Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
the question is asking in which areas require further analysis and investigation P3-16 P3-19 Common-size statement analysis A common-size income statement for Creek Enterprises 2018
the question is asking in which areas require further analysis and investigation
P3-16 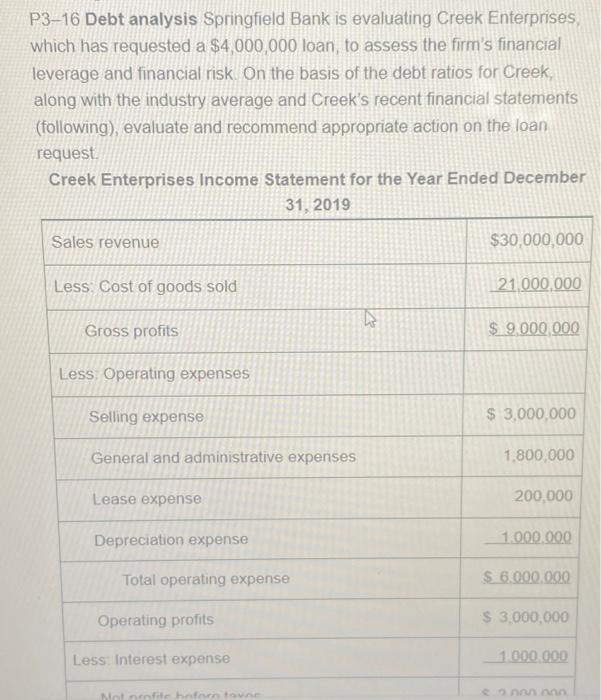
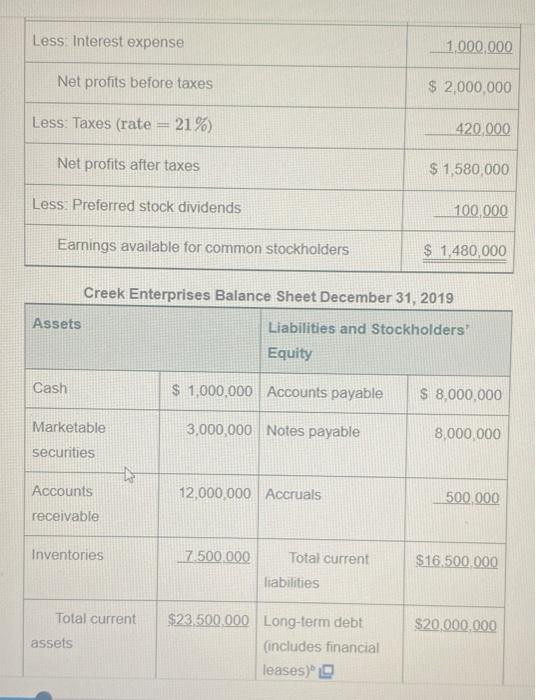
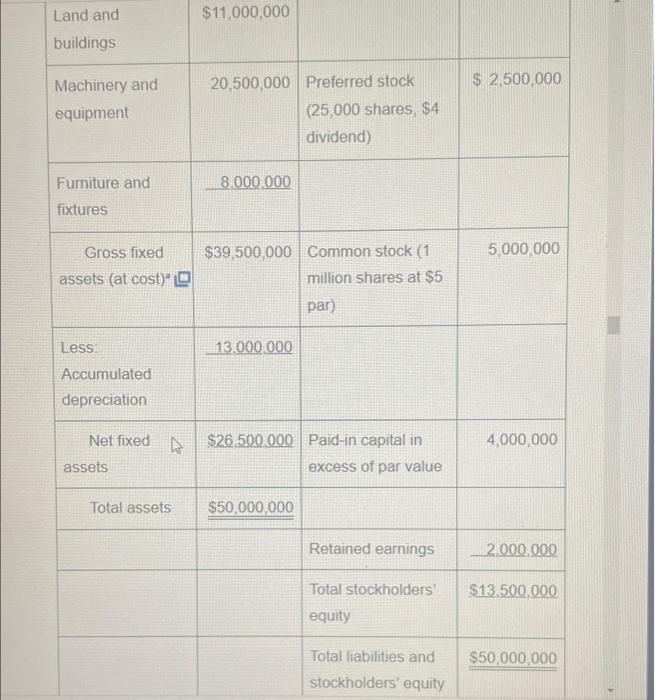
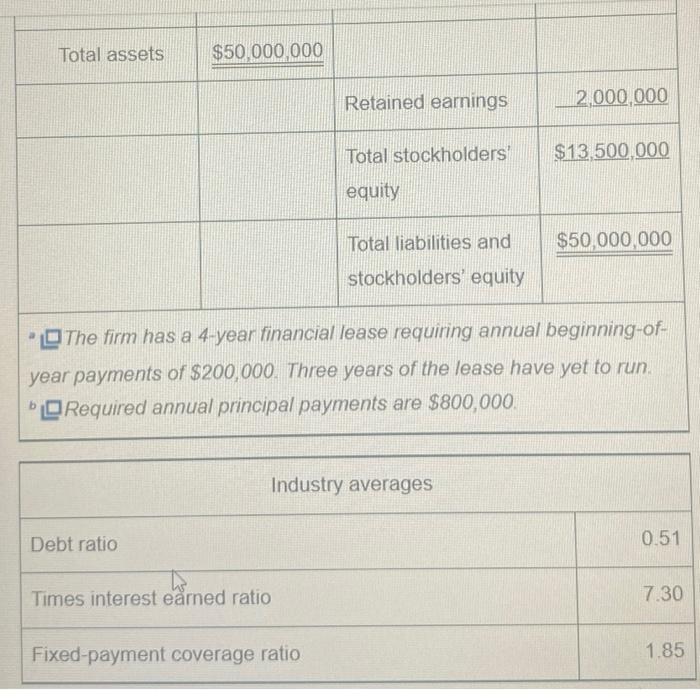
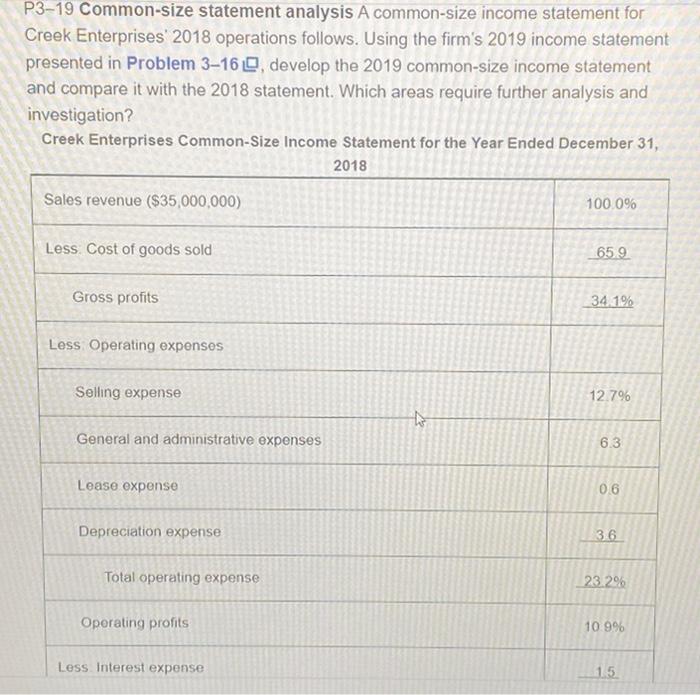
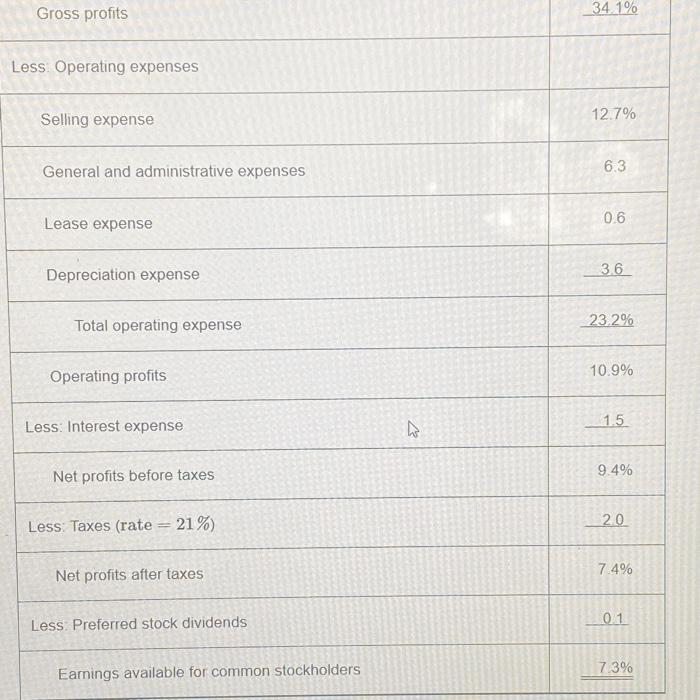
P3-19 Common-size statement analysis A common-size income statement for Creek Enterprises 2018 operations follows. Using the firm's 2019 income statement presented in Problem 3-16, develop the 2019 common-size income statement and compare it with the 2018 statement. Which areas require further analysis and investigation? Creek Enterprises Common-Size Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2018 Sales revenue ($35,000,000) 100.0% Less: Cost of goods sold 65.9 Gross profits 34.1% Less Operating expenses Selling expense 12.7% General and administrative expenses 6.3 Lease expense 0.6 Depreciation expense 36 23.2% 10.9% 15 Total operating expense Operating profits Less Interest expense to Gross profits Less: Operating expenses Selling expense General and administrative expenses Lease expense Depreciation expense Total operating expense Operating profits Less: Interest expense Net profits before taxes 21%) Net profits after taxes Less: Preferred stock dividends Earnings available for common stockholders Less: Taxes (rate = K 34.1% 12.7% 6.3 0.6 3.6 23.2% 10.9% 1.5 9.4% 20 7.4% 0.1 7.3% P3-16 Debt analysis Springfield Bank is evaluating Creek Enterprises, which has requested a $4,000,000 loan, to assess the firm's financial leverage and financial risk. On the basis of the debt ratios for Creek, along with