Question: this all the questions what do need exactly? what information you need End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Check Your Understanding Check your


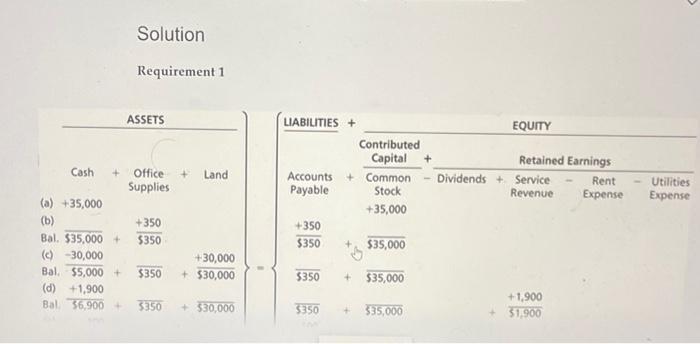
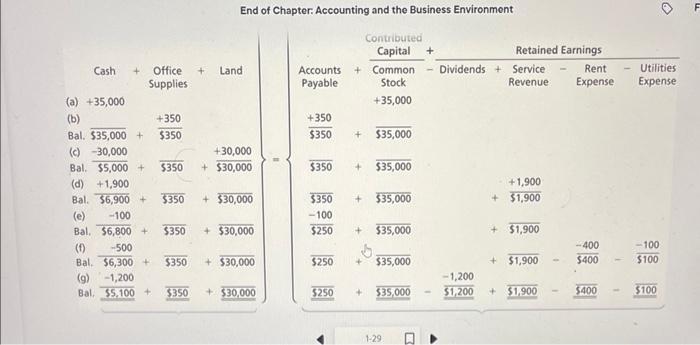
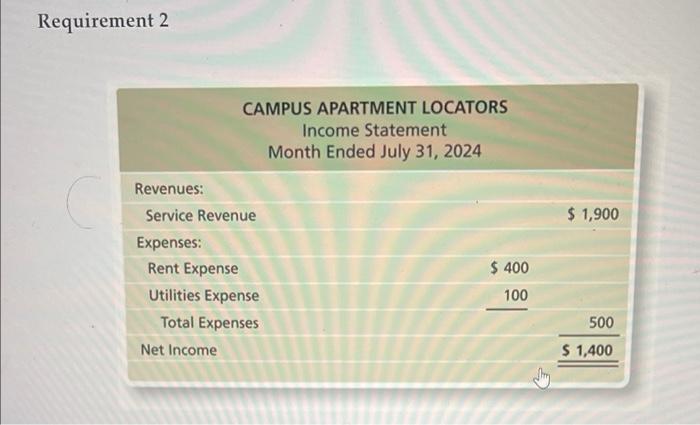
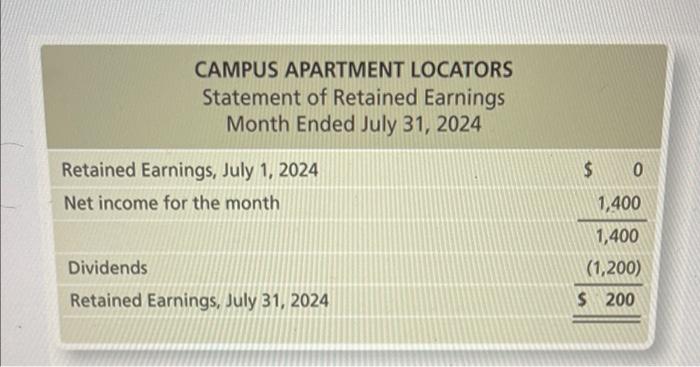
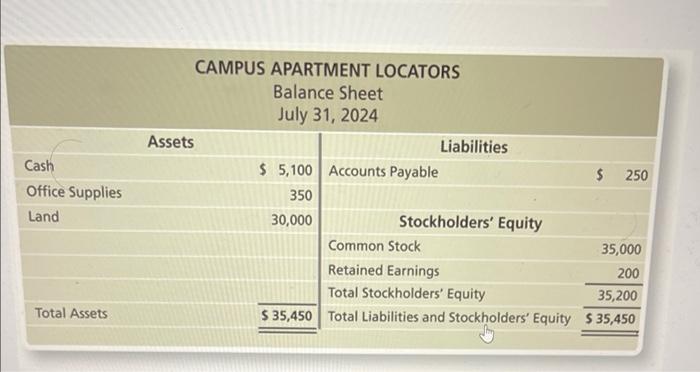
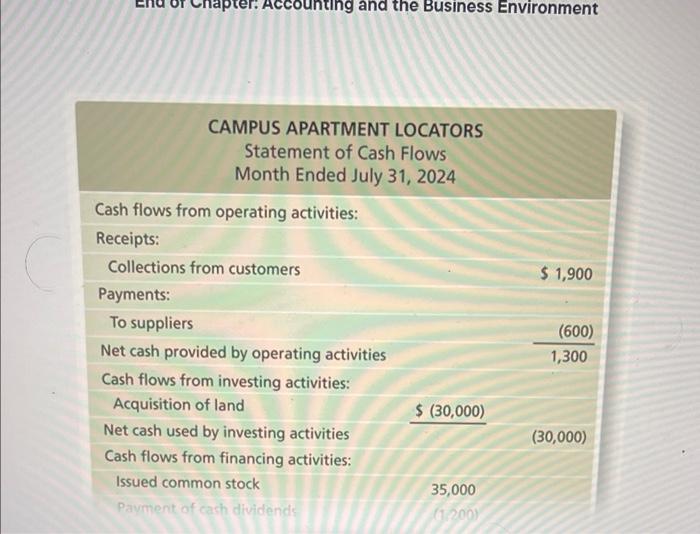
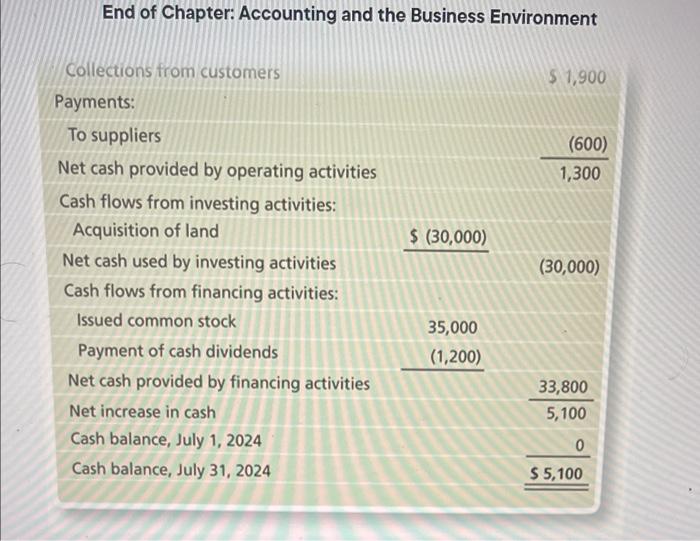
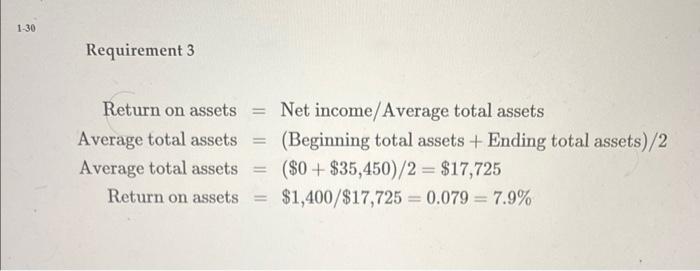













End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Check Your Understanding Check your understanding of the chapter by completing this problem and then looking at the solution. Use this practice to help identify which sections of the chapter you need to study more. Ron Smith opens an apartment-locator business near a college campus: The company will be named Campus Apartment Locators. During the first month of operations, July 2024, the business completes the following transactions: a. Receives a $35,000 contribution from Ron Smith and issues commoni stock to Ron Smith. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment transactions: a. Receives a $35,000 contribution from Ron Smith and issu stock to Ron Smith. b. Purchases $350 of office supplies on account. c. Pays cash of $30,000 to acquire a lot next to campus. d. Locates apartments for clients and receives cash of $1,900. e. Pays $100 on the accounts payable the business created in Transaction (b). f. Pays cash expenses for offie rent, $400, and utilities, $100. g. Pays cash dividends of $1,200 to stockholders. 1. Analyze the preceding transactions in terms of their effects on the accounting equation of Campus Apartment Locators. Use Exhibit F:16 as a guide. (See Learning Objective 4) 2. Prepare the income statement, statement of retained earnings, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows of the business after recording the transactions. (See Learning Objective 5) 3. Calculate the return on assets (ROA). (See Learning Objective 6) Solution Requirement 1 End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Requirement 2 CAMPUS APARTMENT LOCATORS Statement of Retained Earnings Month Ended July 31, 2024 Retained Earnings, July 1, 2024 Net income for the month Dividends Retained Earnings, July 31, 2024 \begin{tabular}{r} (1,200) \\ $200 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} chu or Cnapter: Accounting and the Business Environment End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environmant Return on assets = Net income/Average total assets Average total assets =( Beginning total assets + Ending total assets )/2 Average total assets =($0+$35,450)/2=$17,725 Return on assets =$1,400/$17,725=0.079=7.9% Key Terms Accounting Accounting Equation Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Assets Audit Balance Sheet Certified Financial Planner (CFP) End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Balance Sheet Certified Financial Planner (CFP) Certified Management Accountants (CMAs) Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) Common Stock Contributed Capital Corporation Cost Principle Creditor Dividend Dividend Economic Entity Assumption Equity Expenses Faithful Representation Financial Accounting Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Financial Statements Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) Going Concern Assumption Income Statement International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Liabilities Limited-Liability Company (LLC) Managerial Accounting Monetary Unit Assumption Net Income Net Loss Partnership End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) Retained Earnings Return on Assets (ROA) Revenues Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Sole Proprietorship Statement of Cash Flows Statement of Retained Earnings Stockholder End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Sole Proprietorship Statement of Cash Flows Statement of Retained Earnings Stockholder Transaction Review Things You Should Know 1. Why is accounting important? - Accounting is the language of business. - Accounting