Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Titles: No journal entry required, accounts payable, accounts receivable,accrued payroll,cost of goods sold, depreciation, direct labor efficiency variance, direct labor rate variance, direct materials inventory,
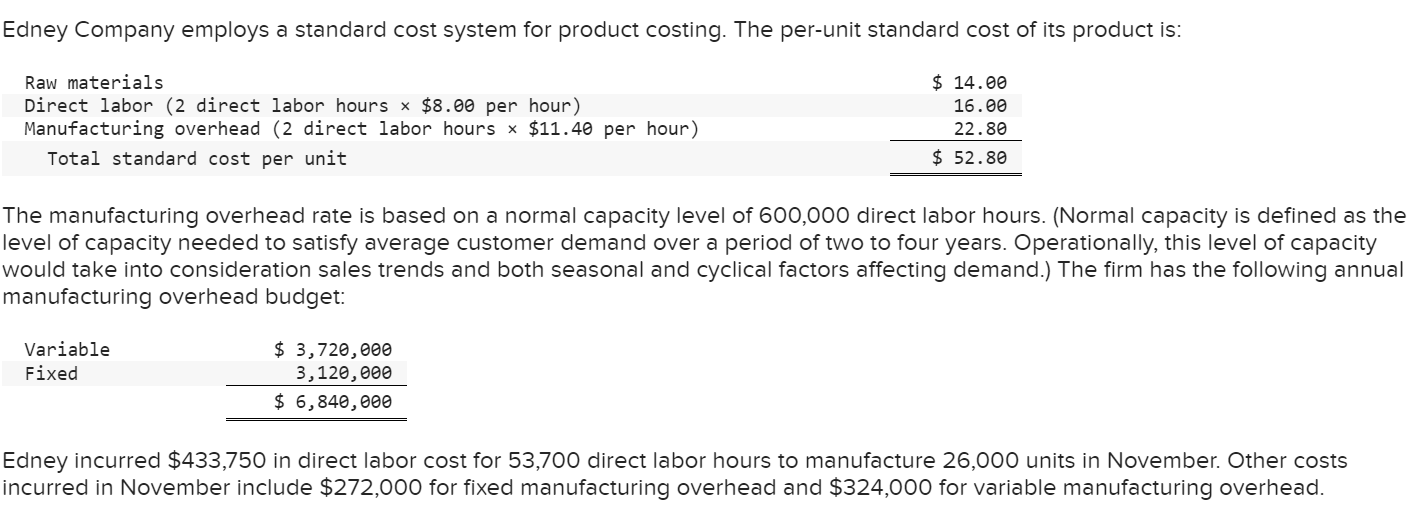


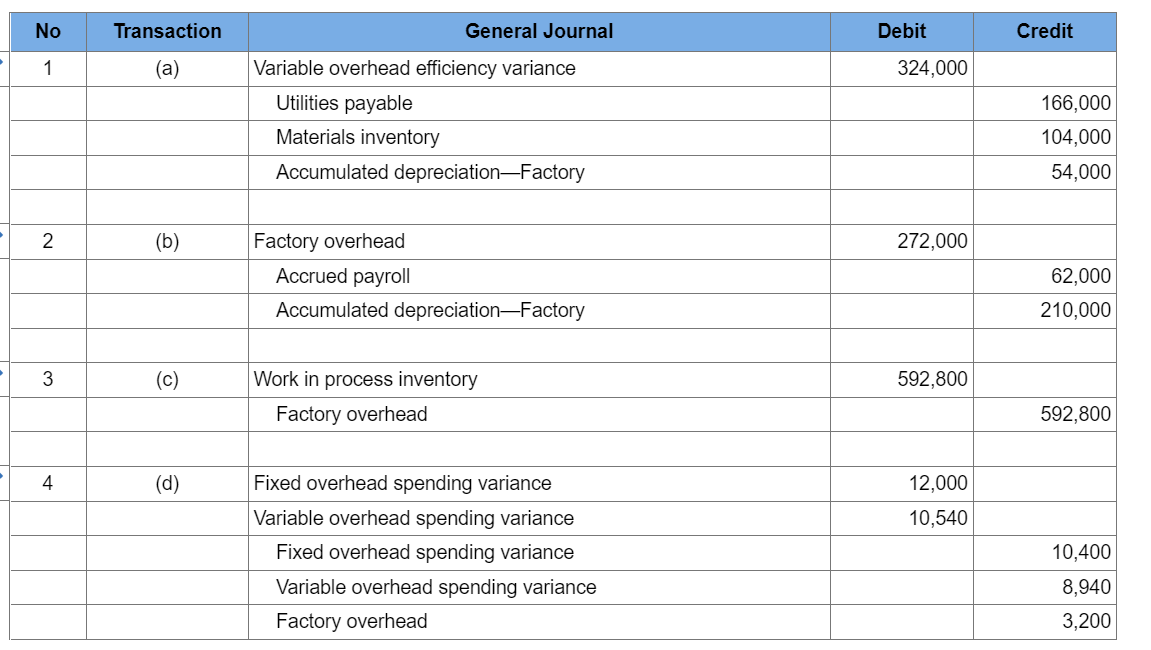

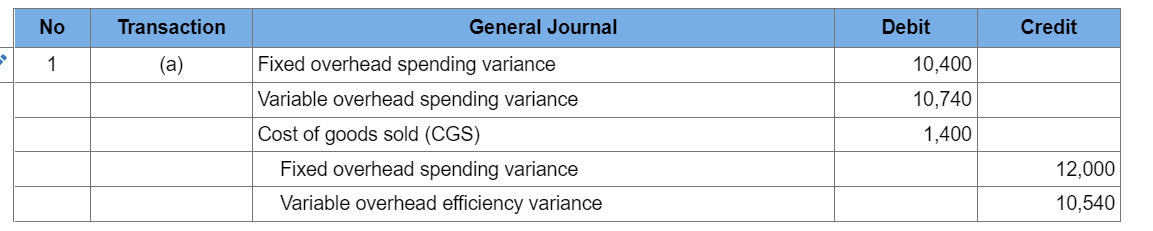
Titles: No journal entry required, accounts payable, accounts receivable,accrued payroll,cost of goods sold, depreciation, direct labor efficiency variance, direct labor rate variance, direct materials inventory, direct materials purchase price variance,direct materials usage variance,finished goods inventory, fixed costs, fixed overhead, insurance, manufacturing, rent, salaries, sales commissions, sales revenue, selling and administrative, variable costs, variable overhead, work-in-process inventory
The manufacturing overhead rate is based on a normal capacity level of 600,000 direct labor hours. (Normal capacity is defined as the level of capacity needed to satisfy average customer demand over a period of two to four years. Operationally, this level of would take into consideration sales trends and both seasonal and cyclical factors affecting demand.) The firm has the following annua manufacturing overhead budget: Edney incurred $433,750 in direct labor cost for 53,700 direct labor hours to manufacture 26,000 units in November. Other costs incurred in November include $272,000 for fixed manufacturing overhead and $324,000 for variable manufacturing overhead. 2. Prepare the following four journal entries: (a) to record actual variable overhead costs, (b) to record actual fixed overhead costs, (c) to record standard overhead costs applied to production, and (d) to record all four overhead cost variances. The company uses a single account, Factory Overhead, to record all overhead costs. Assume that the actual variable manufacturing