Question
There is Node class? import java.util.Random; public class CSE205_Assignment04 { private static Random rnd = new Random(); public static void main(String[] args) { Tree_ctor_test(); Tree_insert1_test();
There is Node class?
import java.util.Random;
public class CSE205_Assignment04 {
private static Random rnd = new Random();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree_ctor_test();
Tree_insert1_test();
Tree_insert3_test();
Tree_insertMany1_test();
Tree_insertMany2_test();
Tree_insertMany3_test();
Tree_insertMany4_test();
}
public static void Tree_ctor_test()
{
Tree
assertEqual("", t.toString(), "Tree_ctor_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_ctor_test: contains", false);
}
public static void Tree_insert1_test()
{
Tree
t.insert(1);
assertEqual("1 ", t.toString(), "Tree_insert1_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_insert1_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(1), "Tree_insert1_test: contains", false);
}
public static void Tree_insert3_test()
{
Tree
t.insert(2);t.insert(1);t.insert(3);
assertEqual("1 2 3 ", t.toString(), "Tree_insert3_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_insert3_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(1), "Tree_insert3_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(2), "Tree_insert3_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(3), "Tree_insert3_test: contains", false);
}
public static void Tree_insertMany1_test()
{
Tree
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
for (int n : arr)
t.insert(n);
assertEqual("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ", t.toString(), "Tree_insertMany1_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_insertMany1_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(11), "Tree_insertMany1_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(1), "Tree_insertMany1_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(10), "Tree_insertMany1_test: contains", false);
}
public static void Tree_insertMany2_test()
{
Tree
int[] arr = {10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
for (int n : arr)
t.insert(n);
assertEqual("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ", t.toString(), "Tree_insertMany2_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_insertMany2_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(11), "Tree_insertMany2_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(1), "Tree_insertMany2_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(10), "Tree_insertMany2_test: contains", false);
}
public static void Tree_insertMany3_test()
{
Tree
int[] arr = {5,3,7,2,9,1,6,10,4,8};
for (int n : arr)
t.insert(n);
assertEqual("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ", t.toString(), "Tree_insertMany3_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_insertMany3_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(11), "Tree_insertMany3_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(1), "Tree_insertMany3_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(10), "Tree_insertMany3_test: contains", false);
}
public static void Tree_insertMany4_test()
{
Tree
int[] arr = {5,3,7,2,9,1,6,10,4,8,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
for (int n : arr)
t.insert(n);
assertEqual("1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ", t.toString(), "Tree_insertMany4_test: toString", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(0), "Tree_insertMany4_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(false, t.contains(11), "Tree_insertMany4_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(1), "Tree_insertMany4_test: contains", false);
assertEqual(true, t.contains(10), "Tree_insertMany4_test: contains", false);
}
public static void assertEqual(int expected, int actual, String message, boolean silentPass)
{
if (expected == actual && ! silentPass)
System.out.printf("--- PASSED: %s ", message);
if (expected != actual)
System.out.printf("*** FAILED: (expected: %d, actual: %d) %s ", expected, actual, message);
}
public static void assertEqual(boolean expected, boolean actual, String message, boolean silentPass)
{
if (expected == actual && ! silentPass)
System.out.printf("--- PASSED: %s ", message);
if (expected != actual)
System.out.printf("*** FAILED: (expected: %s, actual: %s) %s ", expected, actual, message);
}
public static void assertEqual(String expected, String actual, String message, boolean silentPass)
{
if (expected.equals(actual) && ! silentPass)
System.out.printf("--- PASSED: %s ", message);
if (! expected.equals(actual))
System.out.printf("*** FAILED: (expected: %s, actual: %s) %s ", expected, actual, message);
}
}
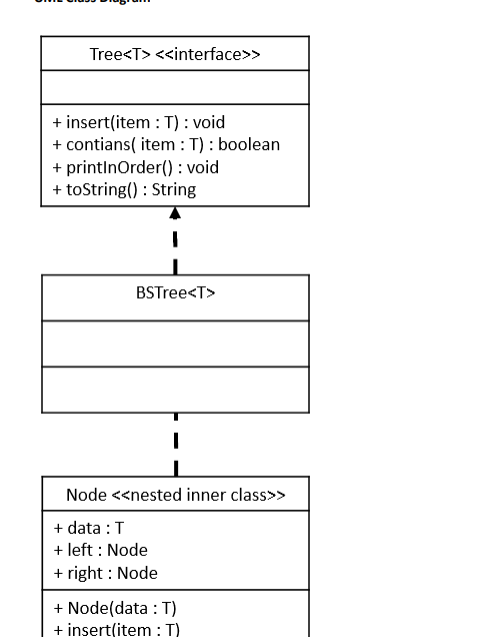
public interface Tree
public void insert(T item);
public boolean contains(T item);
public void printInOrder();
public String toString();
}
public class BSTree
private Node
@Override
public void insert(T item) {
if (root == null)
root = new Node
else
root.insert(item);
}
@Override
public boolean contains(T item) {
// TODO: finish this method
return false;
}
@Override
public void printInOrder() {
// OUTLINE
// void printATree(Node
// if (atRoot == null)
// then there's nothing to print here
// else {
// printATree(atRoot.left);
// print(atRoot.data);
// printATree(atRoot.right);
//}
// }
}
}
class Node
public T data = null;
public Node
public Node
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void insert(T item) {
if (this.data.compareTo(item) == 0)
return;
if (this.data.compareTo(item)
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = new Node
}
else {
this.left.insert(item);
}
}
if (this.data.compareTo(item) > 0) {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = new Node
}
else {
this.right.insert(item);
}
}
}
}
you work with a partner, only submit one lab project with both of your names in the source code file to Blackboard (BB) for grading; you will each earn the same number of points. What to hand in, and by when, is discussed below Assignment Objectives After completing this assignment the student should be able to . Implement a simple binary search tree class in Java according to Interface specifications given in UML. . Implement an in-order traversal algorithm for a binary tree Implement a generic type in Java Assignment Requirements For this assignment you are given the following Java source code files: CSE205_Assignment04.java Tree.java BSTree.java (This file is complete-you will make no changes to this file) (This file is complete-you will make no changes to this file) (you must complete this file) The specifications for the files are given below (including the UML diagram on the following page) Special requirements BSTree Class 1. insert method a. b. Inserts a new item into the binary search tree in the correct location. There should be no duplicate items in the tree. If an item is inserted and that item is already in the tree then this method should simply return without changing the state of the tree 2. contains method 3. printInOrder method 4. toString method Returns true if the tree contains the specified item; otherwise returns false Prints the items in the tree in a space separated list in ascending order Returns a string containing the items in the tree in ascending order and separated by spaces a. a. a. Node Class 1. Your BSTree class must contain a nested inner class called Node 2. This class must have the following attributes a. left Node- representing the left sub-node to this Node object b. right: Node- representing the right sub-node to this Node object c. data: T- holding the data for this Node object 3. This class must have the following methods a. nsert(item T) -this is a recursive method that finds the insertion point and inserts a Node for the new item in the correct position in the sub-tree for which this Node is the rootStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


