Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
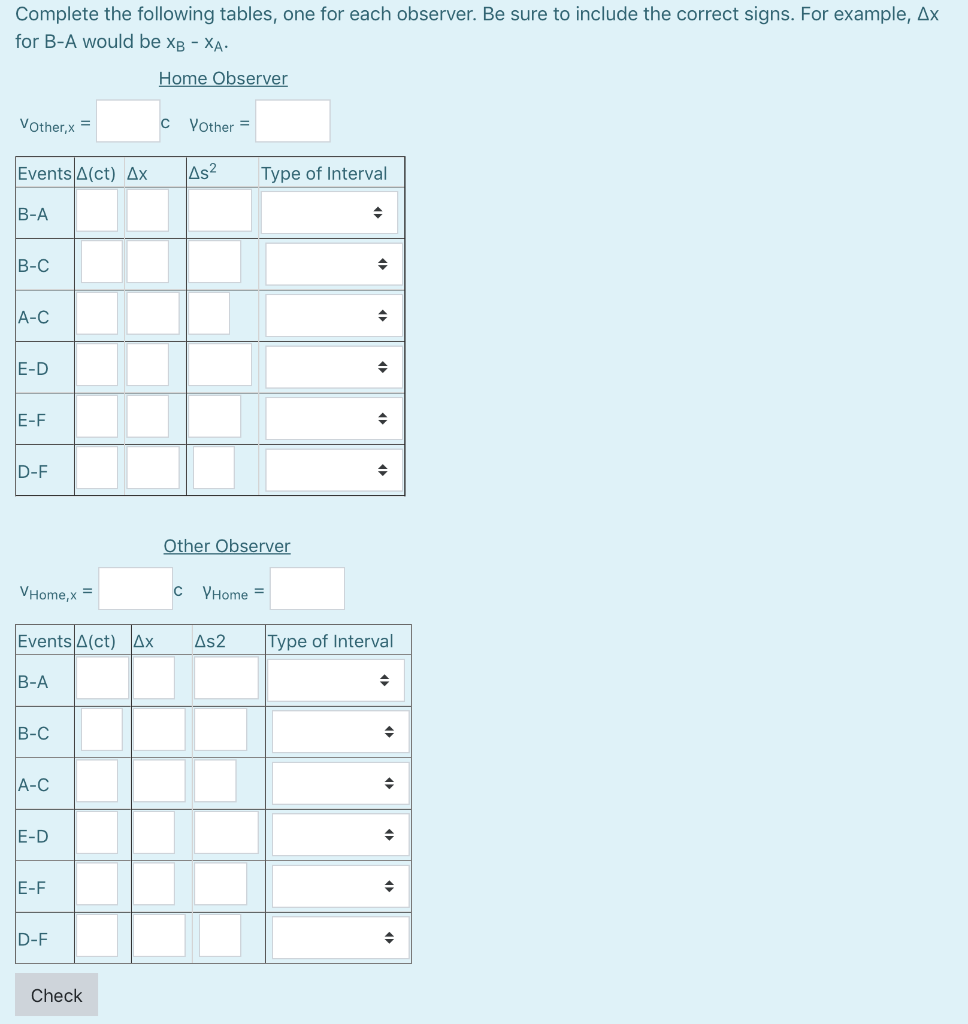
The space-time interval (s) between two events can be calculated by using the space-time metric: s 2 = (ct) 2 - x 2 . Because
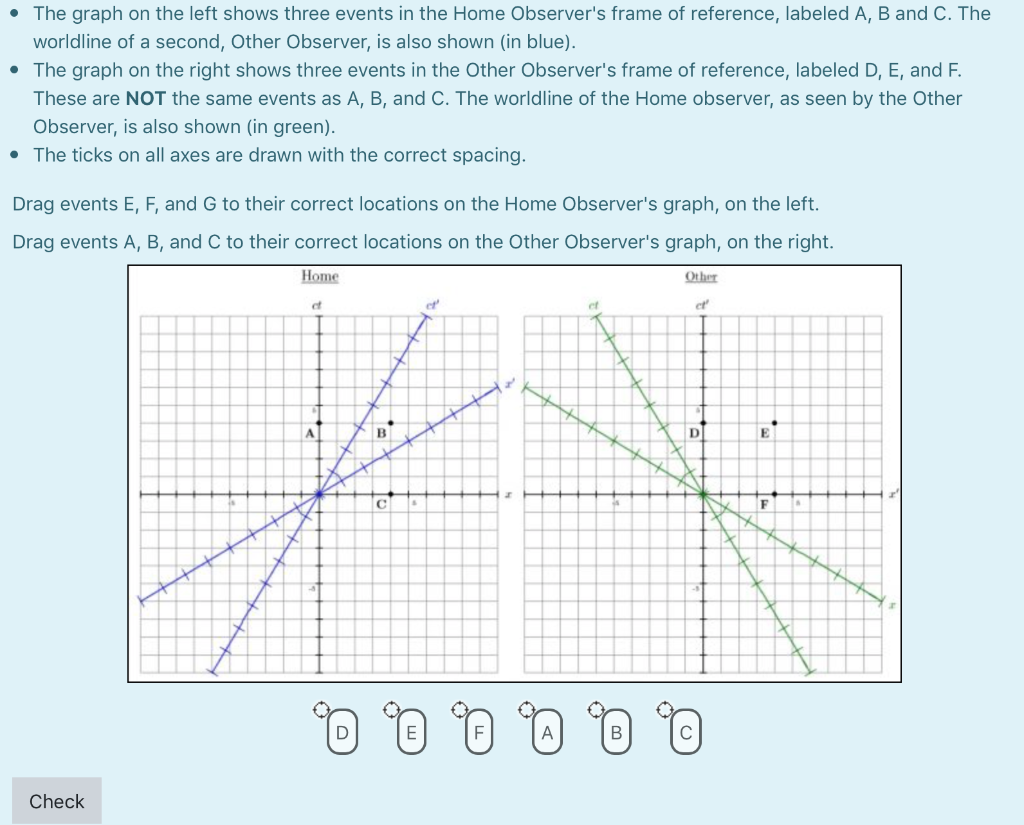
The space-time interval (s) between two events can be calculated by using the space-time metric:
s2 = (ct)2 - x2.
Because of the minus sign, s2 may be positive, negative, or zero:
- If (ct)2 > x2, then the interval is said to be time-like. These events may be causally related; one may cause, or be caused by, the other.
- If (ct)2 2, then the interval is said to be space-like. These events cannot be causally related; neither event could cause the other.
- If (ct)2 = x2, then the interval is said to be light-like. These events may be traversed by a light ray.
The space-time interval between two events is invariant; that is, all observers will agree on it's value.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


