// This function shoulud return a boolean value that is true // if x is negative. You may only use bitwise operations, // you cannot use any comparison operations. Remember, an int // is automatically casted to bool using the rule if it's 0, // it's false, otherwise it's true.
bool is_negative(int x) { return x; // remove this line }
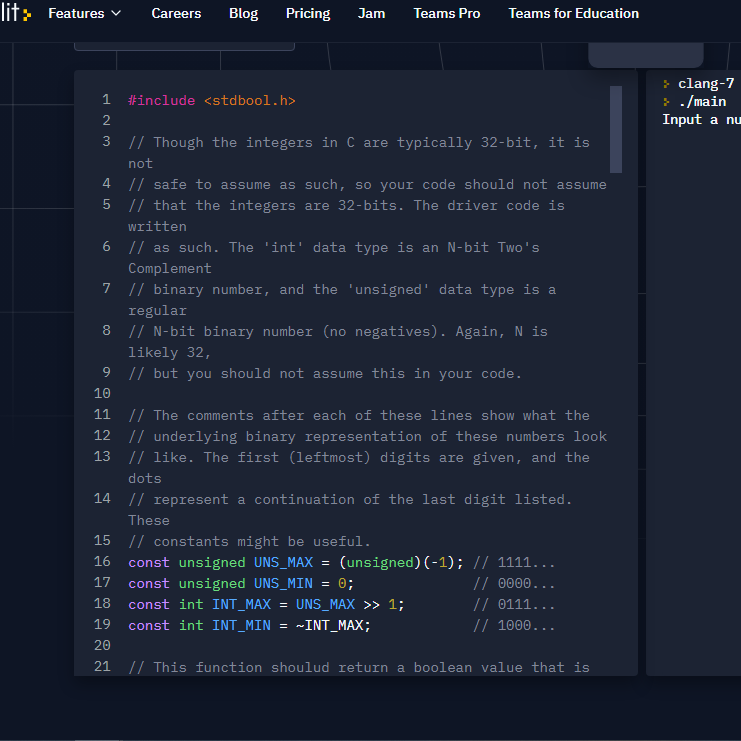
lit: Features Careers Blog Pricing Jam Teams Pro Teams for Education 1 Hinclude
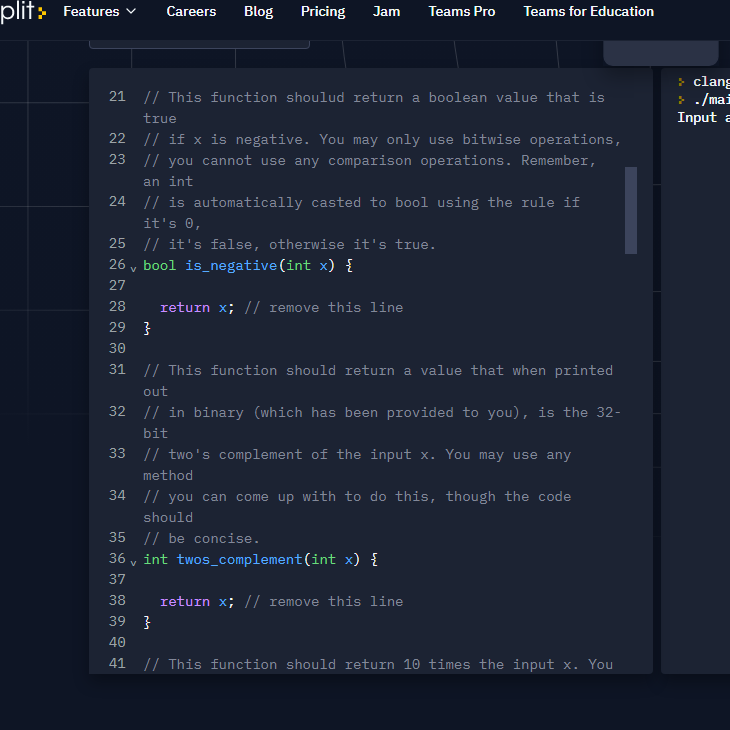
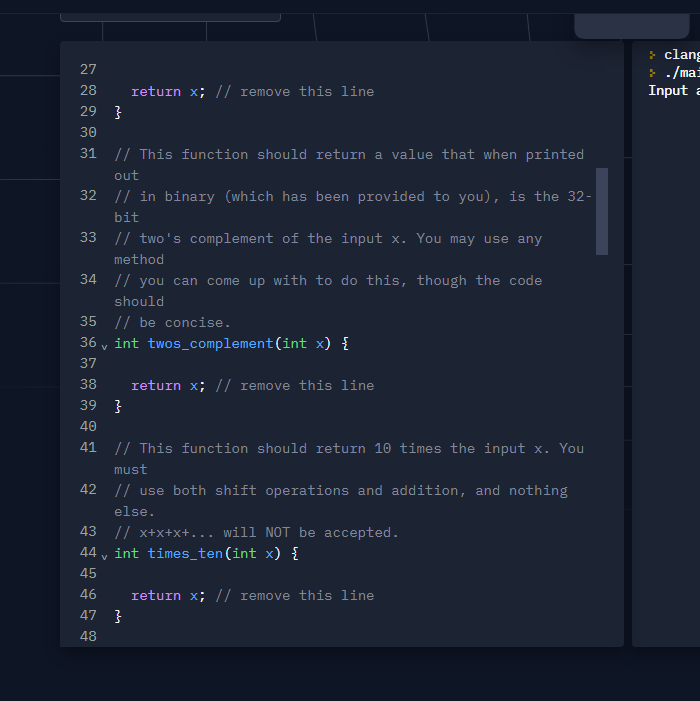
clang-7 ./main Input a nu 2 4. 3 // Though the integers in C are typically 32-bit, it is not // safe to assume as such, so your code should not assume 5 // that the integers are 32-bits. The driver code is written 6 // as such. The 'int' data type is an N-bit Two's Complement 7 // binary number, and the 'unsigned' data type is a regular 8 // N-bit binary number (no negatives). Again, N is likely 32, 9 // but you should not assume this in your code. 10 13 11 // The comments after each of these lines show what the 12 // underlying binary representation of these numbers look // like. The first (leftmost) digits are given, and the dots 14 // represent a continuation of the last digit listed. These 15 // constants might be useful. 16 const unsigned UNS_MAX = (unsigned) (-1); // 1111... 17 const unsigned UNS_MIN = 0; // 0000... 18 const int INT_MAX UNS_MAX >> 1; // 0111... 19 const int INT_MIN -INT_MAX; // 1000... 