this is 14.1
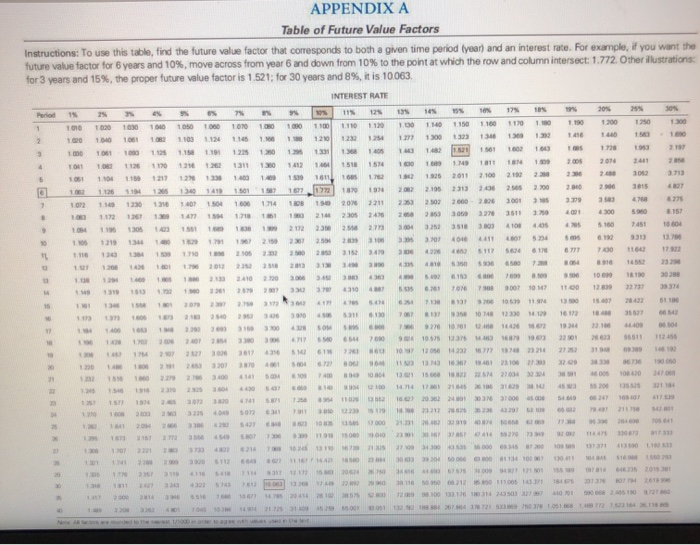
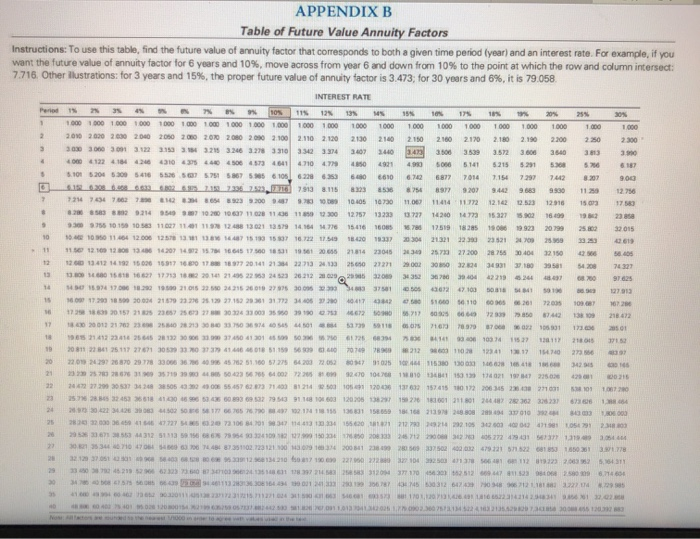
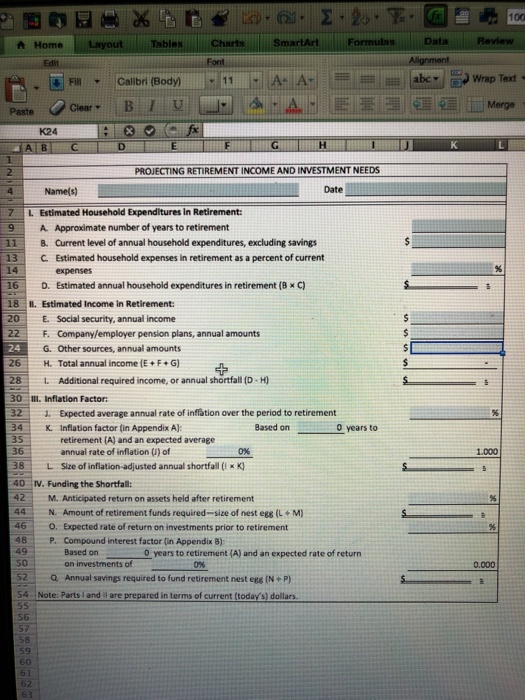
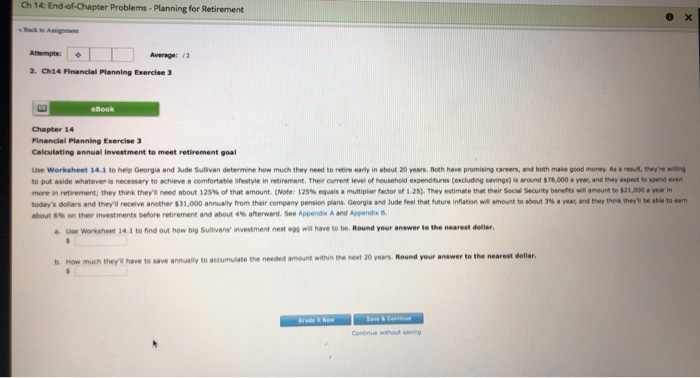
Ch 14: End-of-Chapter Problems - Planning for Retirement Back to A mer Attempts: Average 12 2. Ch14 Financial Planning Exercise 3 elook Chapter 14 Financial Planning Exercise 3 Calculating annual Investment to meet retirement goal Use Worksheet 14.1 to help Georgia and Side Sullivan determine how much they need to retire early in about 20 years. Both have promising careers, and both make good money. As a result, they're willing to put aside whatever is necessary to achieve a comfortable lifestyle in retirement. Their current level of household expenditures (excluding savings) is around $78,000 year, and they expect to spend ever more in retirement; they think they'll need about 125% of that amount. (Note: 125% equals a multiplier factor of 1.25). They estimate that their Social Security benefits will amount to $21,000 a year in today's dollars and they receive another $31,000 annually from their company pension plans, Georgia and Jude feel that future inflation will amount to about a year, and they think they'll be able to eam about on their investments before retirement and about 4% afterward. See Append A and Appendix Use Worksheet 14.1 to find out how big Sullivans investment nest will have to be Round your answer to the nearest dollar. b. How much they have to save annually to accumulate the needed amount within the next 20 years. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. Grade it Now Save & Conti Continue thout wing 2 0 . 6. 2. 2. Y. CE 100 Home Layout Tables Data SmartArt Review Alignment Fill abc Wrap Text Calibri (Body) BIU A Merge K24 X ABCD PROJECTING RETIREMENT INCOME AND INVESTMENT NEEDS Name(s) Date 11 14 Estimated Household Expenditures in Retirement: A Approximate number of years to retirement 8. Current level of annual household expenditures, excluding savings 13 C Estimated household expenses in retirement as a percent of current expenses 16 D. Estimated annual household expenditures in retirement (8 C) 18 1. Estimated Income in Retirement: 20 E. Social security, annual income 22 F. Company/employer pension plans, annual amounts G. Other sources, annual amounts H. Total annual income (E+F+G) 1. Additional required income, or annual shortfall ( DH) IH. Inflation Factor: J. Expected average annual rate of inflation over the period to retirement 34 K. Inflation factor in Appendix A): Based on years to 35 retirement (A) and an expected average 36 annual rate of inflation () of OX L Size of inflation-adjusted annual shortfall (1 x K) 40 IV. Funding the Shortfall: M. Anticipated return on assets held after retirement N. Amount of retirement funds required-size of nest ege (L + M) 46 O. Expected rate of return on investments prior to retirement 48 P. Compound interest factor (in Appendix B): Based on years to retirement (A) and an expected rate of return 50 on investments of 0% QAnnual savings required to fund retirement nest egg ( N P ) 54 Note: Parts and are prepared in terms of current (today's) dollars. 49 0.000 57 APPENDIX A Table of Future Value Factors Instructions: To use this table, find the future value factor that corresponds to both a given time period year and an interest rate. For example, you want the future value factor for 6 years and 10%, move across from year and down from 10% to the point at which the row and column intersect: 1.772 Other illustrations for 3 years and 15%, the proper future value factor is 1521; for 30 years and 8%, it is 10063 INTEREST RATE 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 1100 200 100 101 1412140518 16 31 20 104 10 3 10 10 10 10 10 01100 113 114 149 1501 157 15772 1870 2015 1 on 200 101 1 02 10 2020 23 1 000 11196 305 3 8 22 23 24 38 37 318 319 100 os 10 21 250 28 3 06 S 13 1 1 0 2105 215 1 30 11 12 Toto 8 8 8 8 103 10 300 2017 10 4387 76760300110 1.00 +18 2373 374 5. 