Question
The Problem Deal or No Deal is a popular television game show, broadcast in about 80 countries all over the world. In the US the
The Problem
Deal or No Deal is a popular television game show, broadcast in about 80 countries all over the world. In the US the host of the show is Howie Mandel on NBC. Scientists of several areas studied the strategic significance of the game and even the Wall Street Journal published an article calling the game an economics experiment. For this project, you will construct a Java program to play a slightly simplified version of Deal or No Deal. In the two-player game a contestant (the player) plays (gambles) against a banker. For the program simulating the game the user will be the player and the computer will be the banker. The structure and rules of the game
1. There are 11 numbered briefcases (26 in the real life game), each contains a cash value between $1 and $1,000,000. Different cases contain different values. The individual amounts are public, but nobody knows how the dollar values get distributed in the briefcases.
2. At the start of the game the player selects one out of the 11 briefcases. The selected initial briefcase is set aside, the cash value in the initial briefcase is not revealed until the end of the game. This initial briefcase is not eliminated from the game.
3. The game continues for up to 10 rounds. In each round played in the game (from 1 st round up to the 9 th) three actions are performed in the order as listed. The player must choose one of the remaining briefcases. The selected briefcase together with its cash content is eliminated from the game. When a case has been eliminated, it is opened and the money contained in it is revealed. The banker offers the contestant a deal of quitting the game for a certain amount of cash. The contestant may accept the deal or may reject it. If the deal is accepted, the offered money is the winning of the player and the game is finished. If the deal is rejected, the player enters the next round and the game is continued.
4. The rounds continue until either the player makes a deal, that is accepts the bankers offer, or rejecting all offers the game reaches the last (10th) round when there is only one unopened briefcase left that has never been picked for elimination. If this happens, the banker offers to the player a trade: the initial briefcase for the last remaining unopened one. Should the player refuse the trade, the winning is the money in the initial briefcase, otherwise the winning is the money in the last briefcase.
5. As a result of the rules above, the player always wins some money and the goal for the player to maximize the winning which is either the content of the initial briefcase, or the content of the last briefcase, or the cash offer from the banker in one of the rounds.
6. At the end of the game all remaining briefcases including the initial case are opened and their values revealed.
Analysis and Requirements
Input to set up the game The dollar values contained in the briefcases: 1; 10; 100; 1,000; 4,000; 10,000; 40,000; 100,000; 300,000; 700,000; 1,000,000 Note that additional data used in the code, the number of briefcases (11) and the number of rounds (10) follow from the number of dollar values given above
Input to play the game (each solicited from the user) The serial number of the initial briefcase In each round, the serial number of the briefcase the user eliminates deal or no deal answers to the bankers offers
Output A complete log book (description of every event) of the game The dollar value won by the contestant at the end of the game
Formula The bankers cash offer depends on the serial number of the current round and on the average of the contents of the non-eliminated briefcases. The formula used in a real life game is not public. In this model you have the following formula to apply:
N is the serial number of the round currently finished in the game (0
avg is the average of the dollar values in the remaining briefcases
temp = 0.01 *(75 + 5 * N 3 * max(0, N -5)) * avg*(1+0.15*(avg-55000)/Math.abs(avg 55000))
offer=Math.max(100,1000*Math.round(temp/1000))
Design
Input for setting up the game (see in the Analysis) shall be directly assigned to the relevant variable 1. Briefcase serial numbers selected by the player are solicited on the console
2. Deal or No Deal shall be answered on a JOptionPane confirm dialog
3. The output describing the game events shall be displayed on the console
4. The dollar value won by the contestant shall also be displayed on the JOptionPane dialog
Class design is described below in three steps:
A chart showing the logic of class co-operations A UML diagram for each class
A detailed specification of classes and methods, these should be used together with the UML diagrams
The program will consist of five user-defined classes:
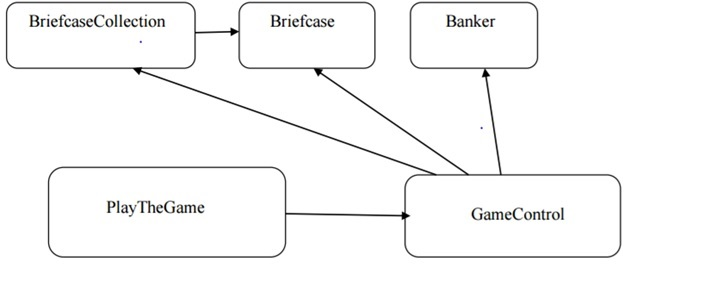
The next chart shows the UML diagrams of the classes. The arrows indicate the same aggregation/access logic as above. The classes are further described in the tables following the UML diagrams. Instance methods that called in other classes must be declared public. All instance fields and all helper methods not called in other classes are to be declared private.
