Question
This example involves a study of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who underwent various types of treatment for prostate cancer (Feagins et al., 2020).
This example involves a study of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who underwent various types of treatment for prostate cancer (Feagins et al., 2020). A retrospective multisite cohort study investigated three different types of treatment received for prostate cancer among persons with IBD: external radiotherapy (XRT), brachytherapy (a type of internal radiation therapy), or treatments that did not involve radiation, such as chemotherapy and hormonal therapy. Persons in the non-radiation group received hormonal therapy, chemotherapy, both hormonal and chemotherapy, or some other type of treatment that did not involve radiation.
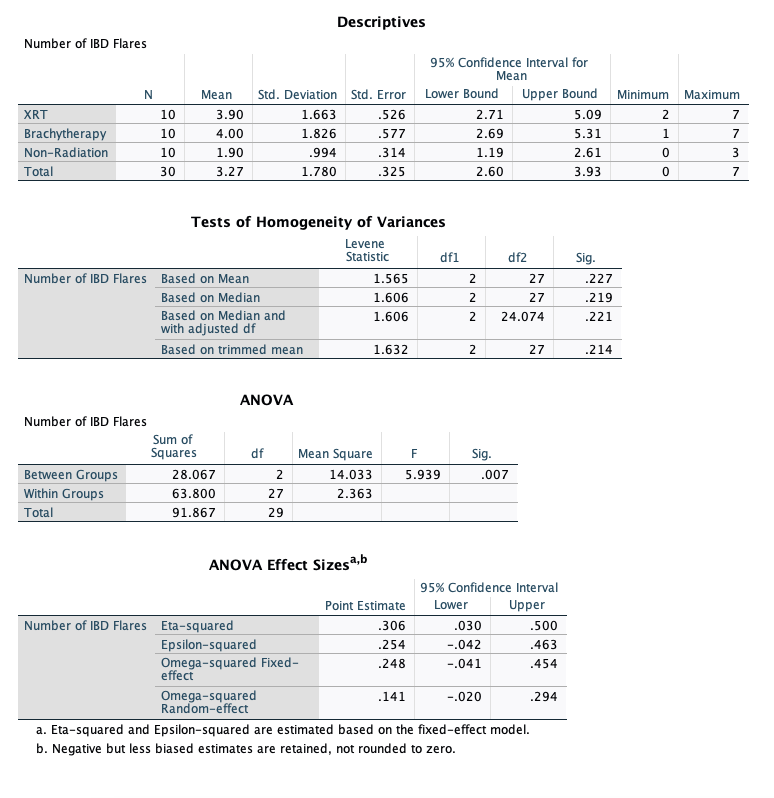
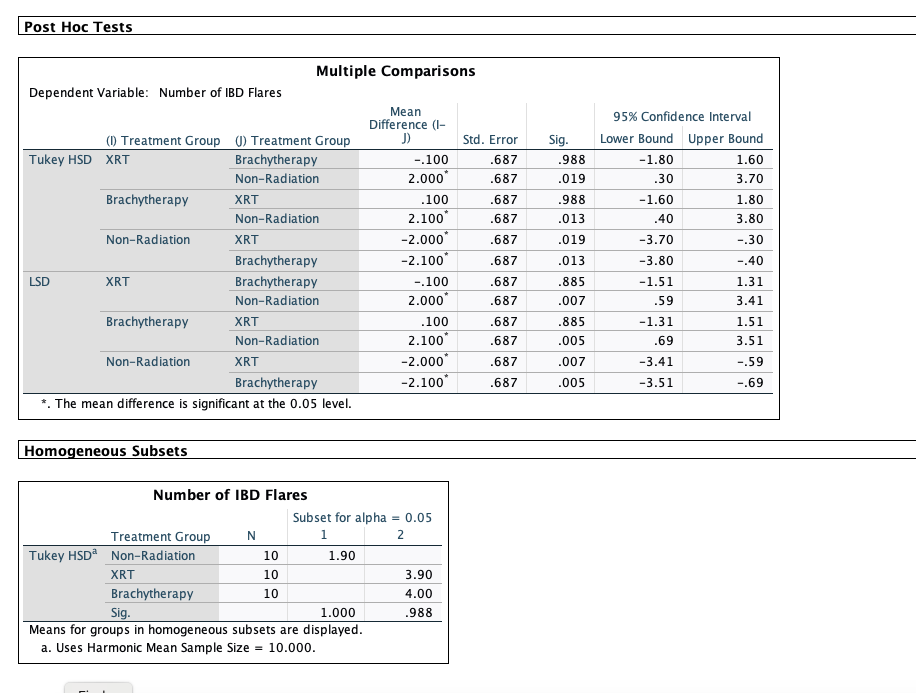
The independent variable in this example is type of treatment (XRT, Brachytherapy, or Non-radiation treatment), and the dependent variable is the number (raw count) of IBD flares experienced by the patient during the span of two years post-treatment. An IBD flare is defined as a reappearance of IBD symptoms (Feagins et al., 2020)..
These data are presented in HW7.sav. The null hypothesis is: "There is no difference between the treatment groups (XRT, Brachy-therapy, and Non-radiation treatment) on number of post-treatment IBD flares among persons with IBD."
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


