This question is due 2 hours from now. Please answer as much as possible and ASAP. Thank you!
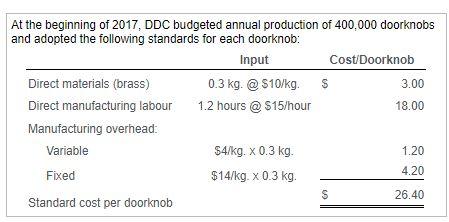
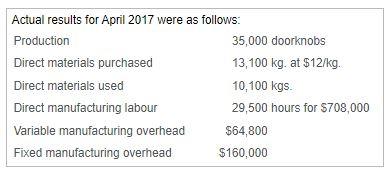


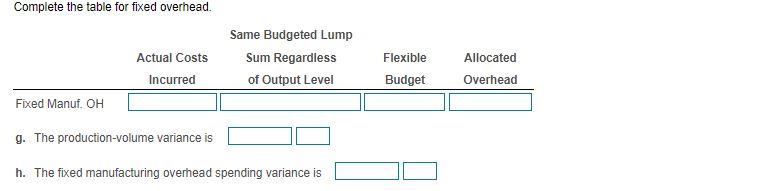
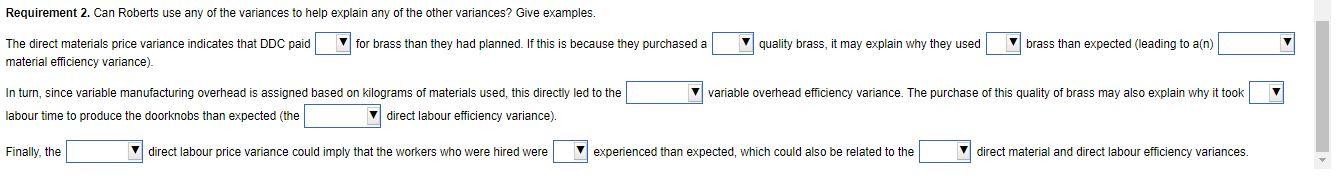
Samuel Roberts is a cost accountant and business analyst for Datura Design Company (DDC), which manufactures expensive brass doorknobs. DDC uses two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labour. Roberts feels that manufacturing overhead is most closely related to material usage. Therefore, DDC allocates manufacturing overhead to production based upon kilograms of materials used. Click the icon to the tandard e click the icon to win n actual morults for Anril At the beginning of 2017, DDC budgeted annual production of 400,000 doorknobs and adopted the following standards for each doorknob: Input Cost/Doorknob Direct materials (brass) 0.3 kg. @ $10/kg $ 3.00 Direct manufacturing labour 1.2 hours @ $15/hour 18.00 Manufacturing overhead: Variable $4/kg. X 0.3 kg 1.20 Fixed $14/kg. x 0.3 kg. 4.20 S 26.40 Standard cost per doorknob Actual results for April 2017 were as follows: Production 35,000 doorknobs Direct materials purchased 13,100 kg, at $12/kg Direct materials used 10,100 kgs. Direct manufacturing labour 29,500 hours for 5708,000 Variable manufacturing overhead $64,800 Fixed manufacturing overhead $160,000 Requirement 1. For the month of April, compute the variances, indicating whether each is favourable (F) or unfavourable (U). Before computing the variances, complete the tables below. Begin by completing the table for direct materials. Actual Input Qty. Actual Costs Incurred 23rf Budgeted Price Purchases Usage Flexible Budget Direct materials a. Direct materials price variance (based on purchases) is b. The direct materials efficiency variance is Now complete the table for direct labour. Actual Input Qty. Actual Costs Incurred Flexible Budget Budgeted Price Direct Manuf. Labour c. The direct manufacturing labour price variance is d. The direct manufacturing labour efficiency variance is Next complete the table for variable overhead. (Abbreviation used: Manuf - Manufacturing) Complete the table for fixed overhead. Actual Costs Incurred Same Budgeted Lump Sum Regardless of Output Level Flexible Budget Allocated Overhead Fixed Manuf. OH g. The production-volume variance is h. The fixed manufacturing overhead spending variance is Requirement 2. Can Roberts use any of the variances to help explain any of the other variances? Give examples. The direct materials price variance indicates that DDC paid material efficiency variance). for brass than they had planned. If this is because they purchased a quality brass, it may explain why they used brass than expected (leading to a(n) variable overhead efficiency variance. The purchase of this quality of brass may also explain why it took In turn, since variable manufacturing overhead is assigned based on kilograms of materials used, this directly led to the labour time to produce the doorknobs than expected (the direct labour efficiency variance). Finally, the direct labour price variance could imply that the workers who were hired were experienced than expected, which could also be related to the direct material and direct labour efficiency variances













