Question
The SuperStar Tennis Ball Company is in negotiations with a Sporting Goods Distribution Retail Sales Company. They have introduced a brand new tennis ball that
The SuperStar Tennis Ball Company is in negotiations with a Sporting Goods Distribution Retail Sales Company. They have introduced a brand new tennis ball that has excellent performance and is widely enjoyed by amateur and professional tennis players in the United States. The contract demand is estimated to be between 80,000 and 100,000 tennis balls. They have determined that in order to push this contract forward that they are expecting $200,000 in marketing and administrative costs.
The dilemma that SuperStar faces is that they have numerous unknowns that they want to run through a simulation to get a profit evaluation. They have told you that they would like to have at least 1,000 simulations to perform on this study. Here are some of the parameters that they would like simulated and the type of random evaluation to take place.
1) They would like to evaluate a randomly simulated selling price (per unit) for each can of tennis balls sold. They have estimated the mean of their sales to be $45, with a standard deviation of 5% of the mean. Use these values to randomly deliver a normal distribution using mean/std deviation.
2) They deal with numerous suppliers that give them procurement costs. It is estimated that 25% of their procurement costs are $10, 50% of their procurement costs are $11, and 25% of their costs are $12. Use these values to randomly deliver a normal distribution using probability.
3) To package, label, and conduct quality assurance inspections on the balls, they hire employees to provide labor. The labor costs (per unit) are estimated to be from $20 to $24, in $1 increments. However, 10% of the labor gets $20, 25% of the labor gets $21, 30% of the labor gets $22, 25% of the labor gets $23, and 10% of the labor gets $24. Use these values to randomly deliver a normal distribution using probability.
4) The postage is estimated to be between $3 and $5 per unit. Use the randbetween function to randomly generate postage costs.
5) The demand is uniformly random, using the demand values above.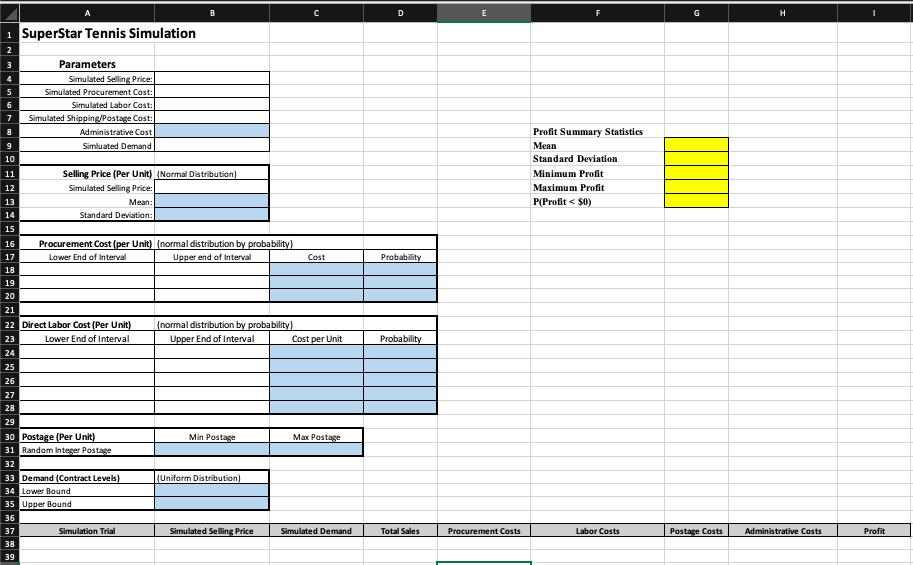
1 SuperStar Tennis Simulation 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 wwwwwww~~~~~~~~~555555: 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 23 24 25 22 Direct Labor Cost (Per Unit) Lower End of Interval 26 27 28 29 32 36 Parameters Postage Unit) 31 Random Integer Postage 37 Simulated Selling Price: Simulated Procurement Cost: Simulated Labor Cost: Simulated Shipping/Postage Cost: Administrative Cost Simluated Demand 38 Selling Price (Per Unit) (Normal Distribution) Simulated Selling Price: Mean: Standard Deviation: 33 Demand (Contract Levels) 34 Lower Bound 35 Upper Bound 39 Procurement Cost (per Unit) (normal distribution by probability) Lower End of Interval Upper end of Interval Simulation Trial (normal distribution by probability) Upper End of Interval Postage (Uniform Distribution) Simulated Selling Price C Cost Cost per Unit Postage Simulated Demand D Probability Probability Total Sales E Procurement Costs Profit Summary Statistics Mean Standard Deviation Minimum Profit Maximum Profit P(Profit < $0) Labor Costs Postage Costs H Administrative Costs Profit
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 Simulating Selling Price per unit Mean 45 Standard Deviation 5 of the mean 005 45 225 To simulate ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