the industry average and Creek's recent financial statements (following), evaluate and recommend appropriate action on the loan request. Creek Enterprises Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales revenue $30,000,000 Less: Cost of goods sold 21,000,000 Gross profits $9,000,000 Less Operating expenses Selling expense $ 3,000,000 General and administrative expenses 1,800,000 Lease expense 200,000 Depreciation expense 1.000.000 $ 6.000.000 $ 3,000,000 1.000.000 $ 2.000.000 Total operating expense Operating profits Less: Interest expense Not profite hoforo tavne 43 Less Interest expense Net profits before taxes Less: Taxes (rate = 21%) Net profits after taxes Less: Preferred stock dividends Earnings available for common stockholders Creek Enterprises Balance Sheet December 31, 2019 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $ 1,000,000 Accounts payable 3,000,000 Notes payable 12,000,000 Accruals 7.500.000 Total current liabilities $23.500.000 Long-term debt (includes financial leases) Assets Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable Inventories to Total current assets 1,000,000 $ 2,000,000 420,000 $ 1,580,000 100,000 $ 1,480,000 $ 8,000,000 8,000,000 500,000 $16.500.000 $20,000,000 Land and buildings Machinery and equipment Furniture and fixtures Gross fixed assets (at cost) Less: Accumulated depreciation Net fixed Total assets assets $11,000,000 20,500,000 Preferred stock (25,000 shares, $4 dividend) 8,000,000 $39,500,000 Common stock (1) million shares at $5 par) 13.000.000 $26.500.000 Paid-in capital in excess of par value $50,000,000 Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ 2,500,000 5,000,000 4,000,000 2,000,000 $13,500,000 $50,000,000 Total assets $50,000,000 Retained earnings 2,000,000 Total stockholders' $13,500,000 equity Total liabilities and $50,000,000 stockholders' equity The firm has a 4-year financial