Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The Robertson-Walker geometry (to be discussed in Chapter 9) has a spacetime interval ds = dt-a(t) [dx + sin x (do+ sin0do)] where the
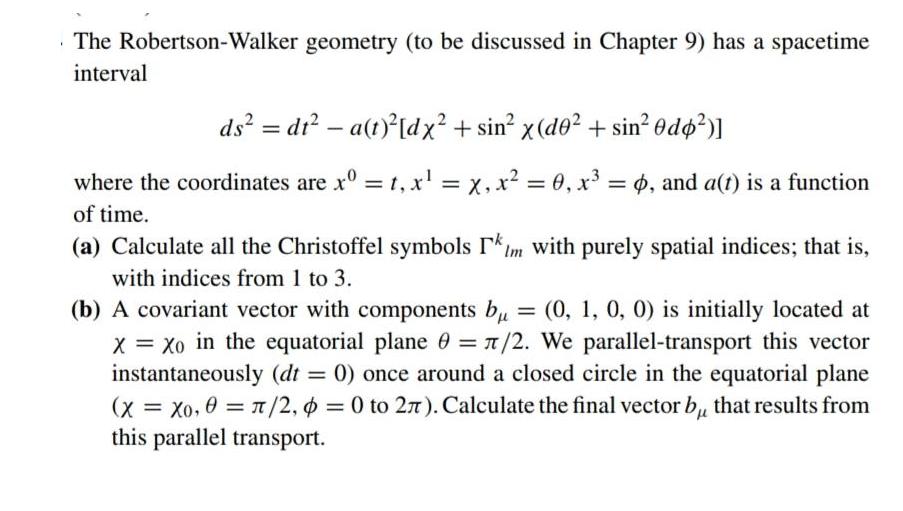
The Robertson-Walker geometry (to be discussed in Chapter 9) has a spacetime interval ds = dt-a(t) [dx + sin x (do+ sin0do)] where the coordinates are x = t, x = x, x = 0, x = 0, and a(t) is a function of time. (a) Calculate all the Christoffel symbols Im with purely spatial indices; that is, with indices from 1 to 3. (b) A covariant vector with components b = (0, 1, 0, 0) is initially located at X = Xo in the equatorial plane 0 = /2. We parallel-transport this vector instantaneously (dt = 0) once around a closed circle in the equatorial plane (x = Xo, 0 = /2, p = 0 to 27). Calculate the final vector bu that results from this parallel transport.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.37 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
A To calculate the Christoffel symbols Gamma k lm with purely spatial indices we can start by taking the derivative of the metric tensor gkl with resp...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