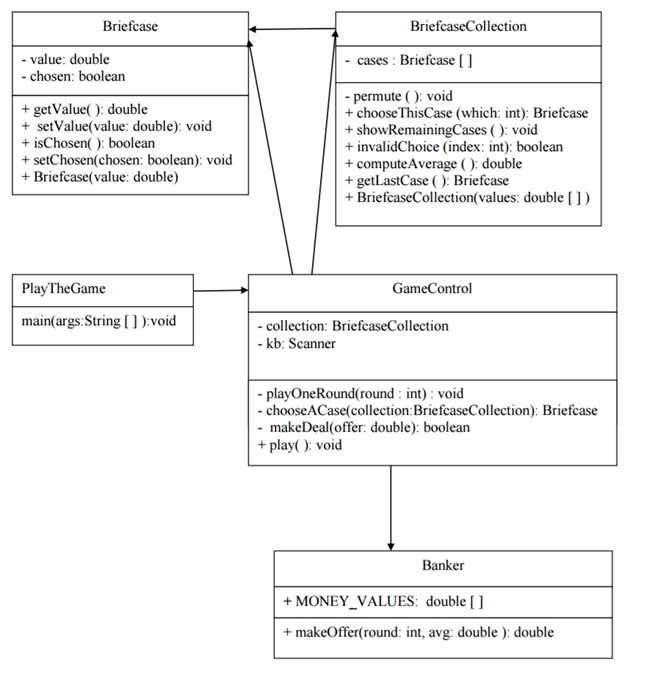
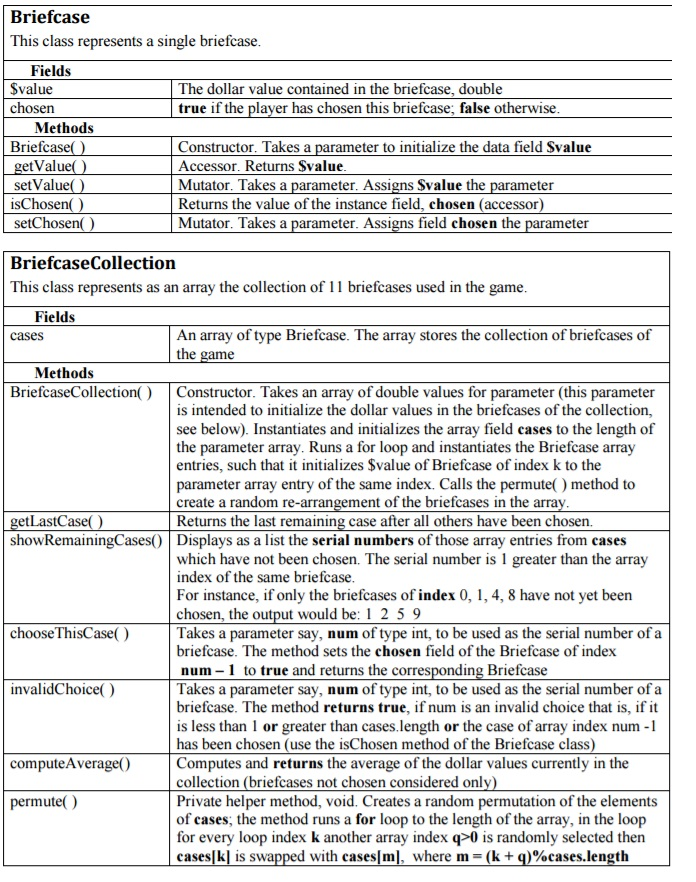
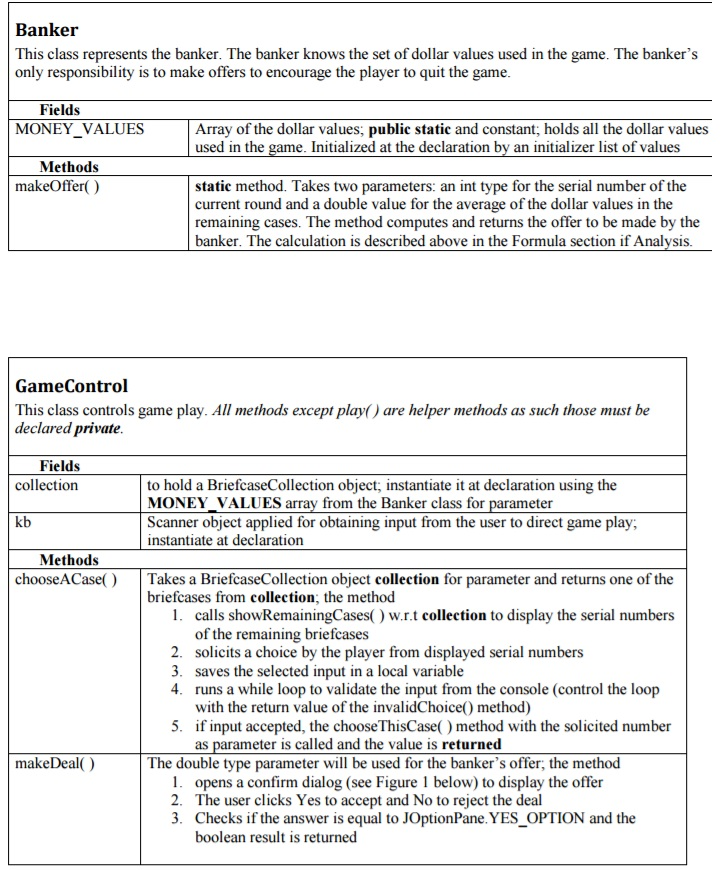
Implementation and Requirements, Hints
4. As it is specified in the above method descriptions, the player answers input questions on the console for selecting a case on a confirm dialog window for accepting/refusing a deal offered
Console input values must be validated, since wrong input may totally throw off the game. If the player selects a non-existing case number (too large, or has already been eliminated), then the wrong input value must be ignored and another value is to be solicited from the player. Process repeats until the input is correct
5. The dollar values used in the game and to be stored in the MONEY_VALUES array of the Banker class are as follows: 1, 10, 100, 1000, 4000, 10000, 40000, 100000, 300000, 700000, 1000000 Use an initializer list to instantiate the array. This array is a public static field since it is independent of any objects.