overhead consists of utilities payable of $166,000, indirect materials of $104,000 (all materials, direct and indirect, are recorded in a single account, Materials Inventory), and $54,000 depreciation on factory equipment (determined under the units-of-production method). Assume that the fixed manufacturing overhead consists of accrued (i.e, unpaid) salaries of $62,000 and factory depreciation of $210,000. All unpaid salaries should be recorded in a single account, Accrued Payroll. 3. Prepare the appropriate journal entry to close all manufacturing overhead variances to the cost of goods sold (COGS) account. (Assume the cost variances you calculated above are for the year, not the month.) Prepare the following four journal entries: (a) to record actual variable overhead costs, (b) to record actual fixed overhead costs, (c) to record standard overhead costs applied to production, and (d) to record all four overhead cost variances. The company uses a single account, Factory Overhead, to record all overhead costs. Assume that the actual variable manufacturing overhead consists of utilities payable of $166,000, indirect materials of $104,000 (all materials, direct and indirect, are recorded in a single account, Materials Inventory), and $54,000 depreciation on factory equipment (determined under the units-of-production method). Assume that the fixed manufacturing overhead consists of accrued (i.e, unpaid) salaries of $62,000 and factory depreciation of $210,000. All unpaid salaries should be recorded in a single account, Accrued Payroll. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Prepare the appropriate journal entry to close all manufacturing overhead variances to the cost of goods sold (COGS) account. (Assume the cost variances you calculated above are for the year, not the month.) (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Show less AStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