is used by decision makers including individuals, businesses, investors, creditors, and taxing authorities. - Accounting can be divided into two major fields: financial accounting and managerial accounting. - Financial accounting is used by external decision makers, and accounting and managerial accounting. - Financial accounting is used by external decision makers, and managerial accounting is used by internal decision makers. - All businesses need accountants. Accountants work in corporate or industry accounting, public accounting, financial services, and governmental accounting. - Accountants can be licensed or certified as a Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Chartered Global Management Accountant (CGMA), Certified Management Accountant (CMA), or Certified Financial Planner (CFP). 2. Wht are the organizations and rules that govern accounting? - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are the rules 2. What are the organizations and rules that govern accounting? - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are the rules that govern accounting in the United States. - The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is responsible for the creation and governance of accounting standards. - Economic entity assumption: Requires an organization to be a separate economic unit such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or limited-liability company. - Cost principle: Acquired assets and services should be recorded at their actual cost. - Going concern assumption: Assumes that an entity will remain in operation for the foreseeable future. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment - Monetary unit assumption: Assumes financial transactions are recorded in a monetary unit. 3. What is the accounting equation? - Assets = Liabilities + Equity - Assets: Items the business owns or controls (examples: cash, furniture, land) - Liabilities: Items the business owes (examples: accounts payable, notes payable, salaries payable) - Equity: Stockholders' claims to the assets through contributed capital and retained earnings (examples: common stock, dividends, revenues, expenses) End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment 4. How do you analyze a transaction? - A transaction affects the financial position of a business and can be measured with faithful representation. - Transactions are analyzed using three steps: Step 1: Identify the accounts and account type (Asset, Liability, or Equity). Step 2: Decide whether each account increases or decreases. Step 3: Determine whether the accounting equation is in balance. 5. How do you prepare financial statements? - Financial statements are prepared in the followingporder: End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment - Financial statements are prepared in the following order: 1. Income statement: - Reports the net income or net loss of a business for a specific period. - Revenues - Expenses = Net Income or Net Loss 2. Statement of retained earnings: - Reports on the changes in retained earnings for a specific period. Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income (or - Net Loss) - Dividends = Ending Retained Earnings End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment = Ending Retained Earnings 3. Balance sheet: - Reports on an entity's assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity as of a specific date. - Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 4. Statement of cash flows: - Reports on a business's cash receipts and cash payments for a specific period. - Includes three sections: Cash flows from operating activities: Involves cash receipts for services and cash payments for expenses. 6. How do you use financial statements to evaluate business performance? - Income statement evaluates profitability. - Statement of retained earnings shows the amount of earnings that were kept and reinvested in the company. