Question
These questions are SQL/PL in the picture, and the solution to these questions in the SQL/PL code is below the picture Required: Correct the codes,
These questions are SQL/PL in the picture, and the solution to these questions in the SQL/PL code is below the picture Required: Correct the codes, implement the output, and take a screenshot of the output
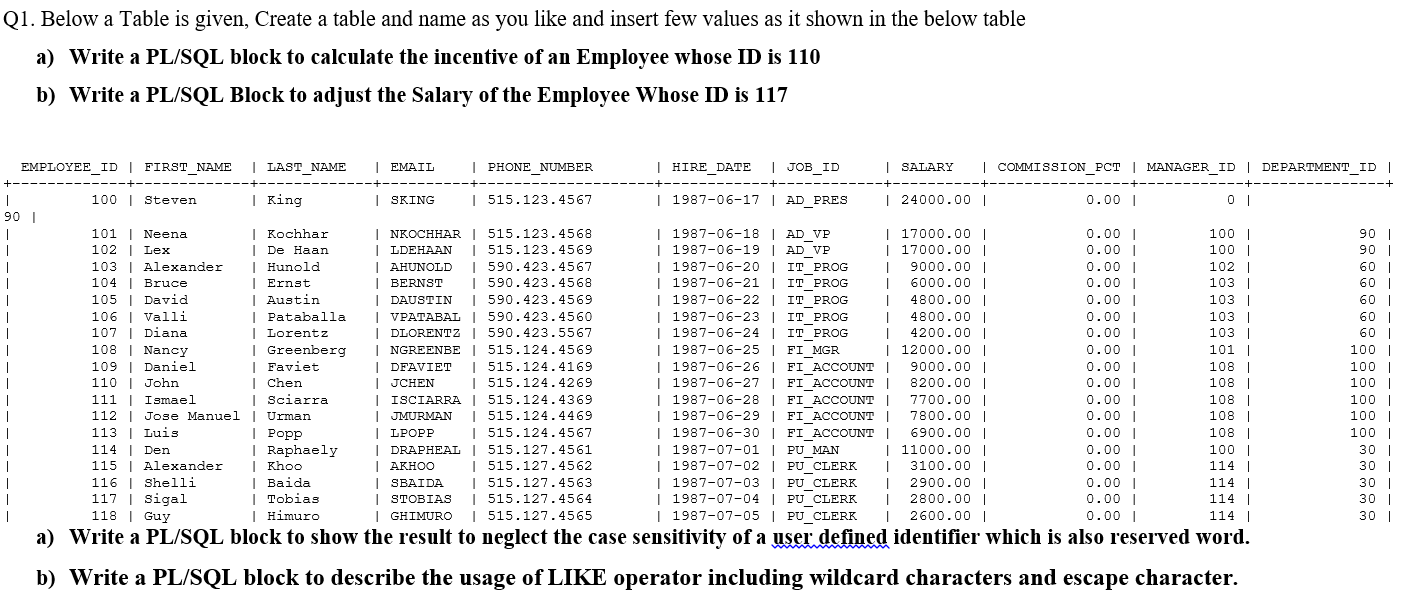
a) Here is a PL/SQL block to calculate the incentive of an employee whose ID is 110:
DECLARE
incentive NUMBER(7,2);
base_salary NUMBER(7,2);
commission_pct NUMBER(5,3);
BEGIN
SELECT salary, commission_pct
INTO base_salary, commission_pct
FROM employee
WHERE employee_id = 110;
incentive := base_salary * commission_pct;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The incentive of Employee 110 is: ' || incentive);
END;
b) Here is a PL/SQL block to adjust the salary of an employee whose ID is 117:
DECLARE
new_salary NUMBER(7,2);
BEGIN
SELECT salary
INTO new_salary
FROM employee
WHERE employee_id = 117;
new_salary := new_salary * 1.1;
UPDATE employee
SET salary = new_salary
WHERE employee_id = 117;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The new salary of Employee 117 is: ' || new_salary);
END;
a) Here is a PL/SQL block to show the result to neglect the case sensitivity of a user-defined identifier, which is also reserved word.
