Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The universality assumption is one of four key assumptions that underlie cognitive neuropsychology. The assumption is that, while each individual brain is unique, the



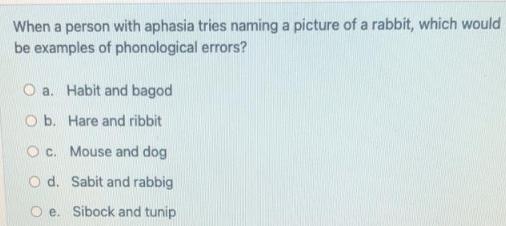
The universality assumption is one of four key assumptions that underlie cognitive neuropsychology. The assumption is that, while each individual brain is unique, the functional architecture is the same for everyone. For example, when recognising an object that we see, we all use the same information processing steps. Which of the following is true of the universality assumption? O a. After identifying which part of the brain is damaged, it allows us to generalise to the wider population and accurately predict which cognitive processes will be impacted O b. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports the use of single case studies in cognitive neuropsychology Oc. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports averaging the results from multiple associations to find multiple dissociations, which are the gold standard of evidence in cognitive neuropsychology Od. It makes a single dissociation between two skills, such as recognising faces versus recognising words, the strongest type of evidence that the two skills are processed by separate cognitive modules. Oe. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports averaging the results from multiple case studies to establish whether two skills, such as recognising faces versus recognising words, are processed by separate cognitive modules Which of the following BEST summarises what analyses of aphasia treatment research has concluded? Select one: O a. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients O b. Less recovery with more intensive treatment O c. More recovery with more intensive treatment Od. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients and more recovery from more intensive treatment e. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients and less recovery from more intensive treatment Which of the following assessments can help you identify a child with 'hyperlexia'? O a. Non-word reading and migratable word reading tests O b. Letter-identification and picture-naming tests OC. Irregular word reading and a test on the meanings of those irregular words O d. Migratable word reading and letter-identification tests Oe. Irregular word reading and nonword reading tests When a person with aphasia tries naming a picture of a rabbit, which would be examples of phonological errors? a. Habit and bagod O b. Hare and ribbit Oc. Mouse and dog O d. Sabit and rabbig e. Sibock and tunip The universality assumption is one of four key assumptions that underlie cognitive neuropsychology. The assumption is that, while each individual brain is unique, the functional architecture is the same for everyone. For example, when recognising an object that we see, we all use the same information processing steps. Which of the following is true of the universality assumption? O a. After identifying which part of the brain is damaged, it allows us to generalise to the wider population and accurately predict which cognitive processes will be impacted O b. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports the use of single case studies in cognitive neuropsychology Oc. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports averaging the results from multiple associations to find multiple dissociations, which are the gold standard of evidence in cognitive neuropsychology Od. It makes a single dissociation between two skills, such as recognising faces versus recognising words, the strongest type of evidence that the two skills are processed by separate cognitive modules. Oe. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports averaging the results from multiple case studies to establish whether two skills, such as recognising faces versus recognising words, are processed by separate cognitive modules Which of the following BEST summarises what analyses of aphasia treatment research has concluded? Select one: O a. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients O b. Less recovery with more intensive treatment O c. More recovery with more intensive treatment Od. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients and more recovery from more intensive treatment e. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients and less recovery from more intensive treatment Which of the following assessments can help you identify a child with 'hyperlexia'? O a. Non-word reading and migratable word reading tests O b. Letter-identification and picture-naming tests OC. Irregular word reading and a test on the meanings of those irregular words O d. Migratable word reading and letter-identification tests Oe. Irregular word reading and nonword reading tests When a person with aphasia tries naming a picture of a rabbit, which would be examples of phonological errors? a. Habit and bagod O b. Hare and ribbit Oc. Mouse and dog O d. Sabit and rabbig e. Sibock and tunip The universality assumption is one of four key assumptions that underlie cognitive neuropsychology. The assumption is that, while each individual brain is unique, the functional architecture is the same for everyone. For example, when recognising an object that we see, we all use the same information processing steps. Which of the following is true of the universality assumption? O a. After identifying which part of the brain is damaged, it allows us to generalise to the wider population and accurately predict which cognitive processes will be impacted O b. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports the use of single case studies in cognitive neuropsychology Oc. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports averaging the results from multiple associations to find multiple dissociations, which are the gold standard of evidence in cognitive neuropsychology Od. It makes a single dissociation between two skills, such as recognising faces versus recognising words, the strongest type of evidence that the two skills are processed by separate cognitive modules. Oe. It allows us to generalise from an individual to the wider population, which supports averaging the results from multiple case studies to establish whether two skills, such as recognising faces versus recognising words, are processed by separate cognitive modules Which of the following BEST summarises what analyses of aphasia treatment research has concluded? Select one: O a. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients O b. Less recovery with more intensive treatment O c. More recovery with more intensive treatment Od. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients and more recovery from more intensive treatment e. More recovery in treated patients than untreated patients and less recovery from more intensive treatment Which of the following assessments can help you identify a child with 'hyperlexia'? O a. Non-word reading and migratable word reading tests O b. Letter-identification and picture-naming tests OC. Irregular word reading and a test on the meanings of those irregular words O d. Migratable word reading and letter-identification tests Oe. Irregular word reading and nonword reading tests When a person with aphasia tries naming a picture of a rabbit, which would be examples of phonological errors? a. Habit and bagod O b. Hare and ribbit Oc. Mouse and dog O d. Sabit and rabbig e. Sibock and tunip
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.45 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The detailed answer for the above question is provided below 1 The statement that best aligns with t...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


