Question
This is what I have so far but I get a segmentation fault when I try to compile it main.c. #include #include lib.h #include #include
This is what I have so far but I get a segmentation fault when I try to compile it
main.c.
#include
int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc == 1){ printf("1: Error "); return 1; } printf("%s",argv[1]); if(argv[1] != NULL){ bool file = file_exists(argv[1]); } // if(file == true){ // return 0; // } // else{ // while(file == false){ // file = file_exists(argv[1]); // } // } // return 1; // } return 0; }
lib.c
#include
bool file_exists(char* argv) { char* p = getenv("PATH"); //printf("The path: %s ",path); char buffer[2048]; int colon_location = 0; //printf ("extracted path: %s ", buffer); DIR* dir = opendir(buffer); struct dirent* entry = readdir(dir); while(entry!= NULL) { printf("Hello!"); while (p[colon_location] != ':') { colon_location++; } memcmp(buffer,p,colon_location); printf("Buffer: %s ", buffer); if (strcmp(buffer,argv)==0){ printf("Path: %s ", buffer); return true; } else{ colon_location++; } } printf("None found :("); return false; }
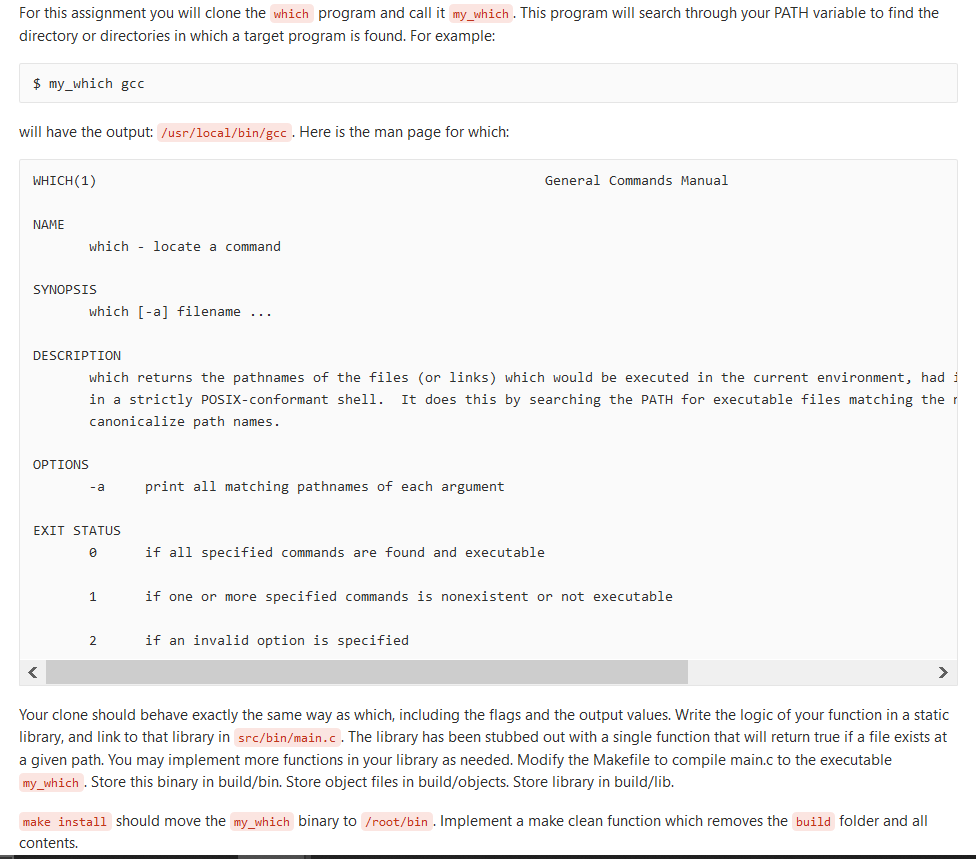
For this assignment you will clone the which program and call it my_which . This program will search through your PATH variable to find the directory or directories in which a target program is found. For example: $ my_which gcc will have the output: /usr/local/bin/gcc. Here is the man page for which: WHICH(1) General Commands Manual NAME which - locate a command SYNOPSIS which [-a] filename ... DESCRIPTION which returns the pathnames of the files (or links) which would be executed in the current environment, hadi in a strictly POSIX-conformant shell. It does this by searching the PATH for executable files matching ther canonicalize path names. OPTIONS -a print all matching pathnames of each argument EXIT STATUS if all specified commands are found and executable if one or more specified commands is nonexistent or not executable if an invalid option is specified Your clone should behave exactly the same way as which, including the flags and the output values. Write the logic of your function in a static library, and link to that library in src/bin/main.c. The library has been stubbed out with a single function that will return true if a file exists at a given path. You may implement more functions in your library as needed. Modify the Makefile to compile main.c to the executable my_which . Store this binary in build/bin. Store object files in build/objects. Store library in build/lib. make install should move the my_which binary to /root/bin . Implement a make clean function which removes the build folder and all contentsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


