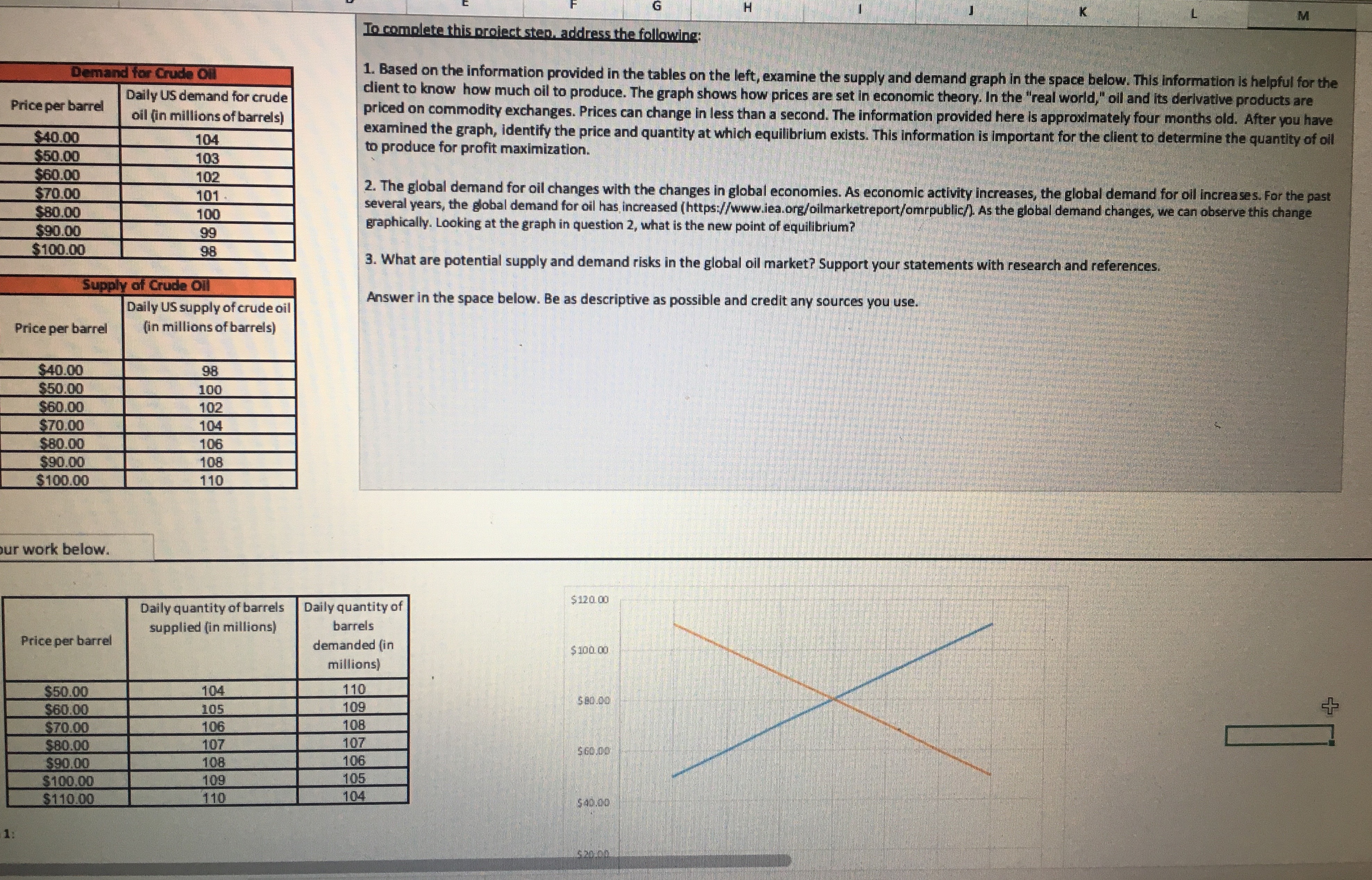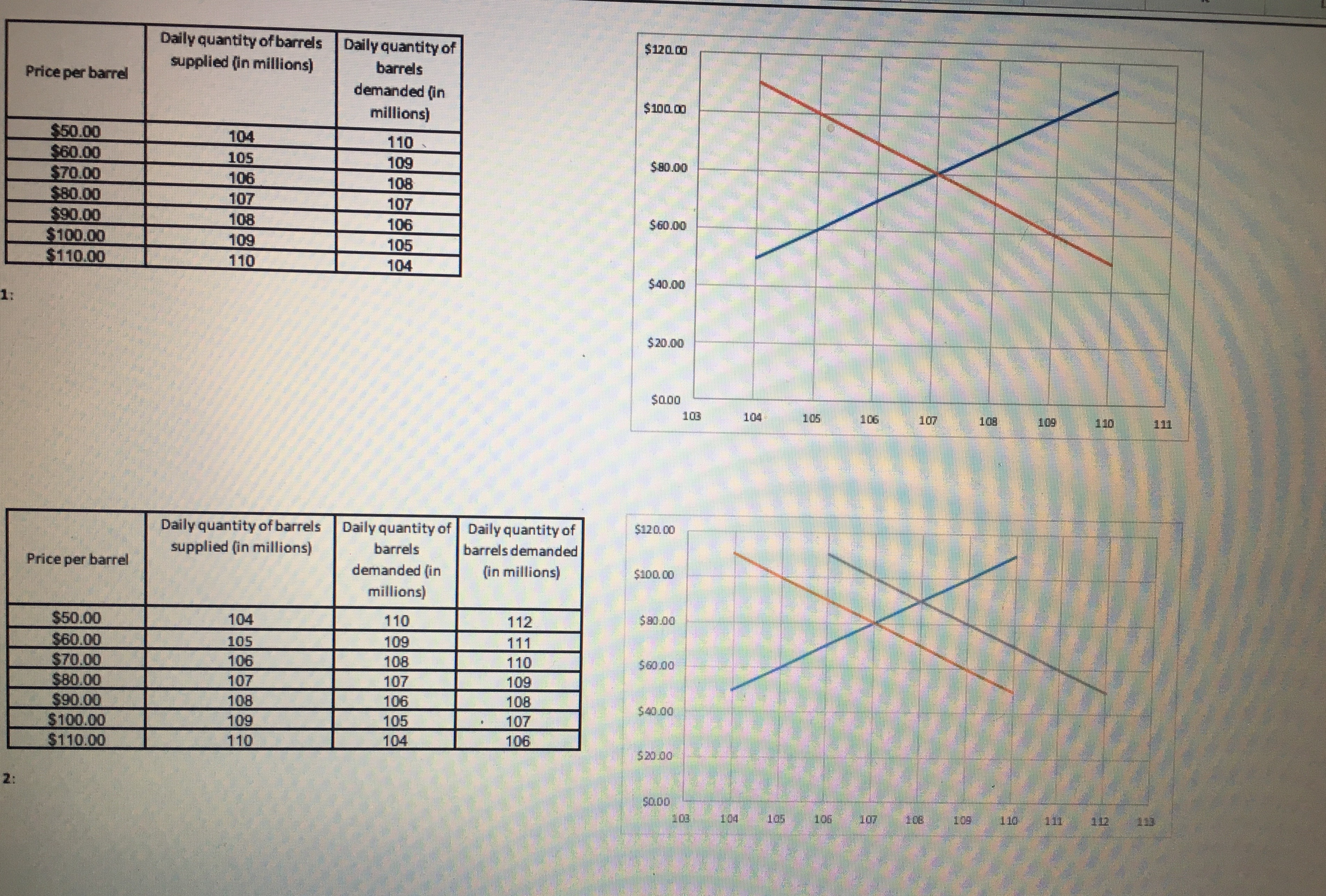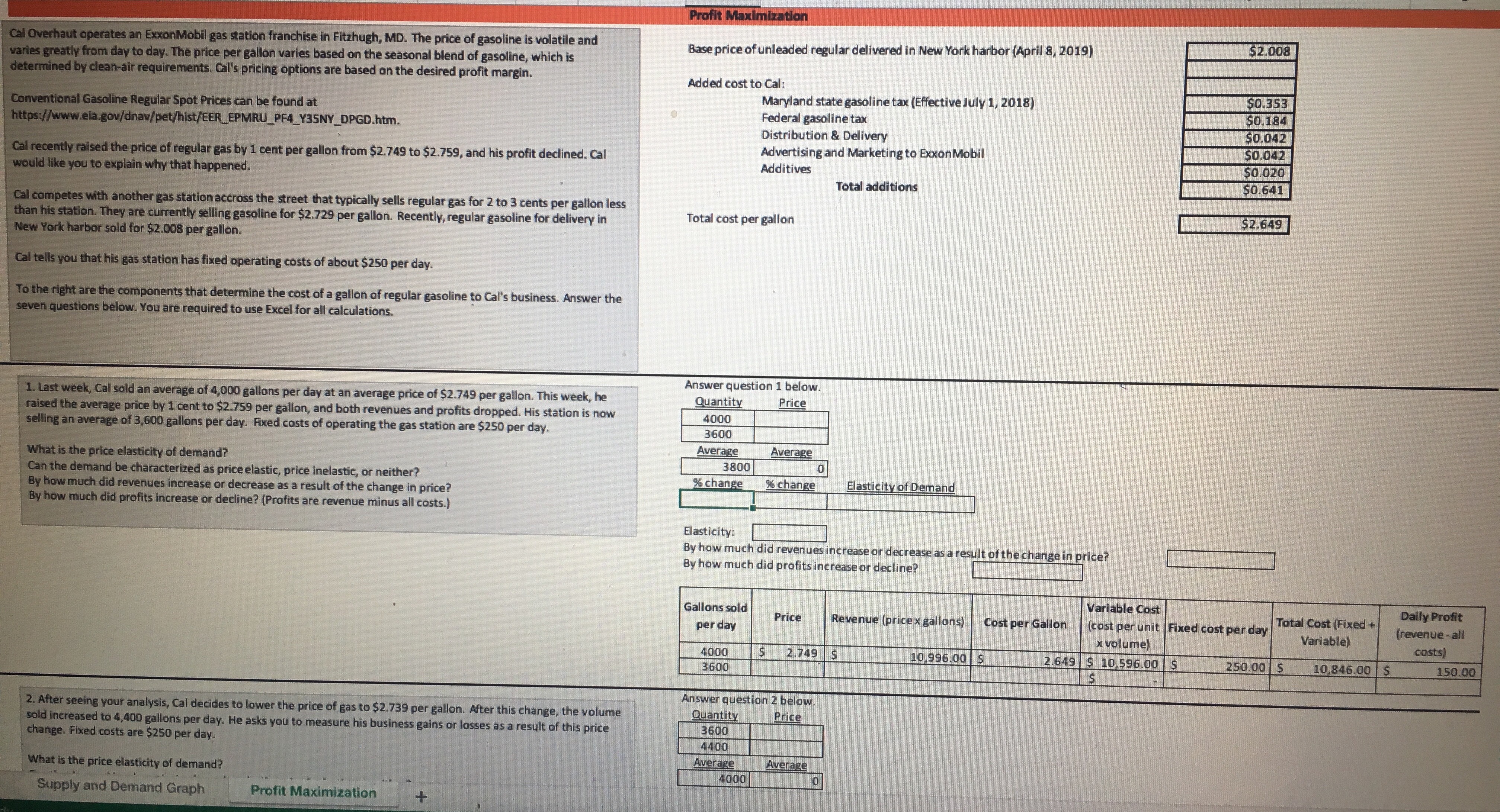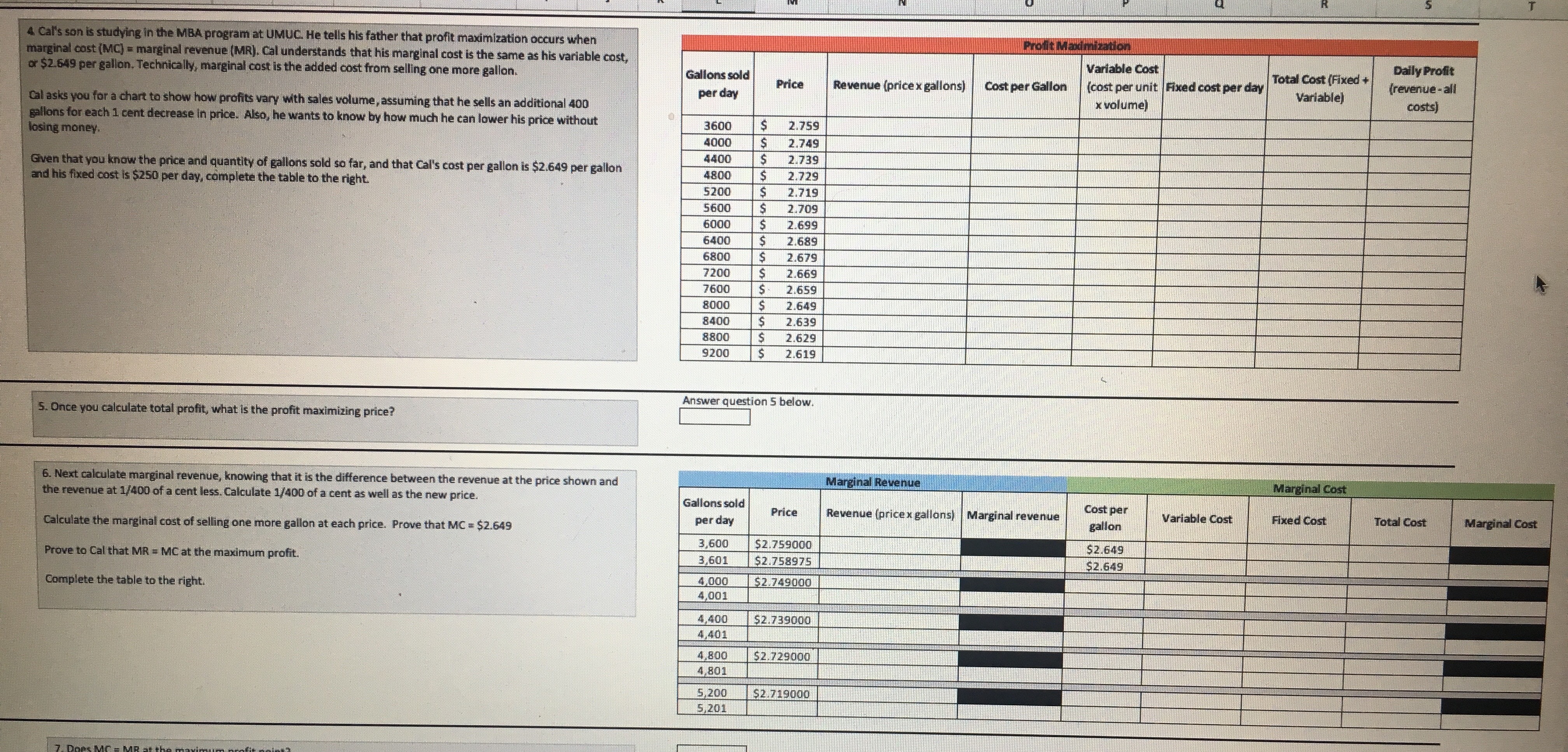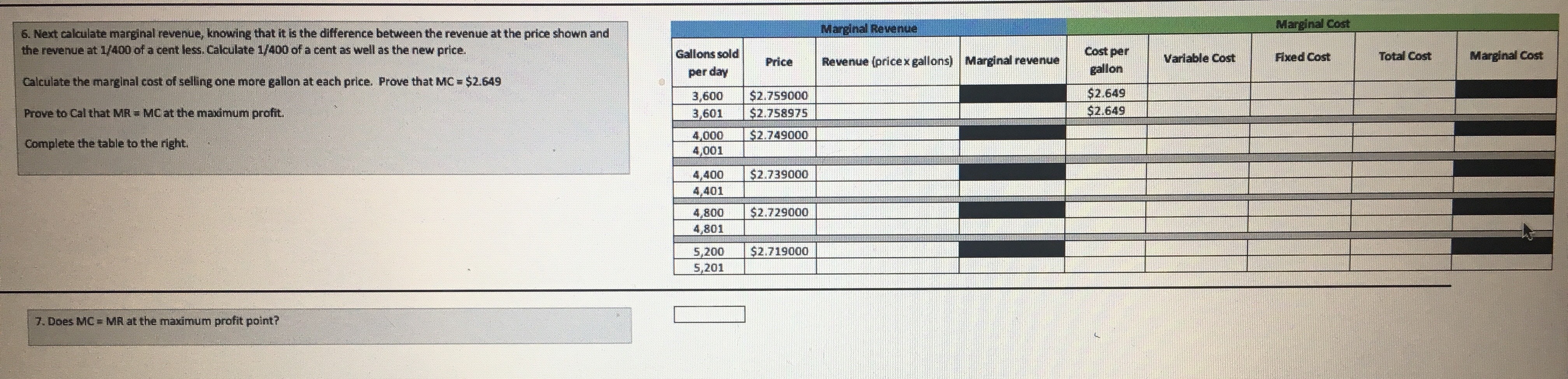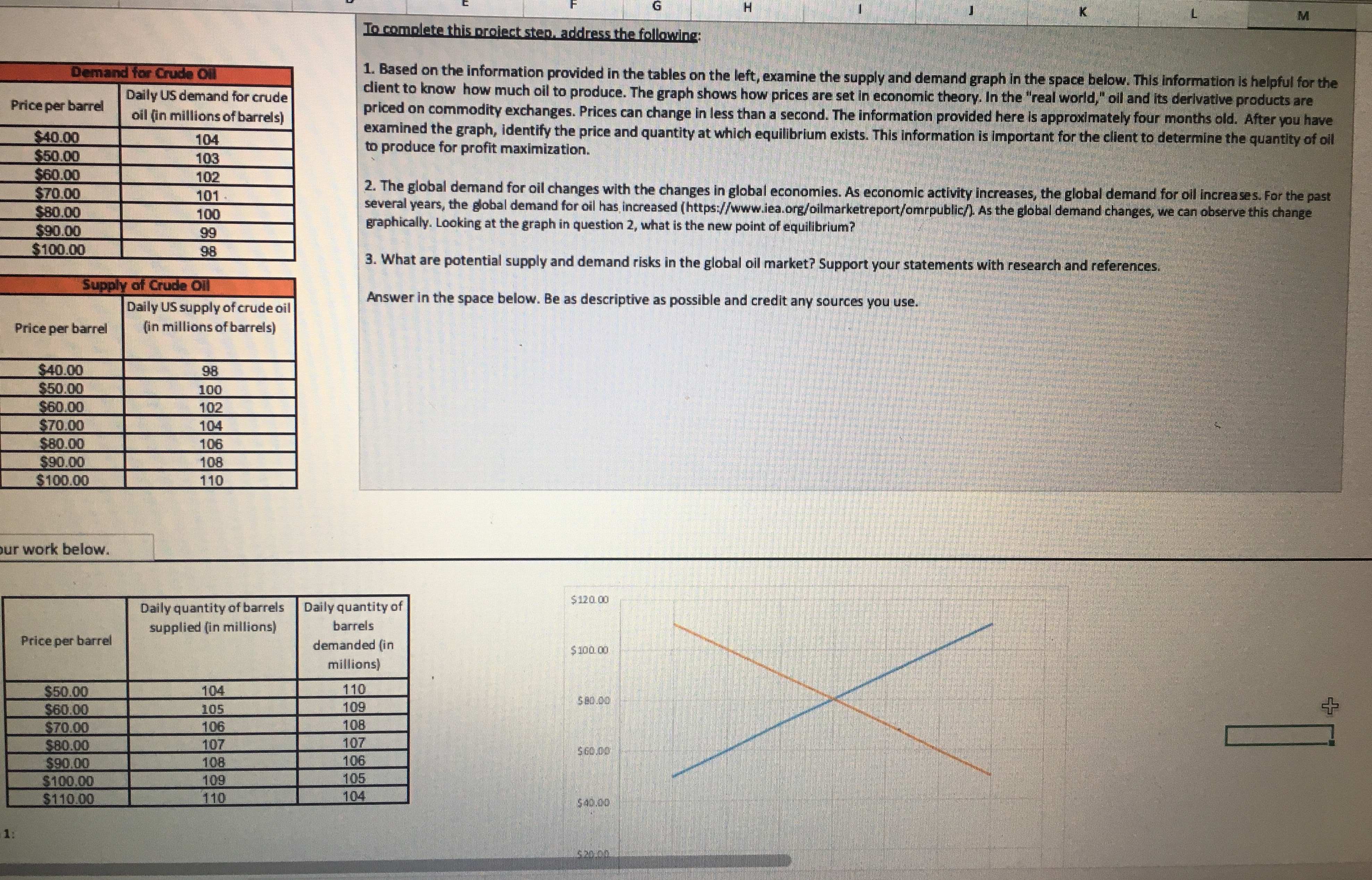
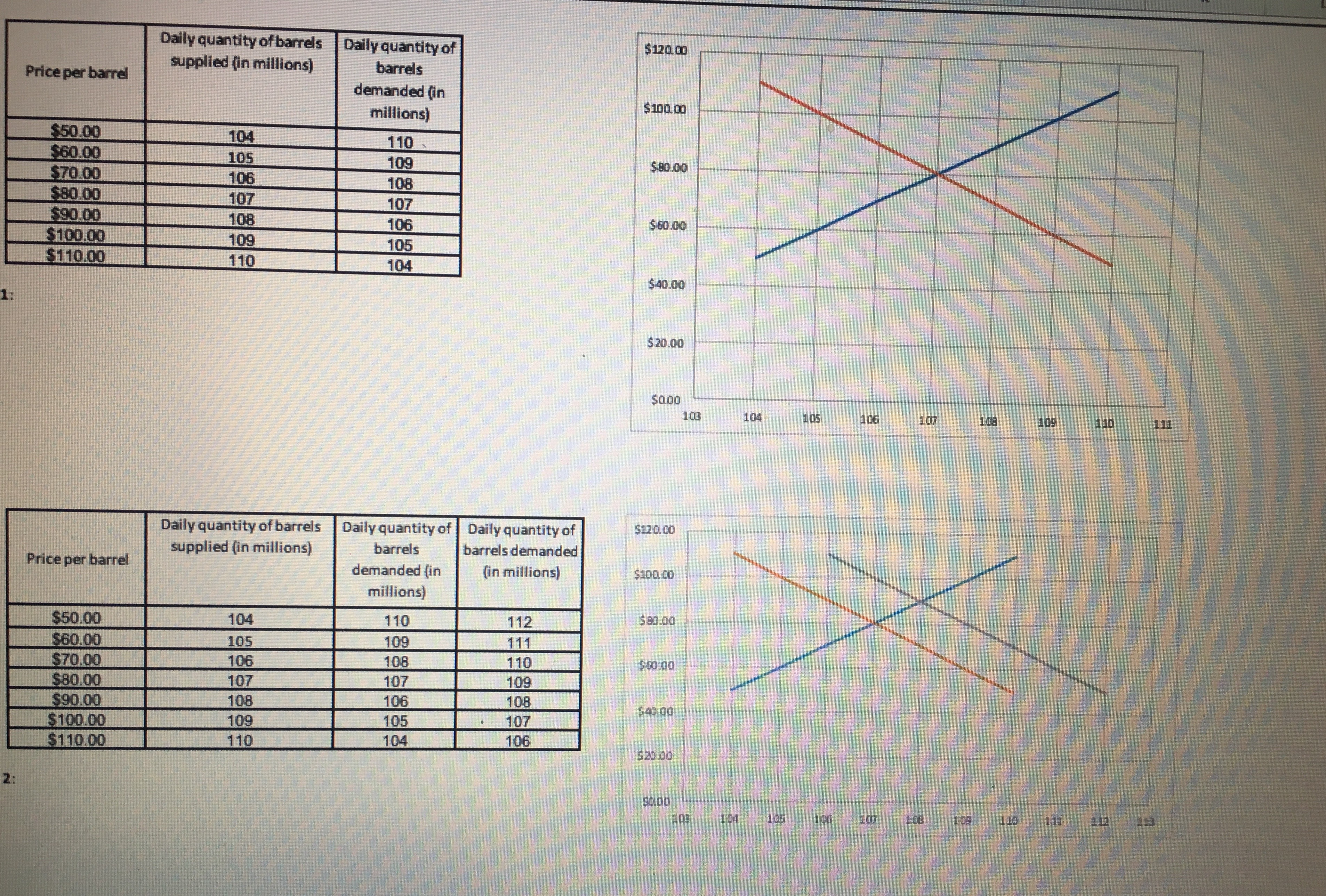
