Question
Timber Design Figure (a) below shows a mono truss that will be used for the extension of a restaurant building to be built in Byron
Timber Design Figure (a) below shows a mono truss that will be used for the extension of a restaurant building to be built in Byron Bay, NSW. The timber species used in the truss is Seasoned Radiata Pine. For analysis purposes, all members of the truss can be assumed to be pin-jointed. The tributary area supported by the mono truss is 9m by 7m in plan projection. You are required to check the connection at node 2 (Figure (a) and (b)). All the members at node 2 have a cross-section of 150x50mm. The side plates to be used at node 2 are also from Radiata Pine and are 35mm thick. Analyse the truss and identify the force in members connected to the joint. Also determine the critical load case and relevant values of k1. Point loads F1 and F2 applied at joint 2 and 4 represent the Permanent and Imposed loads on the truss, respectively, where the imposed load is occupancy live load. Self-weight of the timber can be ignored in the analysis and design of the truss. Possible load combinations as per AS1170.0 (2002) are: 1. 1.35G 2. 1.2G + 1.5Q F1=2.2 kN (Permanent load) F2= 2 kN (Imposed load- considered as 5 months duration load) You are first required to analyse the truss to find the internal actions on joint 2 for both load combinations. Based on the calculated internal actions for the two load cases, you are then required to undertake two design checks as detailed below. - Members of the bottom chord are connected using 60mm long ϕ2.5 nails (Figure (c), Section B-B). Check the suitability of the joint to carry the design load. - The vertical member is connected using an M10 bolt (Figure (c), Section A-A). Check the suitability of the joint to carry the design load. (Connection arrangement/spacing check is not required)

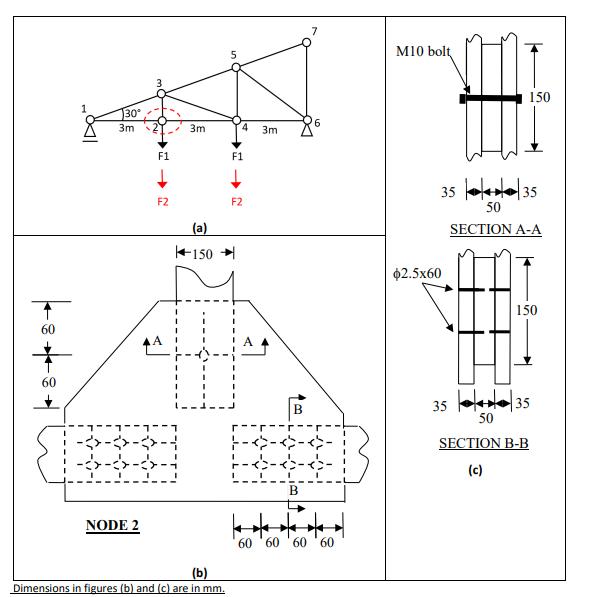
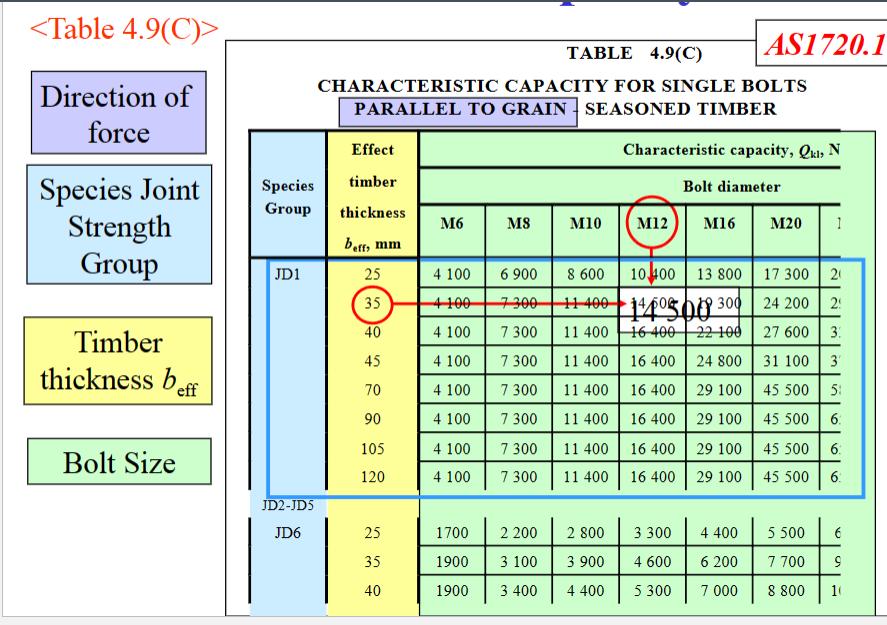
Assessment task 3: Timber Design Figure (a) below shows a mono truss that will be used for the extension of a restaurant building to be built in Byron Bay, NSW. The timber species used in the truss is Seasoned Radiata Pine. For analysis purposes, all members of the truss can be assumed to be pin-jointed. The tributary area supported by the mono truss is 9m by 7m in plan projection. You are required to check the connection at node 2 (Figure (a) and (b)). All the members at node 2 have a cross-section of 150x50mm. The side plates to be used at node 2 are also from Radiata Pine and are 35mm thick. Analyse the truss and identify the force in members connected to the joint. Also determine the critical load case and relevant values of k1. Point loads F1 and F2 applied at joint 2 and 4 represent the Permanent and Imposed loads on the truss, respectively, where the imposed load is occupancy live load. Self-weight of the timber can be ignored in the analysis and design of the truss. Possible load combinations as per AS1170.0 (2002) are: 1.1.35G 2. 1.2G + 1.5Q F1=2.2 kN (Permanent load) F2=2 kN (Imposed load- considered as 5 months duration load) You are first required to analyse the truss to find the internal actions on joint 2 for both load combinations. Based on the calculated internal actions for the two load cases, you are then required to undertake two design checks as detailed below. - Members of the bottom chord are connected using 60mm long $2.5 nails (Figure (c), Section B-B). Check the suitability of the joint to carry the design load. The vertical member is connected using an M10 bolt (Figure (c), Section A-A). Check the suitability of the joint to carry the design load. (Connection arrangement/spacing check is not required)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