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment - Income statement evaluates profitability. - Statement of retained earnings shows the amount of earnings that were kept and reinvested in the company. - Balance sheet details the economic resources the company has, the debts the company owes, and the company's net worth. - Statement of cash flows shows the change in cash. Return on assets (ROA)= Net income/Average total assets. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Check Your Understanding Check your understanding of the chapter by completing this problem and then looking at the solution. Use this practice to help identify which sections of the chapter you need to study more. Ron Smith opens an apartment-locator business near a college campus: The company will be named Campus Apartment Locators. During the first month of operations, July 2024, the business completes the following transactions: a. Receives a $35,000 contribution from Ron Smith and issues commoni stock to Ron Smith. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment transactions: a. Receives a $35,000 contribution from Ron Smith and issu stock to Ron Smith. b. Purchases $350 of office supplies on account. c. Pays cash of $30,000 to acquire a lot next to campus. d. Locates apartments for clients and receives cash of $1,900. e. Pays $100 on the accounts payable the business created in Transaction (b). f. Pays cash expenses for offie rent, $400, and utilities, $100. g. Pays cash dividends of $1,200 to stockholders. 1. Analyze the preceding transactions in terms of their effects on the accounting equation of Campus Apartment Locators. Use Exhibit F:16 as a guide. (See Learning Objective 4) 2. Prepare the income statement, statement of retained earnings, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows of the business after recording the transactions. (See Learning Objective 5) 3. Calculate the return on assets (ROA). (See Learning Objective 6) Solution Requirement 1 End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Requirement 2 CAMPUS APARTMENT LOCATORS Statement of Retained Earnings Month Ended July 31, 2024 Retained Earnings, July 1, 2024 Net income for the month Dividends Retained Earnings, July 31, 2024 \begin{tabular}{r} (1,200) \\ $200 \\ \hline \hline \end{tabular} chu or Cnapter: Accounting and the Business Environment End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environmant Return on assets = Net income/Average total assets Average total assets =( Beginning total assets + Ending total assets )/2 Average total assets =($0+$35,450)/2=$17,725 Return on assets =$1,400/$17,725=0.079=7.9% Key Terms Accounting Accounting Equation Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Assets Audit Balance Sheet Certified Financial Planner (CFP) End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Balance Sheet Certified Financial Planner (CFP) Certified Management Accountants (CMAs) Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) Common Stock Contributed Capital Corporation Cost Principle Creditor Dividend Dividend Economic Entity Assumption Equity Expenses Faithful Representation Financial Accounting Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Financial Statements Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) Going Concern Assumption Income Statement International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Liabilities Limited-Liability Company (LLC) Managerial Accounting Monetary Unit Assumption Net Income Net Loss Partnership End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) Retained Earnings Return on Assets (ROA) Revenues Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Sole Proprietorship Statement of Cash Flows Statement of Retained Earnings Stockholder End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Sole Proprietorship Statement of Cash Flows Statement of Retained Earnings Stockholder Transaction Review Things You Should Know 1. Why is accounting important? - Accounting is the language of business. - Accounting is used by decision makers including individuals, businesses, investors, creditors, and taxing authorities. - Accounting can be divided into two major fields: financial accounting and managerial accounting. - Financial accounting is used by external decision makers, and accounting and managerial accounting. - Financial accounting is used by external decision makers, and managerial accounting is used by internal decision makers. - All businesses need accountants. Accountants work in corporate or industry accounting, public accounting, financial services, and governmental accounting. - Accountants can be licensed or certified as a Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Chartered Global Management Accountant (CGMA), Certified Management Accountant (CMA), or Certified Financial Planner (CFP). 