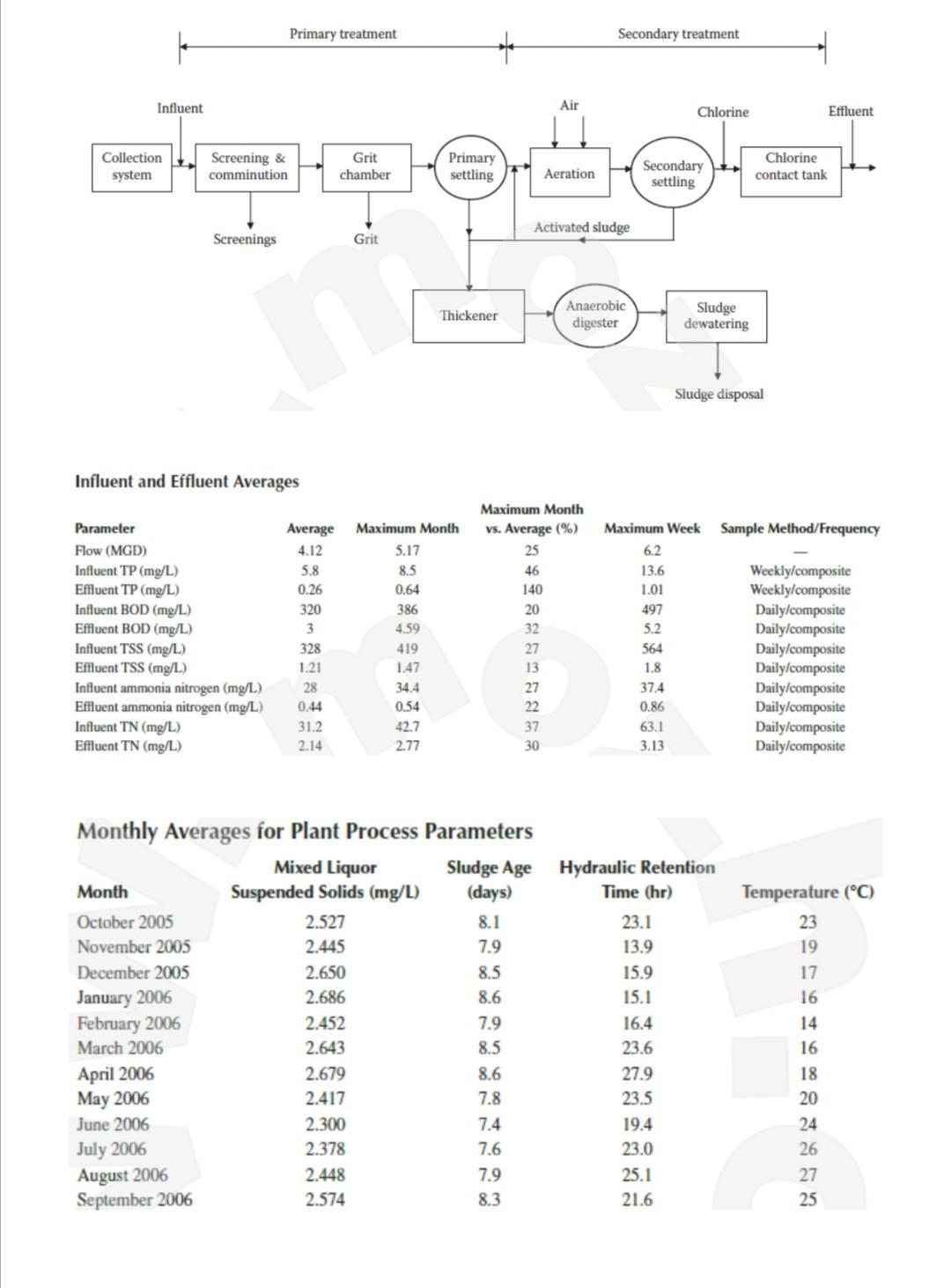
Influent and Effluent Averages Monthlv Averages for Plant Process Parameters
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