40 110 51100 0 0 3 0 16 See 10 * S 760 107 0 5651 1255 APPENDIX B Table of Future Value Annuity Factors Instructions: To use this table, find the future value of annuity factor that corresponds to both a given time period (year) and an interest rate. For example, if you want the future value of annuity factor for 6 years and 10%, move across from year 6 and down from 10% to the point at which the row and column intersect: 7.716. Other illustrations for 3 years and 15%, the proper future value of annuity factor is 3.473, for 30 years and 6%, it is 79.058 o INTEREST RATE so 1 20 10000000000000000000 0001000000000000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 2010 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 2100 2100 2130 210 211 210 2110 210 2190 2300 300 3000 3001 312 313 315 326 327 3310 330 331 347 348 349 356 357 35123606 2540 1224144244310 473 464 104 404 4 514152155291 5.368 8.1016204 630 540 550 575 610 620 630 640 66106 687701471 72 742 1030000 2 37913 3115 3 7 707 98 9930 72 7 3 200 10.406 107 108 109 11 820 900 12.756 12 1 100 110 13.40 120 160 170 180 2005 21814 2015 28.733 27200 560 13 160 161 162 177 20141 212 250 0 0 300 5420 10.01.18 1662 177131821223432200026 3203 70 972 10 15 20 342100017 10 12 3116 101 1 0 2 103 115 11 2011 26 30 33 414618 5115 7070 6 0041114120273 20 2200 33066572 51.160 570 0 1 15380106 21 3303 565 000 15000 NEH ISOLE POSSIBILI DIO OD 2 8 35110272321001 230 32502491 STT 29 30 31 2 2016 Ch 14: End-of-Chapter Problems - Planning for Retirement Back to A mer Attempts: Average 12 2. Ch14 Financial Planning Exercise 3 elook Chapter 14 Financial Planning Exercise 3 Calculating annual Investment to meet retirement goal Use Worksheet 14.1 to help Georgia and Side Sullivan determine how much they need to retire early in about 20 years. Both have promising careers, and both make good money. As a result, they're willing to put aside whatever is necessary to achieve a comfortable lifestyle in retirement. Their current level of household expenditures (excluding savings) is around $78,000 year, and they expect to spend ever more in retirement; they think they'll need about 125% of that amount. (Note: 125% equals a multiplier factor of 1.25). They estimate that their Social Security benefits will amount to $21,000 a year in today's dollars and they receive another $31,000 annually from their company pension plans, Georgia and Jude feel that future inflation will amount to about a year, and they think they'll be able to eam about on their investments before retirement and about 4% afterward. See Append A and Appendix Use Worksheet 14.1 to find out how big Sullivans investment nest will have to be Round your answer to the nearest dollar. b. How much they have to save annually to accumulate the needed amount within the next 20 years. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. Grade it Now Save & Conti Continue thout wing 2 0 . 6. 2. 