Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The purpose of this lab is to experimentally determine the equilibrium constant, Kc. for the following chemical reaction: Fe+ (aq) + SCN- (aq) FeSCN (aq)
The purpose of this lab is to experimentally determine the equilibrium constant, Kc. for the following chemical reaction:




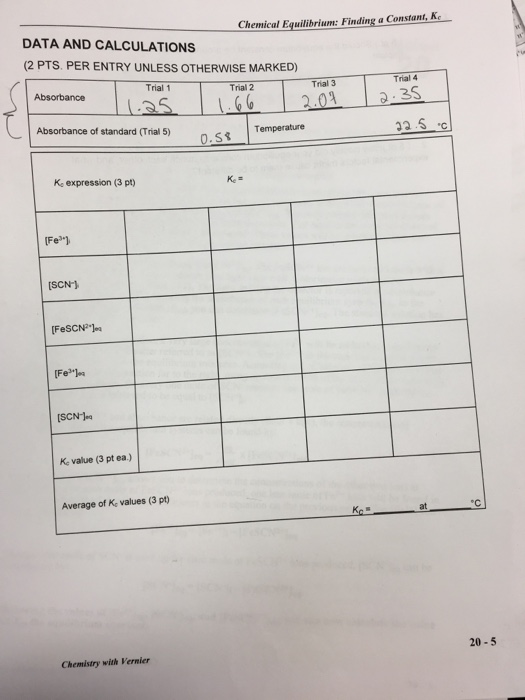

Fe+ (aq) + SCN- (aq) FeSCN (aq) iron(III) thiocyanate thiocyanoiron(III) When Fe+ and SCN are combined, equilibrium is established between these two ions and the FeSCN2+ ion. In order to calculate Ke for the reaction, it is necessary to know the concentrations of all ions at equilibrium: [FeSCN2+leq [SCN-leg, and [Fe leq. You will prepare four equilibrium systems containing different concentrations of these three ions. The equilibrium concentrations of the three ions will then be experimentally determined. These values will be substituted into the equilibrium constant expression to see if K, is indeed constant. You will use a Colorimeter to determine [FeSCN+leq The FeSCN2+ ion produces solutions with a red color. Because the red solutions absorb blue light very well, Colorimeter users will be instructed to use the 470 nm (blue) LED. The light striking the detector is reported as absorbance or percent transmittance. By comparing the absorbance of each equilibrium system, Aeg, to the absorbance of a standard solution, Astd you can determine [FeSCN2+ Jeq. The standard solution has a known FeSCN+ concentration. To prepare the standard solution, a very large concentration of Fe+ will be added to a small initial concentration of SCN (hereafter referred to as [SCN-1;. The [Fe] in the standard solution is 100 times larger than [Fe+] in the equilibrium mixtures. According to LeChatelier's principle, this high concentration forces the reaction far to the right, using up nearly 100% of the SCN-ions. According to the balanced equation, for every one mole of SCN reacted, one mole of FeSCN2+ is produced. Thus [FeSCN2+ Istd is assumed to be equal to [SCN-]i. Assuming [FeSCN2+] and absorbance are related directly (Beer's law), the concentration of FeSCN2+ for any of the equilibrium systems can be found by: Aeq [FeSCN+ leq= x [FeSCN+ ]std Astd Knowing the [FeSCN+ Jeg allows you to determine the concentrations of the other two ions at equilibrium. For each mole of FeSCN2+ ions produced, one less mole of Fe+ ions will be found in the solution (see the 1:1 ratio of coefficients in the equation on the previous page). The [Fe+] can be determined by: [Feleq=[Feli-[FeSCN+ leq Because one mole of SCN is used up for each mole of FeSCN2+ ions produced, [SCN-Jeq can be determined by: [SCN-leq - [SCN-li-[FeSCN+ leq = Knowing the values of [Feleqs [SCN-leqs and [FeSCN2+ legs you can now calculate the value of Ke the equilibrium constant. OBJECTIVE In this experiment, you will determine the equilibrium constant, Ke, for the following chemical reaction: MATERIALS Fe+ (aq) + SCN (aq) FeSCN+ (aq) iron(III) thiocyanate thiocyanoiron (III) Vernier LabQuest LabQuest App Vernier Colorimeter 6 plastic cuvettes five 20 x 150 mm test tubes three 100 mL beakers thermometer PROCEDURE 1. Obtain and wear goggles. 2. Label four 20 x 150 mm test tubes 1-4. Pour about 30 mL of 0.0020 M Fe(NO3)3 into a clean, dry 100 ml beaker. Pipet 5.0 mL of this solution into each of the four labeled test tubes. Use a pipet pump or bulb to pipet all solutions. CAUTION: Fe(NO)s solutions in this experiment are prepared in 1.0 M HNO, and should be handled with care. Pour about 25 mL of the 0.0020 M KSCN into another clean, dry 100 mL beaker. Pipet 2, 3, 4 and 5 mL of this solution into Test Tubes 1-4, respectively. Obtain about 25 mL of distilled water in a 100 ml beaker. Then pipet 3, 2, 1 and 0 mL of distilled water into Test Tubes 1-4, respectively, to bring the total volume of each test tube to 10 mL. Mix each solution thoroughly with a stirring rod. Be sure to clean and dry the stirring rod after each mixing. Measure and record the temperature of one of the above solutions to use as the temperature for the equilibrium constant, Ke. Volumes added to each test tube are summarized below: Test Tube Number 1 2 3 4 Fe(NO3) (mL) 20-2 5 0.0020 M KSCN 0.0020 M Fe(NO3)3 (in 1.0 M HNO3) 0.200 M Fe(NO3)3 (in 1.0 M HNO3) four pipets pipet bulb or pipet pump tissues (preferably lint-free). 5 5 5 KSCN (mL) 2 3 4 5 HO (mL) 3. Prepare a standard solution of FeSCN2+ by pipetting 18 mL of 0.200 M Fe(NO3)3 into a 20x150 mm test tube labeled "5". Pipet 2 mL of 0.0020 M KSCN into the same test tube. Stir thoroughly. Wipe the outside of each cuvette with a lint-free tissue. Handle cuvettes only by the top edge of the ribbed sides. 