lease requiring annual beginning-of- year payments of $200,000. Three years of the lease have yet to run. Required annual principal payments are $800,000. Industry averages Debt ratio 0.51 Times interest earned ratio 7.30 Fixed-payment coverage ratio 1.85 P3-19 Common-size statement analysis A common-size income statement for Creek Enterprises 2018 operations follows. Using the firm's 2019 income statement presented in Problem 3-16, develop the 2019 common-size income statement and compare it with the 2018 statement. Which areas require further analysis and investigation? Creek Enterprises Common-Size Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2018 Sales revenue ($35,000,000) 100.0% Less: Cost of goods sold 65.9 Gross profits 34.1% Less Operating expenses Selling expense 12.7% General and administrative expenses 6.3 Lease expense 0.6 Depreciation expense 36 23.2% 10.9% 15 Total operating expense Operating profits Less Interest expense to Gross profits Less: Operating expenses Selling expense General and administrative expenses Lease expense Depreciation expense Total operating expense Operating profits Less: Interest expense Net profits before taxes 21%) Net profits after taxes Less: Preferred stock dividends Earnings available for common stockholders Less: Taxes (rate = K 34.1% 12.7% 6.3 0.6 3.6 23.2% 10.9% 1.5 9.4% 20 7.4% 0.1 7.3% P3-16 Debt analysis Springfield Bank is evaluating Creek Enterprises, which has requested a $4,000,000 loan, to assess the firm's financial leverage and financial risk. On the basis of the debt ratios for Creek, along with the industry average and Creek's recent financial statements (following), evaluate and recommend appropriate action on the loan request. Creek Enterprises Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales revenue $30,000,000 Less: Cost of goods sold 21,000,000 Gross profits $9,000,000 Less Operating expenses