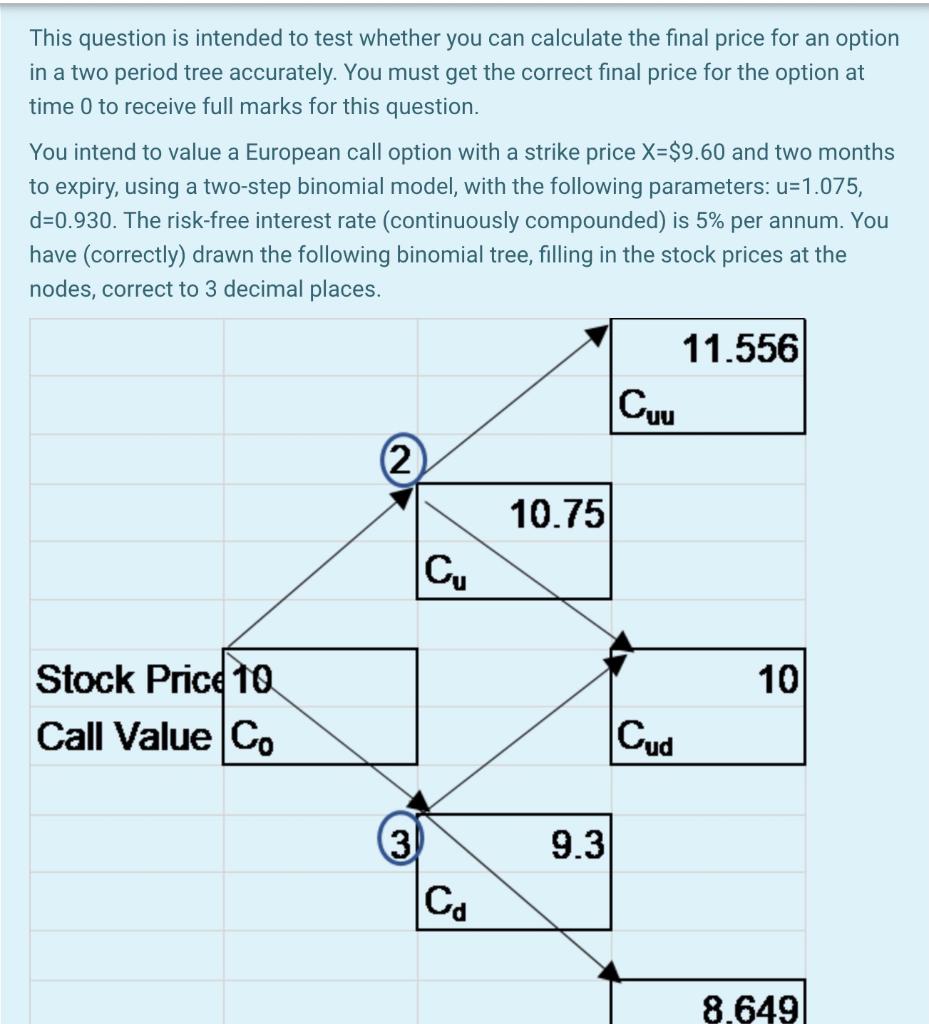

This question is intended to test whether you can calculate the final price for an option in a two period tree accurately. You must get the correct final price for the option at time 0 to receive full marks for this question. You intend to value a European call option with a strike price X=$9.60 and two months to expiry, using a two-step binomial model, with the following parameters: u=1.075, d=0.930. The risk-free interest rate (continuously compounded) is 5% per annum. You have (correctly) drawn the following binomial tree, filling in the stock prices at the nodes, correct to 3 decimal places. 11.556 Cuu 2 10.75 Cu 10 Stock Price 10 Call Value Co Cud 9.3 3 Co 8.649 Time 0 Time 1 Time 2 Two period binomial model Answer the following questions. You must use the numbers given in the binomial tree to calculate the answers. Carry at least three decimal places as you work through this question or your answers will not be accurate to the level required. 1. Fill in the values of the call option at expiry. Cuu = $ Give your answer correct to three decimal places, or your answer will be incorrect. Cud = $ Give your answer correct to three decimal places, or your answer will be incorrect. Cdd = $ Give your answer correct to three decimal places, or your answer will be incorrect. 2. You use the delta hedging approach to calculate the value of the call option (Cu)when the share price is $10.75 in the up-state at time 1. Delta (A) = at the node labelled 2 in the diagram. The riskless portfolio (delta-hedged) consists of A units of shares and one call option. Therefore the value of the call option at node 2 = $ Give your answer correct to three decimal places, or your answer will be incorrect. 3. Using the same approach (or otherwise), the value of the call option in the down state at time 1 (node 3) is $ Give your answer correct to three decimal places, or your answer will be incorrect. 4. Now that you have calculated the fair price of the call option at nodes 2 and node 3 respectively, calculate the fair (arbitrage-free) price of the call option at time 0. The fair price of the call option at time 0 is $ Give your answer correct to two decimal places, or your answer will be incorrect. Do not include the dollar sign "$" in any of your numerical answers









