Question
There will be multiple parts of this question posted separately. Please answer the other questions if you can. Use excel to show all work and
There will be multiple parts of this question posted separately. Please answer the other questions if you can. Use excel to show all work and provide excel file.
Look at the following Balance Sheet and financial information for Flexics Inc. Flexics, Inc. is a leading producer of plasma technology display devices in the USA. One of the company's latest innovations is a patented process that permits the rapid production of customized semiconductor wafers using plasma-based etching technology instead of quartz plates. Flexics, based in Seattle, started business in 1987 and now has production facilities in Vancouver and a research affiliate in Princeton, New Jersey.
In late-1998 Alex Pereira, the founder and CEO of Flexics, was considering options for realization of the value of his shareholding in Flexics. Pereira was seeking a method that would offer greater liquidity and diversification of his and his family's investment in the company. One option was to talk to investment bankers about an initial public offering (IPO). This would allow him to sell some or all of his shares in the market. But he was unhappy about the IPO market in the industry, which was weaker than in 1997 when bankers had talked about an IPO price in the $40-45 range. In the past year, public offerings of similar technology companies had brought price/earnings ratios of about 15. A recent private placement of Flexics shares with a venture capital investor had been done at an effective price of $24 per share. Another possibility was to sell his shares to Photronics, which was rumored to be interested in buying a stake in Flexics. Among the other options he was considering was a leveraged buy-out by management. Pereira liked the idea of giving key officers a greater stake and control, but he wanted to get a good price for his shares. He was willing to receive payment partly in cash, and partly in the form of a $30 million, 15% pre-payable subordinated note.
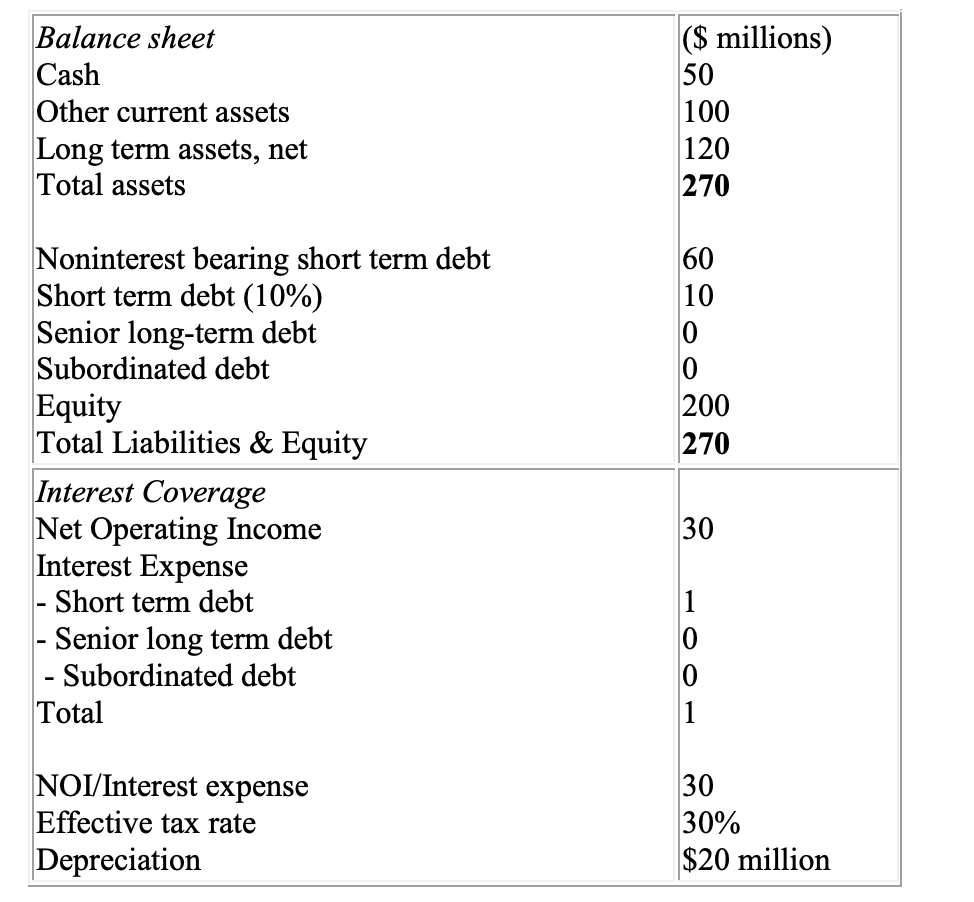
Management had discussed the LBO possibility with Seattle Partners, a venture capital firm that was familiar with Flexics. The firm's advisors had calculated that of the minimum amount of $216 million needed for the LBO, $20 million would have to come from management, as much as $120 million could be raised through a senior debt issuance led by Bank of America (BofA), and the remainder from a private equity group led by Seattle Partners. B of A indicated the rate would be 12% and that lenders would need a Net Operating Income/Interest Expense ratio of at least 2x. At this time 35% of the 9 million shares outstanding were held by the founder and his family, and the remainder was held by venture capital and private equity groups. Net operating income was $30 million. Other key indicators are listed above.
Flexics shares were expected to be (based on information of similar companies) trading at a P/E of 10.6 on earnings of $2.26 per share. Based on past performance the company was expected to generate free cash flows of $2.57 per share next year, an increase of 3.6% from the current level of $2.48. The Treasury bond yield was 4.5%, the companys beta, based on comparable companies, was about 1.3 and the long run market return was 11.5%.
At the current price levels, how much cash can the CEO generate by selling all his shares?
Balance sheet Cash Other current assets Long term assets, net Total assets ($ millions) 50 100 120 270 60 10 0 0 200 270 Noninterest bearing short term debt Short term debt (10%) Senior long-term debt Subordinated debt Equity Total Liabilities & Equity Interest Coverage Net Operating Income Interest Expense - Short term debt - Senior long term debt - Subordinated debt Total 30 1 0 0 1 NOI/Interest expense Effective tax rate Depreciation 30 30% $20 million Balance sheet Cash Other current assets Long term assets, net Total assets ($ millions) 50 100 120 270 60 10 0 0 200 270 Noninterest bearing short term debt Short term debt (10%) Senior long-term debt Subordinated debt Equity Total Liabilities & Equity Interest Coverage Net Operating Income Interest Expense - Short term debt - Senior long term debt - Subordinated debt Total 30 1 0 0 1 NOI/Interest expense Effective tax rate Depreciation 30 30% $20 millionStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


