The Problem
There are lots of ways to try to compare the similarity of documents. One way is to focus on the character n-grams that occur in two tracts of text.
n-grams and text comparison
The n-grams found in a text consists of every sequence of n characters. We are going to record the bigrams found in every word (space separated element) and use the counts from two documents to find their similarity.
Consider the sample sentence fragment:"the rat race"
In order, the bigrams (n=2) would be: th, he, ra, at, ra, ac, ce.
Overall the counts would be th:1, he:1, ra:2, at:1, ce:1.
If we take all the spaces out of the sentence to get theratrace, the tri-grams (n=3) would be:
the her era rat atr tra rac ace
Using this information, we could measure the similarity of two documents based on the bigram profile: the list of bigrams and their counts. One (not great) measure is https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosine_similarity#Ochiai_coefficient . Essentially this would be:
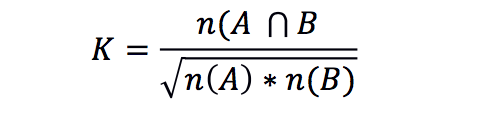
Where n is the number of elements in the two quantities A and B. The measure ranges from 0.0 1.0 . We are going to measure this coefficient for various n-grams of provided documents.
Basic Premise
You are going to build a map where the string represents a particular n-gram and the long represents the frequency of finding that n-gram in the document being processed.
Your Tasks
Complete the Project 7 by writing code for the following functions. Details of type for the functions can be found in functions.h (provided for you, see details below). The
map_to_string : returns a single string of the map, where each element is printed as string:long, comma separated elements. No comma at the end, see test cases
vector_to_string : returns a single string of the argument vector>, where each element is printed as string:long, comma separated elements. No comma at the end! This
vector is convenient for sorting, (can't sort a map) as you'll see below, see test cases
clean_string : for the provided string argument returns a new string where the only contents are alphabetic characters in lower case of the argument string
generate_ngrams : for the provided argument string, generates all the ngrams of a given n for that string. Returns a vector of all the ngrams found (no counting at this point, just a
vector of ngrams, could have repeats).
process_line : does the following
o calls clean_string to clean up the provided string argument o calls generate_ngrams on the string (n is provided as an argument) o records the frequency of the ngrams in the argument map reference.
pair_frequency_greaterthan : takes in two pairs and returns whether the first pair is greaterthan the second pair based on the .second of both pairs.
top_n : return a vector> of the argument map that is sorted in frequency order, highest to lowest. Provide only the top n values, n provided as an argument.
If you sort the vector to find this ordering, than pair_frequency_greaterthan is useful. It is a two-layered ordering: first by frequency, second alphabetically. Thus you always print
the element with the highest frequency. However, if two or more elements are tied in frequency, then print those tied frequency elements in alphabetical order.
pair_string_lessthan : takes in two pair and returns whether the first pair is lessthan the second pair based on the .first of both pairs.
ochiai : calculates the ochiai value for the two argument maps. If you use set_intersection to find the intersection set, then pair_string_lessthan is useful.
Test Cases
Test cases are provided in the subdirectory test of the project directory (because it is getting confusing), at least one for each function . However! It is time you start writing your own tests. The tests I provide are not complete, and we are free to write extra tests for grading purposes. Do a good job and test your code. Just because you pass the one (probably simple) test does not necessarily mean your code is fine. Think about your own testing!!!!
Assignment Notes
You are given the following files:
main.cpp This file includes the main function where the test cases will be run:
---------- main.cpp start----------
#include using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; using std::boolalpha; #include using std::setprecision; #include