Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
This is for the pacman search.py I need to implement these functions. This is the template that was provided just need the implementation of depth
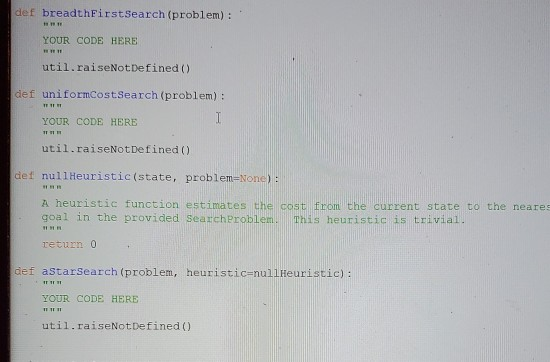
This is for the pacman search.py I need to implement these functions. This is the template that was provided
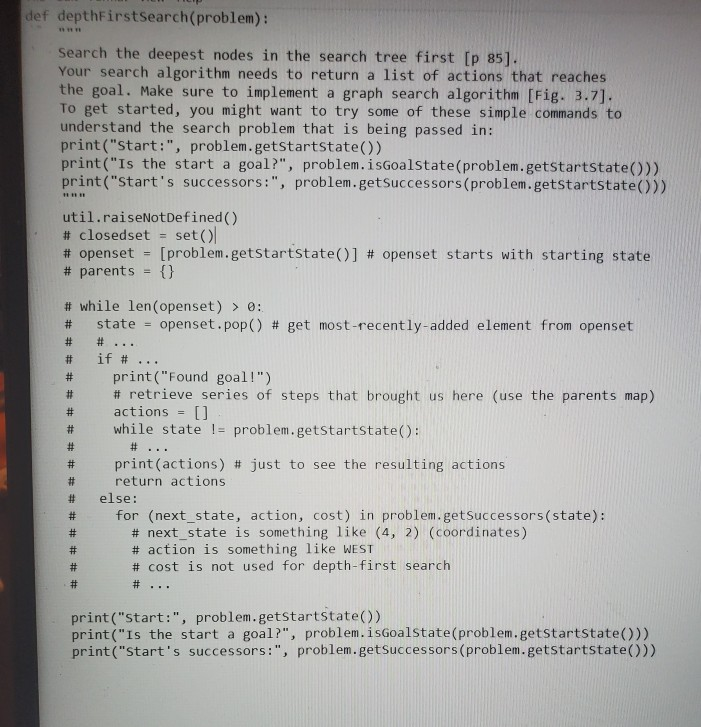
just need the implementation of depth first search while keeping track of the parents
def breadthFirst Search (problem): YOUR CODE HERE util.raiseNot Defined() def uniformCost Search (problem): YOUR CODE HERE util.raiseNot Defined() det nullHeuristic (state, problem-None): A heuristic function estimates the cost from the current state to the neares goal in the provided Search Problem. This heuristic is trivial. return 0 def astar Search (problem, heuristic=nullHeuristic): YOUR CODE HERE util.raiseNot Defined() def depthFirstSearch(problem): Search the deepest nodes in the search tree first [p 85]. Your search algorithm needs to return a list of actions that reaches the goal. Make sure to implement a graph search algorithm [Fig. 3.7]. To get started, you might want to try some of these simple commands to understand the search problem that is being passed in: print("Start:", problem.getStartState() print("Is the start a goal?", problem.isGoalstate(problem.getstartstate())) print("Start's successors:", problem.getSuccessors (problem.getstartstate())) util.raiseNot Defined() # closedset = setol # openset = [problem.getStartState()] # openset starts with starting state # parents = {} # while len(openset) > 0: state = openset.pop() # get most recently added element from openset # # ... if #... print("Found goal!") # retrieve series of steps that brought us here (use the parents map) actions = [] while state != problem.getStartState(): print(actions) # just to see the resulting actions return actions else: for (next_state, action, cost) in problem.getSuccessors(state): # next_state is something like (4, 2) (coordinates) # action is something like WEST # cost is not used for depth-first search print("start:", problem.getStartstate() print("Is the start a goal?", problem.isGoalstate (problem.getStartstate()) print("Start's successors:", problem.getSuccessors(problem.getstartstate())Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