3 2 1 0 4. Prepare a blank by filling a cuvette 3/4 full with distilled water. To correctly use cuvettes, remember: Dislodge any bubbles by gently tapping the cuvette on a hard surface. Always position the cuvette so the light passes through the clear sides. Chemistry with Vernier Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Ke 5. Connect the Colorimeter to LabQuest and choose New from the File menu. 6. Calibrate the Colorimeter. a. Place the blank in the cuvette slot of the Colorimeter and close the lid. b. Press the button on the Colorimeter to select a wavelength of 470 nm. Press the CAL button on the Colorimeter. When the LED stops flashing, the calibration is complete. 7. Set up the data collection mode. a. On the Meter screen, tap Mode. Change the mode to Events with Entry. b. Enter the Name (Concentration) and Units (mol/L). Select OK. 8. You are now ready to collect absorbance data for the four equilibrium systems and the standard solution. a. With the Test Tube 1 solution, fill a new cuvette 3/4 full, and place it in the device. b. When the value displayed on the screen has stabilized, tap Keep and enter 1 (the trial number). Select OK. The absorbance and concentration values have now been saved for the first solution. Write the absorbance value on the report sheet for trial 1. c. With the Test Tube 1 solution, fill a new cuvette 3/4 full with Test Tube 2 solution, and place it in the device. Press run twice, and then "append". After the reading stabilizes, tap Keep and enter 2. Select OK to continue. Again, record the absorbance value for Trial 2, in your data table. d. Repeat the procedure to find the absorbance of the solutions in Test Tubes 3, 4, and 5 (the standard solution) with a new cuvette for each. Record the absorbance values, for each Trial, in your data table. e. Stop data collection. f. Examine the data points on the displayed graph. YOU SHOULD HAVE A STRAIGHT LINE INCREASING UP TO THE RIGHT. If you do not please contact your instructor!! g. If you want to check any data values, tap any data point. As you tap a data point, the absorbance and concentration values are displayed to the right of the graph. h. Dispose of all solutions in the waste container. Cuvettes and pipettes are also disposable. Lean any Sharpie off of the glassware.. PROCESSING THE DATA 1. Write the K expression for the reaction in the Data and Calculation table. 2. Calculate the initial concentration of Fe+, based on the dilution that results from adding KSCN solution and water to the original 0.0020 M Fe(NO3)3 solution. See Step 2 of the procedure for the volume of each substance used in Trials 1-4. Calculate [Fe3+]; using the equation: Fe(NO3)3 mL [Feli= total mL This should be the same for all four test tubes. (0.0020 M) LabQuest 20 3. Calculate the initial concentration of SCN", based on its dilution by Fe(NO3)3 and water: KSCN mL [SCN-li total ml (0.0020 M) In Test Tube 1, [SCN-];-(2 mL/10 mL)(0.0020 M) = 0.00040 M. Calculate this for the other three test tubes. 4. [FeSCN2Jeq is calculated using the formula: Aeg X Astd x [FeSCN+]std [FeSCN2 Jeq where Aeq and Asd are the absorbance values for the equilibrium and standard test tubes, respectively, and [FeSCN2 Isid (1/10)(0.0020) = 0.00020 M. Calculate [FeSCNleq for each of the four trials. 5. [Feleq: Calculate the concentration of Fe+ at equilibrium for Trials 1-4 using the equation: [Fe leq=[Fe+]-[FeSCN* Jeq 6. [SCN-Jeq: Calculate the concentration of SCN- at equilibrium for Trials 1-4 using the equation: [SCN-Jeq [SCN-]-[FeSCN2+ leq 7. Calculate K for Trials 1-4. Be sure to show the Ke expression and the values substituted in for each of these calculations. 8. Using your four calculated K, values, determine an average value for Ke. How constant were your Ke values? DATA AND CALCULATIONS (2 PTS. PER ENTRY UNLESS OTHERWISE MARKED) Trial 1 1.25 Absorbance of standard (Trial 5) Absorbance K. expression (3 pt) [Fe] [SCN-] [FeSCN] [Fe] [SCN-Jea K value (3 pt ea.) Average of K, values (3 pt) Chemistry with Vernier Chemical Equilibrium: Finding a Constant, Ke Trial 2 1.66 0.58 Ke= Trial 3 2.07 Temperature Trial 4 2.35 32.5 c 76 C 20-5 LabQuest 20 1. (5 pt.) Should the equilibrium constant be around the same for all of the test solution Explain. 2. (5 pt.)How closely did your equilibrium constants match each other, and what experimental factors might cause them to be different?
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.53 Rating (146 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