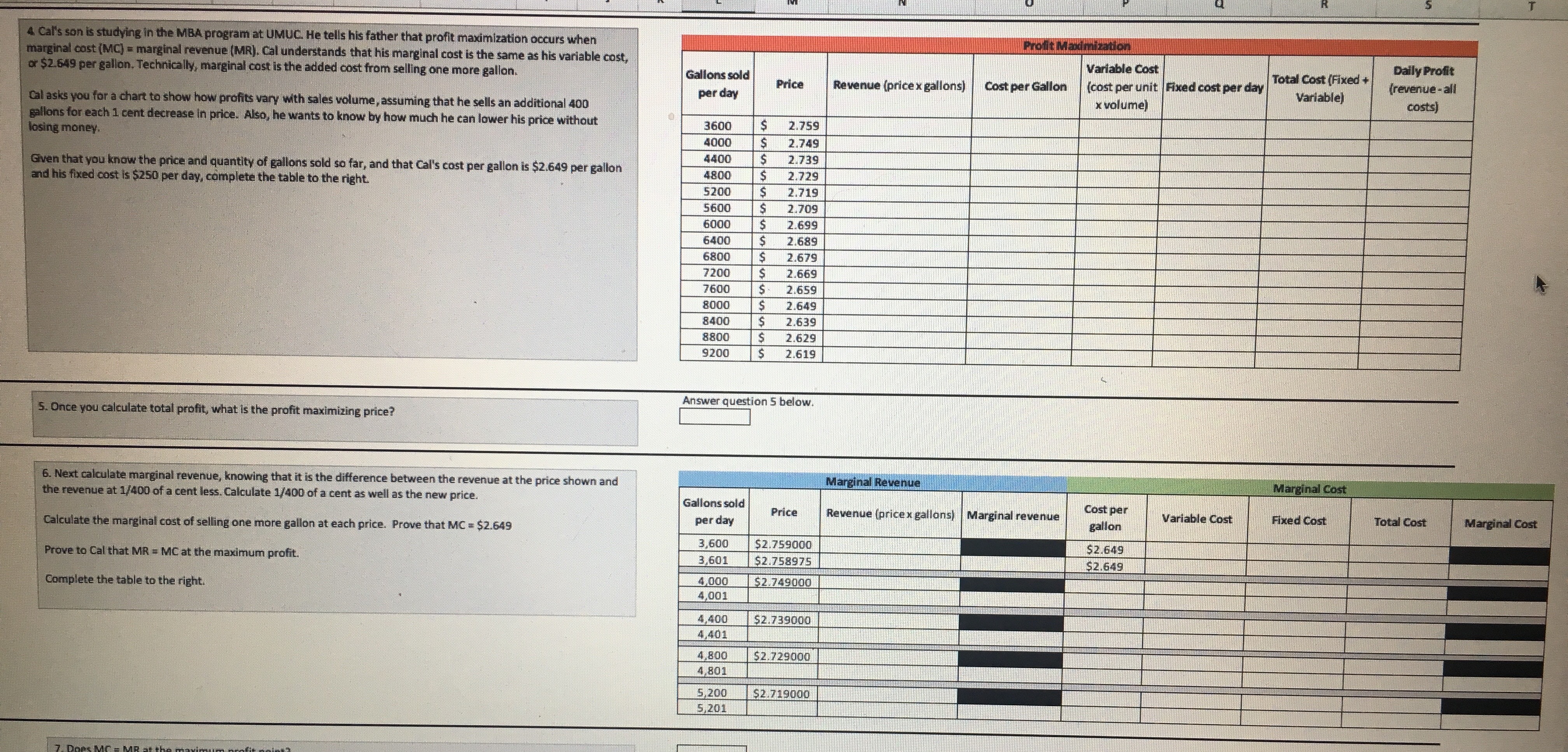
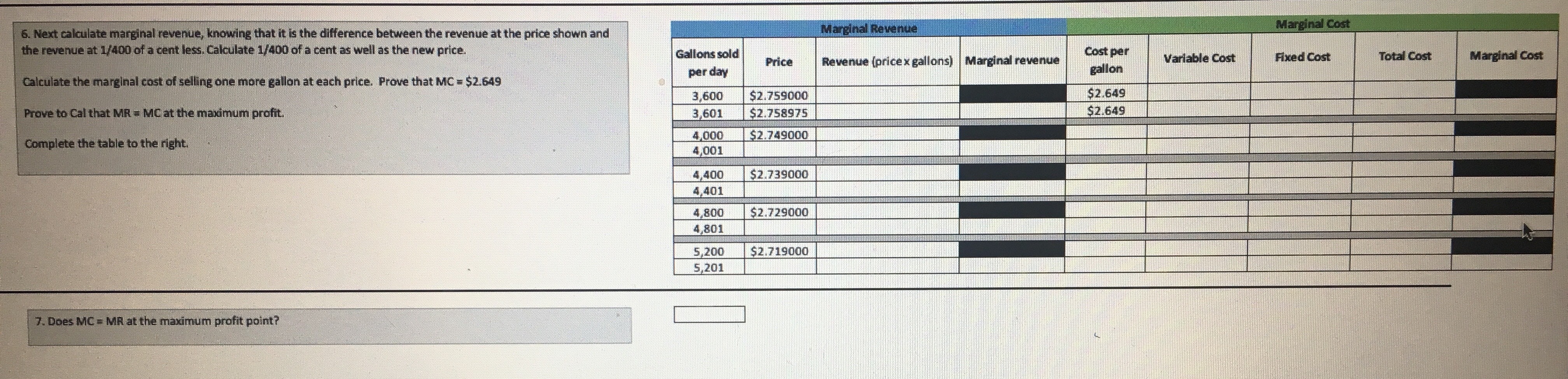
To complete this project step. address the following: M Demand for Crude Oil Price per barrel Daily US demand for crude 1. Based on the information provided in the tables on the left, examine the supply and demand graph in the space