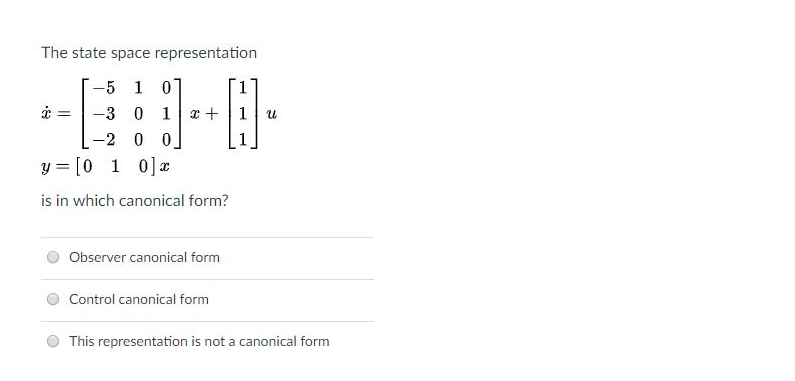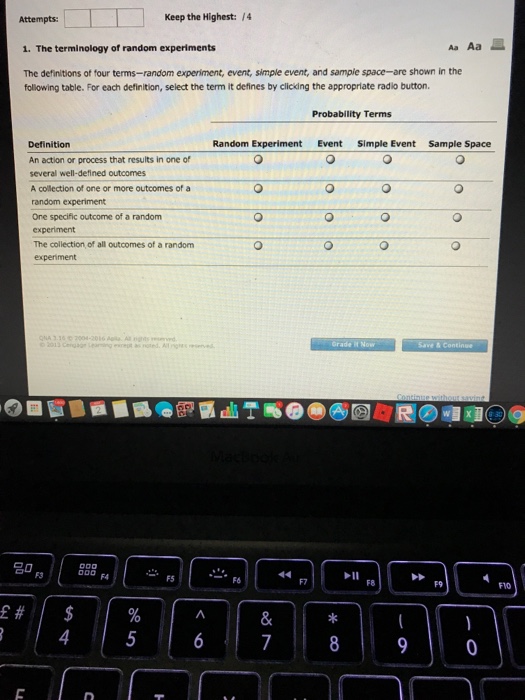


The state space representation 5 1 0 -3 0 -20 0 y = [0 1 0]x is in which canonical form? O Observer canonical form O Control canonical form O This representation is not a canonical form_ Which one is correct about randomized experiments? Check all that apply 3 It is impossible to run randomized experiments in social sciences. \"1 It is impossible to run a perfect randomized experiment. so randomized experiments are useless Although randomized experiments are impossible in some cases, it is always informative to think about an \"ideal\" experiment, whenever we study causal effect of one variable on a variable of interest. \"3 Randomized experiments are so valuable that justies spending huge amount of money. whenever it is possible. Attempts: Keep the Highest: /4 1. The terminology of random experiments As Aa The definitions of four terms-random experiment, event, simple event, and sample space-are shown in the following table. For each definition, select the term it defines by clicking the appropriate radio button. Probability Terms Definition Random Experiment Event Simple Event Sample Space An action or process that results in one of O O O several well-defined outcomes A collection of one or more outcomes of a O O O O random experiment One specific outcome of a random O O O O experiment The collection, of all outcomes of a random O O O O experiment Grade I Now Save & Continue Continue without urine w x MacBook F3 DOO FA FS 14 F7 FB F9 f # LA % V 4 5 OO OQUESTION 5 What is the disadvantage of using 2 one-way ANOVAs instead of conducting a two-way ANOVA? O One-way ANOVAs show only the main effects and not the interactions, You're more likely to violate the homogeneity of variances assumption with a one-way ANOVA. O One-way ANOVAs needlessly raise the power of the statistical tests, O You have to run post-hoc tests if you conduct multiple one-way ANOVAs.For, G(5) = 5/(5 +25+1) Represent this system in 1. controllable canonical form (3) 2. observable canonical form (3) 3. is the system observable (4) 4. is the system controllable (4 )