2. Y. CE 100 Home Layout Tables Data SmartArt Review Alignment Fill abc Wrap Text Calibri (Body) BIU A Merge K24 X ABCD PROJECTING RETIREMENT INCOME AND INVESTMENT NEEDS Name(s) Date 11 14 Estimated Household Expenditures in Retirement: A Approximate number of years to retirement 8. Current level of annual household expenditures, excluding savings 13 C Estimated household expenses in retirement as a percent of current expenses 16 D. Estimated annual household expenditures in retirement (8 C) 18 1. Estimated Income in Retirement: 20 E. Social security, annual income 22 F. Company/employer pension plans, annual amounts G. Other sources, annual amounts H. Total annual income (E+F+G) 1. Additional required income, or annual shortfall ( DH) IH. Inflation Factor: J. Expected average annual rate of inflation over the period to retirement 34 K. Inflation factor in Appendix A): Based on years to 35 retirement (A) and an expected average 36 annual rate of inflation () of OX L Size of inflation-adjusted annual shortfall (1 x K) 40 IV. Funding the Shortfall: M. Anticipated return on assets held after retirement N. Amount of retirement funds required-size of nest ege (L + M) 46 O. Expected rate of return on investments prior to retirement 48 P. Compound interest factor (in Appendix B): Based on years to retirement (A) and an expected rate of return 50 on investments of 0% QAnnual savings required to fund retirement nest egg ( N P ) 54 Note: Parts and are prepared in terms of current (today's) dollars. 49 0.000 57 APPENDIX A Table of Future Value Factors Instructions: To use this table, find the future value factor that corresponds to both a given time period year and an interest rate. For example, you want the future value factor for 6 years and 10%, move across from year and down from 10% to the point at which the row and column intersect: 1.772 Other illustrations for 3 years and 15%, the proper future value factor is 1521; for 30 years and 8%, it is 10063 INTEREST RATE 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 1100 200 100 101 1412140518 16 31 20 104 10 3 10 10 10 10 10 01100 113 114 149 1501 157 15772 1870 2015 1 on 200 101 1 02 10 2020 23 1 000 11196 305 3 8 22 23 24 38 37 318 319 100 os 10 21 250 28 3 06 S 13 1 1 0 2105 215 1 30 11 12 Toto 8 8 8 8 103 10 300 2017 10 4387 76760300110 1.00 +18 2373 374 5. 40 110 51100 0 0 3 0 16 See 10 * S 760 107 0 5651 1255 APPENDIX B Table of Future Value Annuity Factors Instructions: To use this table, find the future value of annuity factor that corresponds to both a given time period (year) and an interest rate. For example, if you want the future value of annuity factor for 6 years and 10%, move across from year 6 and down from 10% to the point at which the row and column intersect: 7.716. Other illustrations for 3 years and 15%, the proper future value of annuity factor is 3.473, for 30 years and 6%, it is 79.058 o INTEREST RATE so 1 20 10000000000000000000 0001000000000000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 2010 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 200 2100 2100 2130 210 211 210 2110 210 2190 2300 300 3000 3001 312 313 315 326 327 3310 330 331 347 348 349 356 357 35123606 2540 1224144244310 473 464 104 404 4 514152155291 5.368 8.1016204 630 540 550 575 610 620 630 640 66106 687701471 72 742 1030000 2 37913 3115 3 7 707 98 9930 72 7 3 200 10.406 107 108 109 11 820 900 12.756 12 1 100 110 13.40 120 160 170 180 2005 21814 2015 28.733 27200 560 13 160 161 162 177 20141 212 250 0 0 300 5420 10.01.18 1662 177131821223432200026 3203 70 972 10 15 20 342100017 10 12 3116 101 1 0 2 103 115 11 2011 26 30 33 414618 5115 7070 6 0041114120273 20 2200 33066572 51.160 570 0 1 15380106 21 3303 565 000 15000 NEH ISOLE POSSIBILI DIO OD 2 8 35110272321001 230 32502491 STT 29 30 31 2 2016
 this is 14.1
this is 14.1