DECLARE
l_salary NUMBER;
BEGIN
SELECT salary INTO l_salary
FROM "EMPLOYEE"
WHERE employee_id = 110;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The salary of Employee ID 110 is: ' || l_salary);
END;
b)Here is a PL/SQL block to describe the usage of LIKE operator including wildcard characters and escape character
DECLARE
v_search_string VARCHAR2(20) := '_lex';
v_count NUMBER;
BEGIN
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO v_count
FROM "EMPLOYEES"
WHERE last_name LIKE v_search_string ESCAPE '_';
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Number of employees with last name matching pattern: ' || v_count);
END;
Here is an example PL/SQL code to insert the data provided into an "EMPLOYEES" table:
DECLARE
-- variable to store the value of the "EMPLOYEE_ID" column
v_employee_id NUMBER;
-- variable to store the value of the "FIRST_NAME" column
v_first_name VARCHAR2(20);
-- variable to store the value of the "LAST_NAME" column
v_last_name VARCHAR2(25);
-- variable to store the value of the "EMAIL" column
v_email VARCHAR2(25);
-- variable to store the value of the "PHONE_NUMBER" column
v_phone_number VARCHAR2(20);
-- variable to store the value of the "HIRE_DATE" column
v_hire_date DATE;
-- variable to store the value of the "JOB_ID" column
v_job_id VARCHAR2(10);
-- variable to store the value of the "SALARY" column
v_salary NUMBER;
-- variable to store the value of the "COMMISSION_PCT" column
v_commission_pct NUMBER;
-- variable to store the value of the "MANAGER_ID" column
v_manager_id NUMBER;
-- variable to store the value of the "DEPARTMENT_ID" column
v_department_id NUMBER;
BEGIN
-- insert the first row of data into the "EMPLOYEES" table
v_employee_id := 90;
v_first_name := 'Steven';
v_last_name := 'King';
v_email := 'SKING';
v_phone_number := '515.123.4567';
v_hire_date := TO_DATE('1987-06-17', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
v_job_id := 'AD_PRES';
v_salary := 24000.00;
v_commission_pct := 0.00;
v_manager_id := 0;
v_department_id := null;
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id)
VALUES (v_employee_id, v_first_name, v_last_name, v_email, v_phone_number, v_hire_date, v_job_id, v_salary, v_commission_pct, v_manager_id, v_department_id);
-- insert the rest of the data into the "EMPLOYEES" table
-- (You can copy and paste the same code as above and change the values to insert the rest of the data)
END;
PL/SQL code to insert the above data into a table named "employees":
DECLARE
v_employee_id employees.employee_id%TYPE := 90;
v_first_name employees.first_name%TYPE := 'Steven';
v_last_name employees.last_name%TYPE := 'King';
v_email employees.email%TYPE := 'SKING';
v_phone_number employees.phone_number%TYPE := '515.123.4567';
v_hire_date employees.hire_date%TYPE := to_date('1987-06-17', 'YYYY-MM-DD');
v_job_id employees.job_id%TYPE := 'AD_PRES';
v_salary employees.salary%TYPE := 24000;
v_commission_pct employees.commission_pct%TYPE := 0;
v_manager_id employees.manager_id%TYPE := 0;
v_department_id employees.department_id%TYPE := null;
BEGIN
INSERT INTO employees
(employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id)
VALUES
(v_employee_id, v_first_name, v_last_name, v_email, v_phone_number, v_hire_date, v_job_id, v_salary, v_commission_pct, v_manager_id, v_department_id);
COMMIT;
END;
declare
cursor emp_cur is
select employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id
from employees;
begin
open emp_cur;
loop
fetch emp_cur into
employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, job_id, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id;
exit when emp_cur%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(
employee_id || ' ' || first_name || ' ' || last_name || ' ' || email || ' ' || phone_number || ' ' || hire_date || ' ' || job_id || ' ' || salary || ' ' || commission_pct || ' ' || manager_id || ' ' || department_id
);
end loop;
close emp_cur;
end;
21. Below a Table is given, Create a table and name as you like and insert few values as it shown in the below table a) Write a PL/SQL block to calculate the incentive of an Employee whose ID is 110 b) Write a PL/SQL Block to adjust the Salary of the Employee Whose ID is 117
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


