Question
The Pump Division has one plant dedicated to the design and manufacture of large, highly technical, customized pumps. Typically the contract life (production cycle) is
The Pump Division has one plant dedicated to the design and manufacture of large, highly technical, customized pumps.
Typically the contract life (production cycle) is one to three years. Most original equipment (OE) orders are obtained by
preparing and submitting a bid proposal from a cost estimate analysis and conducting negotiating sessions with the
customer. Sometimes orders are accepted as loss leaders in order to establish a position in the more profitable aftermarket
business.
The contracts generally are fixed price. When coupled with the highly technical specifications and the length of the "in
process" time, there is a high risk of job cost overruns. Company policy is to record revenue and costs on a completed
contract basis, rather than as a percent of completion.
After a major decline in profitability, combined with several unfavorable year-end surprise inventory adjustments, new
plant management decided to undertake a review of the operation to identify the key factors that affect inventory control.
Management analysis revealed the following:
? The cost estimating function reported to the sales department.
? Final job costs varied significantly from original cost estimates. It was difficult to determine the source of variances
until analyses were made upon completion of the jobs.
? The negotiated pricing of a contract was almost always on the basis of "whatever it takes to get the order," particularly
when there was excess productive capacity in the industry.
? Progress payments/advanced payments were secured on some contracts, but such payments often were dropped if
pricing competition was severe.
? When inflation was at double-digit levels, the company attempted to insert escalation clauses into contracts based on
government indexes. However, most often, this resulted in fixed-price contracts with some estimate of inflation
included.
? During the audit at the end of each year, a lower-of-cost-or-market analysis was made on major jobs in process. It was
this exercise that revealed unfavorable inventory adjustments in recent years. Two examples are shown below:
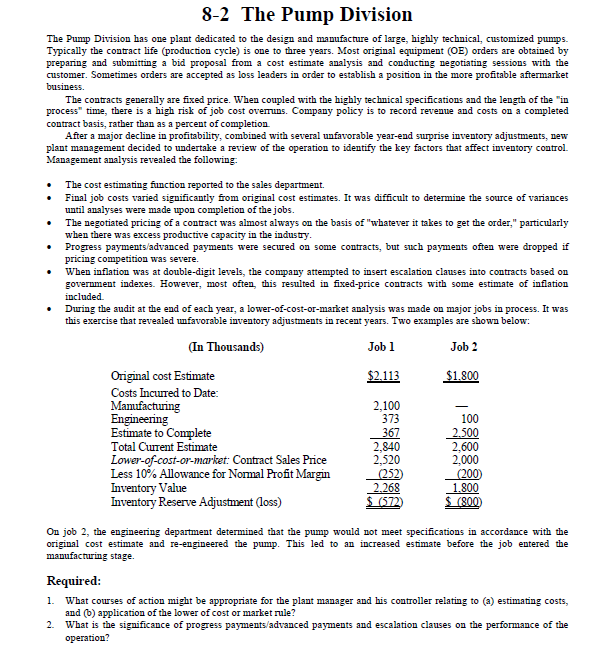
(In Thousands) Job 1 Job 2
Original cost Estimate $2,113 $1,800
Costs Incurred to Date:
Manufacturing 2,100 ?
Engineering 373 100
Estimate to Complete 367 2,500
Total Current Estimate 2,840 2,600
Lower-of-cost-or-market: Contract Sales Price 2,520 2,000
Less 10% Allowance for Normal Profit Margin (252) (200)
Inventory Value 2,268 1,800
Inventory Reserve Adjustment (loss) $ (572) $ (800)
On job 2, the engineering department determined that the pump would not meet specifications in accordance with the
original cost estimate and re-engineered the pump. This led to an increased estimate before the job entered the
manufacturing stage.
Required:
1. What courses of action might be appropriate for the plant manager and his controller relating to (a) estimating costs,
and (b) application of the lower of cost or market rule?
2. What is the significance of progress payments/advanced payments and escalation clauses on the performance of the
operation?
8-2 The Pump Division The Pump Division has one plant dedicated to the design and manufacture of large, highly technical, customized pumps. Typically the contract life (production cycle) is one to three years. Most original equipment (OE) orders are obtained by preparing and submitting a bid proposal from a cost estimate analysis and conducting negotiating sessions with the customer. Sometimes orders are accepted as loss leaders in order to establish a position in the more profitable aftermarket business. The contracts generally are fixed price. When coupled with the highly technical specifications and the length of the "in process" time, there is a high risk of job cost overruns. Company policy is to record revenue and costs on a completed contract basis, rather than as a percent of completion. After a major decline in profitability, combined with several unfavorable year-end surprise inventory adjustments, new plant management decided to undertake a review of the operation to identify the key factors that affect inventory control. Management analysis revealed the following: The cost estimating function reported to the sales department. Final job costs varied significantly from original cost estimates. It was difficult to determine the source of variances until analyses were made upon completion of the jobs. The negotiated pricing of a contract was almost always on the basis of "whatever it takes to get the order," particularly when there was excess productive capacity in the industry. Progress payments/advanced payments were secured on some contracts, but such payments often were dropped if pricing competition was severe. When inflation was at double-digit levels, the company attempted to insert escalation clauses into contracts based on government indexes. However, most often, this resulted in fixed-price contracts with some estimate of inflation included. During the audit at the end of each year, a lower-of-cost-or-market analysis was made on major jobs in process. It was this exercise that revealed unfavorable inventory adjustments in recent years. Two examples are shown below: (In Thousands) Job 1 Job 2 Original cost Estimate $2.113 $1.800 Costs Incurred to Date: Manufacturing 2,100 _ Engineering 373 100 Estimate to Complete 367 2.500 Total Current Estimate 2,840 2,600 Lower-of-cost-or-market: Contract Sales Price 2,520 2,000 Less 10% Allowance for Normal Profit Margin (252) (200) Inventory Value 2,268 1.800 Inventory Reserve Adjustment (loss) $ (572) $ (800) On job 2, the engineering department determined that the pump would not meet specifications in accordance with the original cost estimate and re-engineered the pump. This led to an increased estimate before the job entered the manufacturing stage. Required: 1. What courses of action might be appropriate for the plant manager and his controller relating to (a) estimating costs, and (b) application of the lower of cost or market rule? 2. What is the significance of progress payments/advanced payments and escalation clauses on the performance of the operation?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


