This is all one question, just very long.
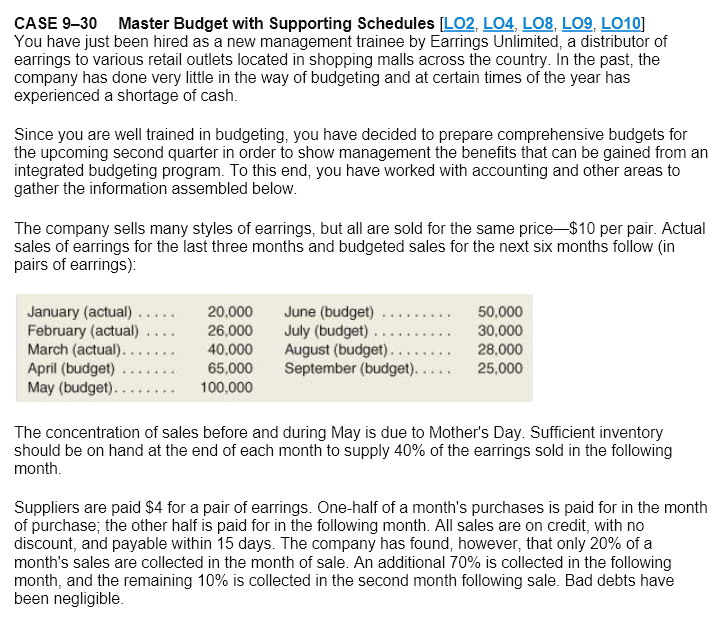



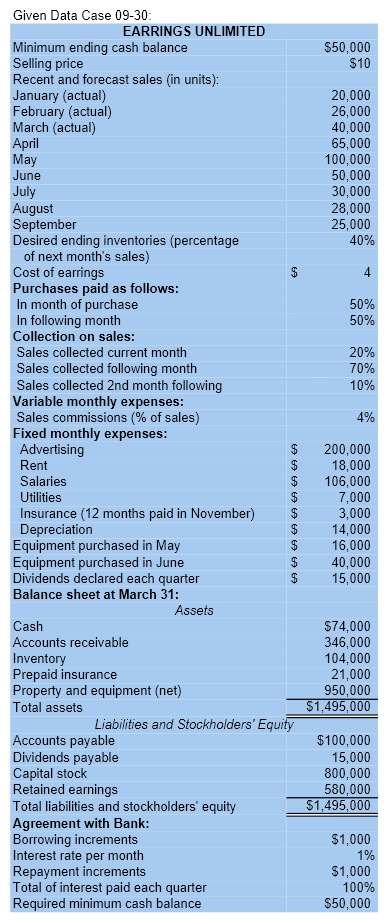
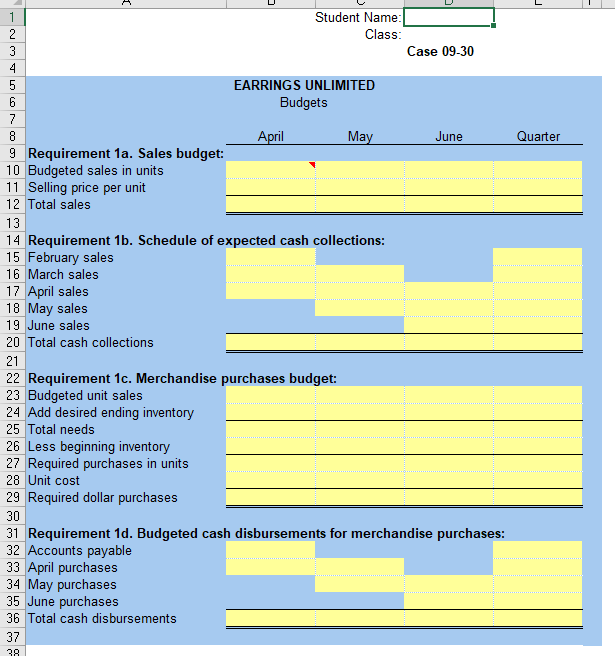
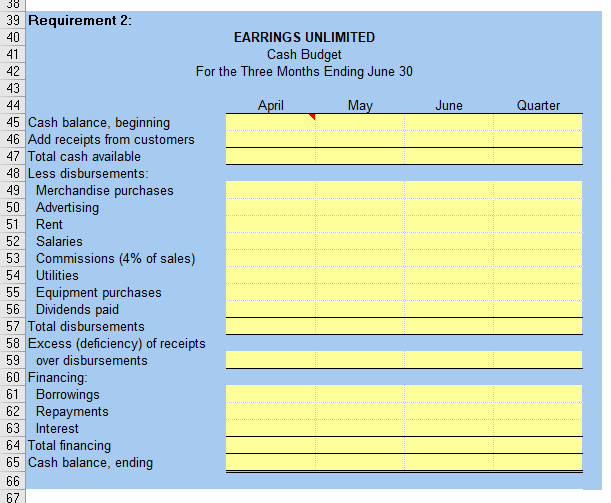

CASE 930 Master Budget with Supporting Schedules [LO2, L04, LOB, L09, L010) You have just been hired as a new management trainee by Earrings Unlimited, a distributor of earrings to various retail outlets located in shopping malls across the country. In the past, the company has done very little in the way of budgeting and at certain times of the year has experienced a shortage of cash. Since you are well trained in budgeting, you have decided to prepare comprehensive budgets for the upcoming second quarter in order to show management the benefits that can be gained from an integrated budgeting program. To this end, you have worked with accounting and other areas to gather the information assembled below. The company sells many styles of earrings, but all are sold for the same price$10 per pair. Actual sales of earrings for the last three months and budgeted sales for the next six months follow (in pairs of earrings): .... January (actual) ..... February (actual) March (actual). April (budget) May (budget). 20,000 26,000 40,000 65,000 100,000 June (budget) July (budget) August (budget). September (budget). 50,000 30,000 28,000 25,000 The concentration of sales before and during May is due to Mother's Day. Sufficient inventory should be on hand at the end of each month to supply 40% of the earrings sold in the following month. Suppliers are paid $4 for a pair of earrings. One-half of a month's purchases is paid for in the month of purchase, the other half is paid for in the following month. All sales are on credit, with no discount, and payable within 15 days. The company has found, however, that only 20% of a month's sales are collected in the month of sale. An additional 70% is collected in the following month, and the remaining 10% is collected in the second month following sale. Bad debts have been negligible. Monthly operating expenses for the company are given below: Variable: Sales commissions ...... 4% of sales Fixed: Advertising. $200,000 Rent... $18,000 Salaries $106,000 Utilities. $7,000 Insurance $3,000 Depreciation. $14,000 Insurance is paid on an annual basis, in November of each year. The company plans to purchase $16,000 in new equipment during May and $40,000 in new equipment during June; both purchases will be for cash. The company declares dividends of $15,000 each quarter, payable in the first month of the following quarter. A listing of the company's ledger accounts as of March 31 is given below: $ 74,000 Assets Cash... Accounts receivable ($26,000 February sales; $320,000 March sales). Inventory .... Prepaid insurance Property and equipment (net) Total assets 346,000 104,000 21,000 950,000 $1.495,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable..... Dividends payable Capital stock .... Retained earnings Total liabilities and stockholders' equity. $ 100,000 15,000 800,000 580,000 $1,495,000 The company maintains a minimum cash balance of $50,000. All borrowing is done at the beginning of a month; any repayments are made at the end of a month. The company has an agreement with a bank that allows the company to borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month and for simplicity we will assume that interest is not compounded. At the end of the quarter, the company would pay the bank all of the accumulated interest on the loan and as much of the loan as possible (in increments of $1,000), while still retaining at least $50,000 in cash. Required: Prepare a master budget for the three-month period ending June 30. Include the following detailed budgets: 1. a. A sales budget, by month and in total. b. A schedule of expected cash collections from sales, by month and in total. C. A merchandise purchases budget in units and in dollars. Show the budget by month and in total. d. A schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases, by month and in total. 2. A cash budget. Show the budget by month and in total. Determine any borrowing that would be needed to maintain the minimum cash balance of $50,000. 3. A budgeted income statement for the three-month period ending June 30. Use the contribution approach. 4. A budgeted balance sheet as of June 30. $ Given Data Case 09-30: EARRINGS UNLIMITED Minimum ending cash balance $50,000 Selling price $10 Recent and forecast sales (in units): January (actual) 20,000 February (actual) 26,000 March (actual) 40,000 April 65,000 May 100,000 June 50,000 July 30,000 August 28,000 September 25,000 Desired ending inventories (percentage 40% of next month's sales) Cost of earrings 4 Purchases paid as follows: In month of purchase 50% In following month 50% Collection on sales: Sales collected current month 20% Sales collected following month 70% Sales collected 2nd month following 10% Variable monthly expenses: Sales commissions (% of sales) 4% Fixed monthly expenses: Advertising $ 200,000 Rent $ 18,000 Salaries 106,000 Utilities $ 7,000 Insurance (12 months paid in November) 3,000 Depreciation 14,000 Equipment purchased in May 16,000 Equipment purchased in June $ 40,000 Dividends declared each quarter $ 15,000 Balance sheet at March 31: Assets Cash $74,000 Accounts receivable 346,000 Inventory 104,000 Prepaid insurance 21,000 Property and equipment (net) 