Question
This question examines calculation of age-adjusted death rates using the direct method. [NOTE: Use the death rates calculated in Question #9] Table 2. Age-adjusted death
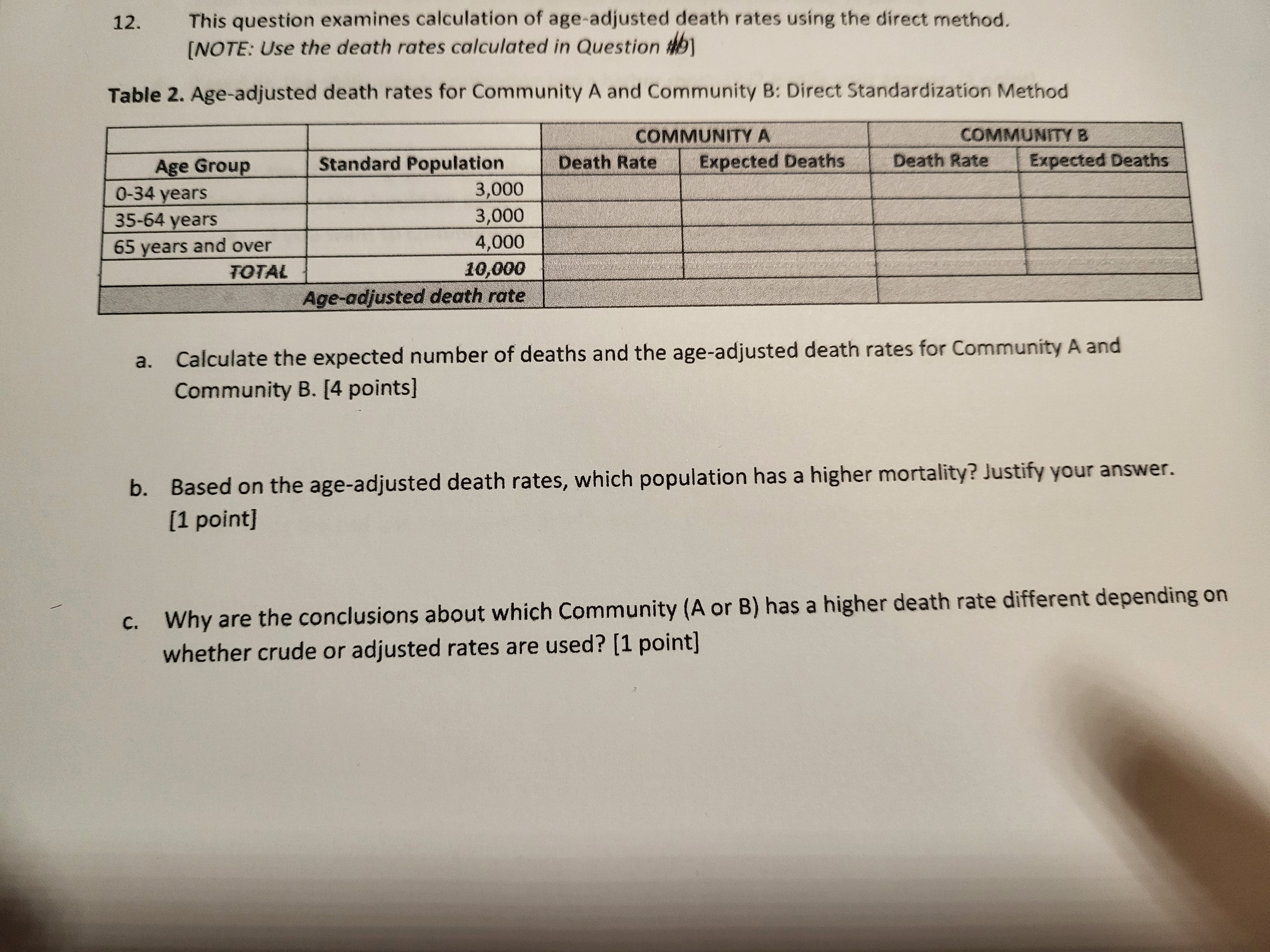
This question examines calculation of age-adjusted death rates using the direct method. [NOTE: Use the death rates calculated in Question #9] Table 2. Age-adjusted death rates for Community A and Community B: Direct Standardization Method COMMUNITY A COMMUNITY B Age Group Standard Population Death Rate Expected Deaths Death Rate Expected Deaths 0-34 years 3,000 35-64 years 3,000 65 years and over 4,000 TOTAL 10,000 Age-adjusted death rate a. Calculate the expected number of deaths and the age-adjusted death rates for Community A and Community B. [4 points] b. Based on the age-adjusted death rates, which population has a higher mortality? Justify your answer.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