6. Note that eliminating a briefcase from the collection simply means to change the chosen field to the boolean true value.
7. There are several options to create a random permutation of an array. For every index k choose randomly two other indices and swap the elements of those indices; this process may not affect the element of index k For every index k choose randomly another index (including k) and swap the two entries For every index k apply a cyclic rotation by a random shift and swap the two entries. For our array used in the game this means to select q randomly between 1 and 10, define m = (k+q)%11 and swap the two entries at index k and m The last procedure is recommended, it completes the specification of the permute method in the design section. You may also implement the second item
8. The only static method in the program, other than main is makeOffer ( ) in the Banker class. This is a utility method working only on its parameters. There is no need to create a Banker object. To call the method or access the array, the class name Banker is the prefix to use.
9. There are no explicit constructors in the Banker, GameControl and PlatTheGame classes. Banker and the main are not instantiated and only the default constructor of GameControl is used. The other two classes all have explicit constructors with various functionalities.
10. The play( ) method of the GameControl class must be public. The other three methods are helpers, that is, they are called internally only in the class, as such make them private. The same holds for the permute() method of the BriefcaseCollection class. All other methods in any of the classes must be public.
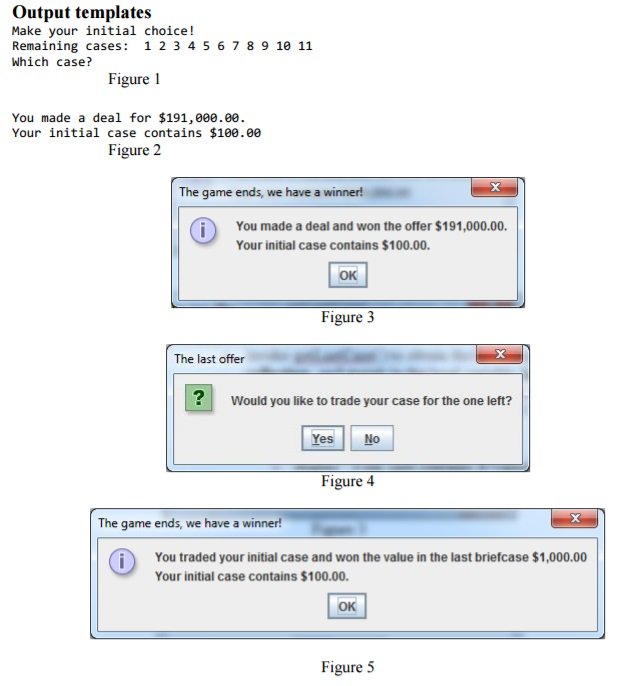
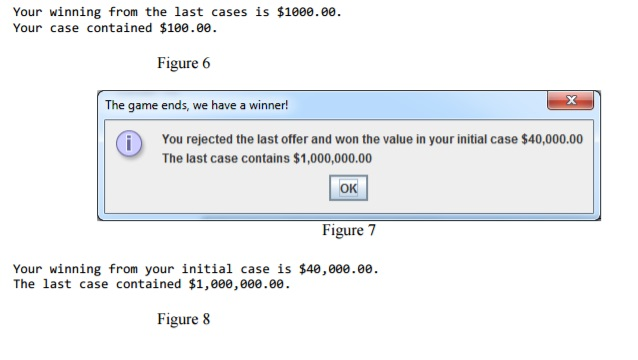
11. Numeric figures in the output messages should be formatted as shown on the samples and Figures
12. Dollar values and case numbers displayed in output are generated by random events, therefore they are not suitable for testing purposes
13. When working on implementation, carefully and simultaneously study the UML diagrams and the class/method specifications.
Briefcase Collection Play The Game Briefcase Banker Game ControlStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