Selling expense $ 3,000,000 General and administrative expenses 1,800,000 Lease expense 200,000 Depreciation expense 1.000.000 $ 6.000.000 $ 3,000,000 1.000.000 $ 2.000.000 Total operating expense Operating profits Less: Interest expense Not profite hoforo tavne 43 Less Interest expense Net profits before taxes Less: Taxes (rate = 21%) Net profits after taxes Less: Preferred stock dividends Earnings available for common stockholders Creek Enterprises Balance Sheet December 31, 2019 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity $ 1,000,000 Accounts payable 3,000,000 Notes payable 12,000,000 Accruals 7.500.000 Total current liabilities $23.500.000 Long-term debt (includes financial leases) Assets Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable Inventories to Total current assets 1,000,000 $ 2,000,000 420,000 $ 1,580,000 100,000 $ 1,480,000 $ 8,000,000 8,000,000 500,000 $16.500.000 $20,000,000 Land and buildings Machinery and equipment Furniture and fixtures Gross fixed assets (at cost) Less: Accumulated depreciation Net fixed Total assets assets $11,000,000 20,500,000 Preferred stock (25,000 shares, $4 dividend) 8,000,000 $39,500,000 Common stock (1) million shares at $5 par) 13.000.000 $26.500.000 Paid-in capital in excess of par value $50,000,000 Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ 2,500,000 5,000,000 4,000,000 2,000,000 $13,500,000 $50,000,000 Total assets $50,000,000 Retained earnings 2,000,000 Total stockholders' $13,500,000 equity Total liabilities and $50,000,000 stockholders' equity The firm has a 4-year financial lease requiring annual beginning-of- year payments of $200,000. Three years of the lease have yet to run. Required annual principal payments are $800,000. Industry averages Debt ratio 0.51 Times interest earned ratio 7.30 Fixed-payment coverage ratio 1.85 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