2. Wht are the organizations and rules that govern accounting? - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are the rules 2. What are the organizations and rules that govern accounting? - Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are the rules that govern accounting in the United States. - The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is responsible for the creation and governance of accounting standards. - Economic entity assumption: Requires an organization to be a separate economic unit such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or limited-liability company. - Cost principle: Acquired assets and services should be recorded at their actual cost. - Going concern assumption: Assumes that an entity will remain in operation for the foreseeable future. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment - Monetary unit assumption: Assumes financial transactions are recorded in a monetary unit. 3. What is the accounting equation? - Assets = Liabilities + Equity - Assets: Items the business owns or controls (examples: cash, furniture, land) - Liabilities: Items the business owes (examples: accounts payable, notes payable, salaries payable) - Equity: Stockholders' claims to the assets through contributed capital and retained earnings (examples: common stock, dividends, revenues, expenses) End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment 4. How do you analyze a transaction? - A transaction affects the financial position of a business and can be measured with faithful representation. - Transactions are analyzed using three steps: Step 1: Identify the accounts and account type (Asset, Liability, or Equity). Step 2: Decide whether each account increases or decreases. Step 3: Determine whether the accounting equation is in balance. 5. How do you prepare financial statements? - Financial statements are prepared in the followingporder: End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment - Financial statements are prepared in the following order: 1. Income statement: - Reports the net income or net loss of a business for a specific period. - Revenues - Expenses = Net Income or Net Loss 2. Statement of retained earnings: - Reports on the changes in retained earnings for a specific period. Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income (or - Net Loss) - Dividends = Ending Retained Earnings End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment = Ending Retained Earnings 3. Balance sheet: - Reports on an entity's assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity as of a specific date. - Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity 4. Statement of cash flows: - Reports on a business's cash receipts and cash payments for a specific period. - Includes three sections: Cash flows from operating activities: Involves cash receipts for services and cash payments for expenses. 6. How do you use financial statements to evaluate business performance? - Income statement evaluates profitability. - Statement of retained earnings shows the amount of earnings that were kept and reinvested in the company. End of Chapter: Accounting and the Business Environment - Income statement evaluates profitability. - Statement of retained earnings shows the amount of earnings that were kept and reinvested in the company. - Balance sheet details the economic resources the company has, the debts the company owes, and the company's net worth. - Statement of cash flows shows the change in cash. Return on assets (ROA)= Net income/Average total assets
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


