Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
This is not a continuation of serial problem from chapter 1. please solve all parts relevannt. Required a. Prepare journal entries for the December transactions.
This is not a continuation of serial problem from chapter 1. please solve all parts relevannt.


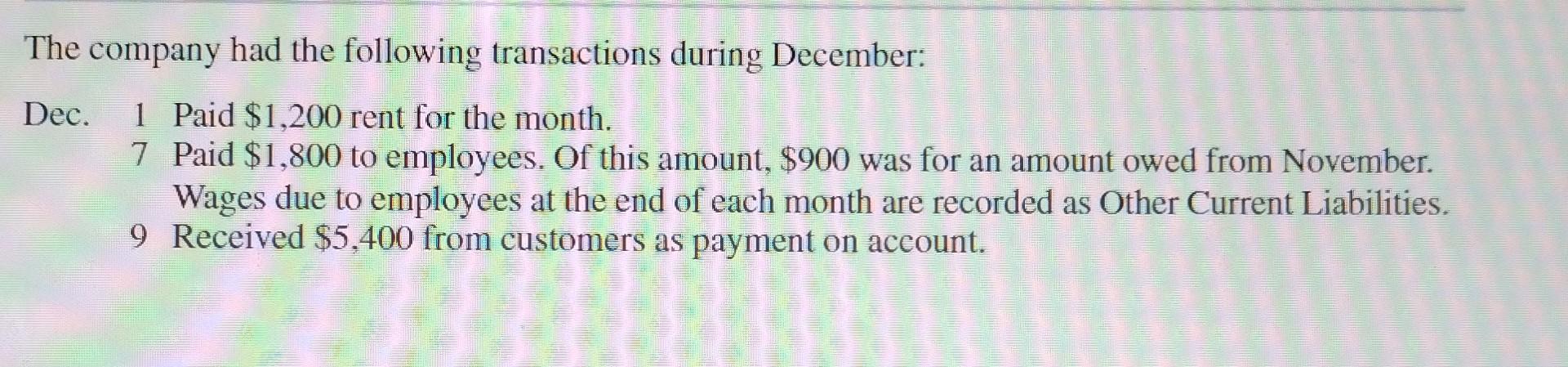

Required a. Prepare journal entries for the December transactions. b. Prepare a classified income statement for the month of December. c. Calculate Kate's gross profit percentage and return on sales ratio for December. Kate was a little worried about some of the practices of Fred Abbott, the CEO of Sentiments, and decided that an association with Sentiments could damage the reputation of her own company. Kate is very concerned that her business be viewed as socially responsible, and any damage to her reputation at this early stage could prove very difficult to overcome. She therefore decided to concentrate her efforts on producing a quality product that consumers would be proud to purchase and send to their loved ones. As expected, November saw a boom in Kate's greeting card business. She invested in additional computer graphics equipment, which she partially funded with a bank loan of $15,000 and an additional investment of her own funds into the business. The loan carries an interest rate of six percent with interest payments required semiannually. The entire principal balance is due in one balloon payment in two years. Kate uses a perpetual inventory system. As of December 2, Kate's Cards had the following account balances: The company had the following transactions during December: Dec. 1 Paid $1,200 rent for the month. 7 Paid $1,800 to employees. Of this amount, $900 was for an amount owed from November. Wages due to employees at the end of each month are recorded as Other Current Liabilities. 9 Received $5,400 from customers as payment on aceount. Dec. 12 Sold, for cash, $11,000 of greeting cards. This merchandise had cost $6,000 to produce. 14 Purchased additional inventory totaling $7,000 on account with terms of 2/10,n/45. 15 Paid cash for supplies (listed as Other Current Assets) in the amount of $600. 19 Sold, on account with terms of 2/10,n/30, greeting cards totaling $6,000. The merchandise had cost $4,000 to produce. 21 Paid additional wages of $1,400. 25 Paid the total owed for the merchandise that was purchased on December 14. 28 Received payment in full from the customer that purchased the merchandise on December 19. 31 Depreciation for the month totaled $900. 31 A physical count of inventory and supplies revealed that $13,000 and $2,000, respectively, were on hand at year-end. Assume that Other Current Assets consists only of the cost of supplies. Required a. Prepare journal entries for the December transactions. b. Prepare a classified income statement for the month of December. c. Calculate Kate's gross profit percentage and return on sales ratio for December. Kate was a little worried about some of the practices of Fred Abbott, the CEO of Sentiments, and decided that an association with Sentiments could damage the reputation of her own company. Kate is very concerned that her business be viewed as socially responsible, and any damage to her reputation at this early stage could prove very difficult to overcome. She therefore decided to concentrate her efforts on producing a quality product that consumers would be proud to purchase and send to their loved ones. As expected, November saw a boom in Kate's greeting card business. She invested in additional computer graphics equipment, which she partially funded with a bank loan of $15,000 and an additional investment of her own funds into the business. The loan carries an interest rate of six percent with interest payments required semiannually. The entire principal balance is due in one balloon payment in two years. Kate uses a perpetual inventory system. As of December 2, Kate's Cards had the following account balances: The company had the following transactions during December: Dec. 1 Paid $1,200 rent for the month. 7 Paid $1,800 to employees. Of this amount, $900 was for an amount owed from November. Wages due to employees at the end of each month are recorded as Other Current Liabilities. 9 Received $5,400 from customers as payment on aceount. Dec. 12 Sold, for cash, $11,000 of greeting cards. This merchandise had cost $6,000 to produce. 14 Purchased additional inventory totaling $7,000 on account with terms of 2/10,n/45. 15 Paid cash for supplies (listed as Other Current Assets) in the amount of $600. 19 Sold, on account with terms of 2/10,n/30, greeting cards totaling $6,000. The merchandise had cost $4,000 to produce. 21 Paid additional wages of $1,400. 25 Paid the total owed for the merchandise that was purchased on December 14. 28 Received payment in full from the customer that purchased the merchandise on December 19. 31 Depreciation for the month totaled $900. 31 A physical count of inventory and supplies revealed that $13,000 and $2,000, respectively, were on hand at year-end. Assume that Other Current Assets consists only of the cost of supplies
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