20 21 // This function shoulud return a boolean value that is plit: Features v Careers Blog Pricing Jam Teams Pro Teams for Education > clang } ./mai Input V 21 // This function shoulud return a boolean value that is true 22 // if x is negative. You may only use bitwise operations, 23 // you cannot use any comparison operations. Remember, an int 24 // is automatically casted to bool using the rule if it's o, 25 // it's false, otherwise it's true. 26 y bool is negative(int x) { 27 28 return x; // remove this line 29 } 30 31 // This function should return a value that when printed out 32 // in binary (which has been provided to you), is the 32- bit 33 // two's complement of the input x. You may use any method 34 // you can come up with to do this, though the code should 35 // be concise. 36 v int twos_complement(int x) { 37 38 return x; // remove this line 39} 40 41 // This function should return 10 times the input x. You V clang } ./ma Input a V 27 28 return x; // remove this line 29} 30 31 // This function should return a value that when printed out 32 // in binary (which has been provided to you), is the 32- bit 33 // two's complement of the input x. You may use any method 34 // you can come up with to do this, though the code should 35 // be concise. 36 v int twos_complement(int x) { 37 38 return x; // remove this line 39} 40 41 // This function should return 10 times the input x. You must 42 // use both shift operations and addition, and nothing else. 43 // x+x+x+... will NOT be accepted. 44 v int times_ten(int x) { 45 46 return x; // remove this line 47 } 48