950,000 Total assets $1,495,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable $100,000 Dividends payable 15,000 Capital stock 800,000 Retained earnings 580,000 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $1,495,000 Agreement with Bank: Borrowing increments $1,000 Interest rate per month 1% Repayment increments $1,000 Total of interest paid each quarter 100% Required minimum cash balance $50,000 M T N O May Quarter Student Name: 2 Class: Case 09-30 4 5 EARRINGS UNLIMITED 6 Budgets 7 8 April June 9 Requirement 1a. Sales budget: 10 Budgeted sales in units 11 Selling price per unit 12 Total sales 13 14 Requirement 1b. Schedule of expected cash collections: 15 February sales 16 March sales 17 April sales 18 May sales 19 June sales 20 Total cash collections 21 22 Requirement 1c. Merchandise purchases budget: 23 Budgeted unit sales 24 Add desired ending inventory 25 Total needs 26 Less beginning inventory 27 Required purchases in units 28 Unit cost 29 Required dollar purchases 30 31 Requirement 1d. Budgeted cash disbursements for merchandise purchases: 32 Accounts payable 33 April purchases 34 May purchases 35 June purchases 36 Total cash disbursements 37 38 June Quarter 30 39 Requirement 2: 40 EARRINGS UNLIMITED 41 Cash Budget 42 For the Three Months Ending June 30 43 44 April May 45 Cash balance, beginning 46 Add receipts from customers 47 Total cash available 48 Less disbursements: 49 Merchandise purchases 50 Advertising 51 Rent 52 Salaries 53 Commissions (4% of sales) 54 Utilities 55 Equipment purchases 56 Dividends paid 57 Total disbursements 58 Excess (deficiency) of receipts 59 over disbursements 60 Financing 61 Borrowings 62 Repayments 63 Interest 64 Total financing 65 Cash balance, ending 66 67 C A B 69 EARRINGS UNLIMITED 70 Budgeted Income Statement 71 For the Three Months Ending June 30 72 73 Sales in units 74 Sales 75 Variable expenses: 76 Cost of goods sold 77 Commissions 78 Contribution margin 79 Fixed expenses: 80 Advertising 81 Rent 82 Salaries 83 Utilities 84 Insurance 85 Depreciation 86 Net operating income 87 Less interest expense 88 Net income 89 90 91 EARRINGS UNLIMITED 92 Budgeted Balance Sheet 93 June 30 94 95 Assets 96 Cash 97 Accounts receivable 98 Inventory 99 Prepaid insurance 100 Property and equipment, net 101 Total assets 102 103 Liabilities and Equity 104 Accounts payable, purchases 105 Dividends payable 106 Capital stock, no par 107 Retained earnings 108 Total liabilities and equity 109 110 Accounts receivable at June 30: 111 May sales 112 June sales 113 Total 114 115 Retained earnings at June 30: 116 Balance, March 31 117 Add net income 118 Total 119 Less dividends declared 120 Balance, June 30 121 122 123















