Question
To assess the relative merits of two methods (Cooperative learning vs. Tiered Lessons) of instruction for elementary computer programming, a curriculum researcher randomly selected fifth
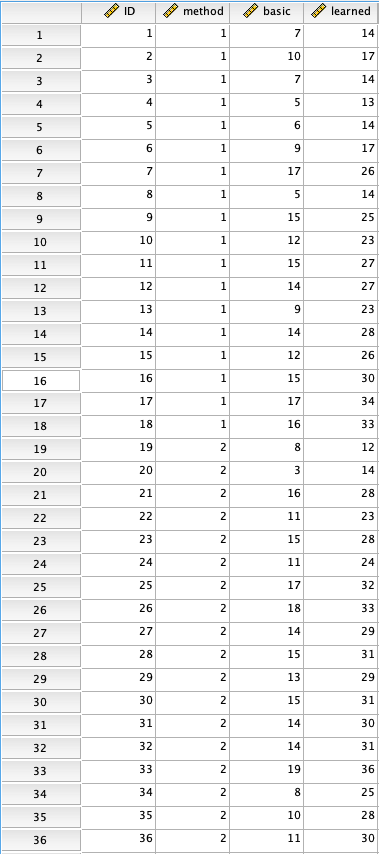
To assess the relative merits of two methods (Cooperative learning vs. Tiered Lessons) of instruction for elementary computer programming, a curriculum researcher randomly selected fifth graders from each of two elementary schools in a certain school district. Each group, within the setting of its home school, received a six-week course of instruction in one of the two instructional methods. After the six-weeks, the 36 subjects were measured on how well they learned the prescribed contents of the subject matter. Well aware of the broad range of pre-existing individual differences that are likely to be found in situations of this sort, the curriculum researcher took the precaution of measuring subjects beforehand with respect to their pre-existing levels of the subject matter.
Note the following variables in the dataset:
ID:ID number to de-identify the participants in the study.
Method:Method of instruction.Nominally scaled variable consisting of two values:
1: Cooperative learning
2: Tiered Lessons
Basic:Pre-test score of knowledge of Subject Matter
Learned:Post-test score of knowledge of Subject Matter
Is thechangein knowledge of subject matter different for students in the Cooperative Learning method compared to students in Tiered Lessons method?
1. What are the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses? Use the appropriate statistical symbols.
2. Provide andinterpreta side-by-side box plot.
3. Check the assumption of homogeneity of variance. Provide the name of the test(s) used, thep-value (s) for the statistical test (s) of the assumption and determine whether the statistical assumption has been violated or not.
4.Check the assumption of normality.Provide the name of the test(s) used, thep-value (s) for the statistical test (s) of the assumption and determine whether the statistical assumption has been violated or not.
Irrespective of the check on the assumption of normality above, proceed assuming the normality assumption is satisfied (Even if it is not, with equal sample sizes the test is robust against violations to normality).
5. Report the appropriate test statistic.
6. Provide the p-value. Formulate conclusion in terms of the problem while rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