below. This information is helpful for the client to know how much oil to produce. The graph shows how prices are set in economic theory. In the "real world," oil and its derivative products are oil (in millions of barrels) priced on commodity exchanges. Prices can change in less than a second. The information provided here is approximately four months old. After you have $40.00 104 $50.00 examined the graph, identify the price and quantity at which equilibrium exists. This information is important for the client to determine the quantity of oil 103 to produce for profit maximization. $60.00 102 $70.00 101 $80.00 2. The global demand for oil changes with the changes in global economies. As economic activity increases, the global demand for oil increases. For the past 100 several years, the global demand for oil has increased (https://www.iea.org/oilmarketreport/omrpublic/). As the global demand changes, we can observe this change $90.00 99 graphically. Looking at the graph in question 2, what is the new point of equilibrium? $100.00 98 3. What are potential supply and demand risks in the global oil market? Support your statements with research and references. Supply of Crude Oil Daily US supply of crude oil Answer in the space below. Be as descriptive as possible and credit any sources you use. Price per barrel (in millions of barrels) $40.00 98 $50.00 100 $60.00 102 $70.00 104 $80.00 106 $90.00 108 $100.00 110 ur work below. Daily quantity of barrels Daily quantity of $120. 00 Price per barrel supplied (in millions) barrels demanded (in millions) $ 100. 00 $50.00 104 110 $60.00 105 109 $ 80.00 $70.00 106 108 $80.00 107 107 $90.00 108 106 60.00 $100.00 109 105 $110.00 110 104Daily quantity of barrels supplied (in millions) Daily quantity of $120.00 Price per barrel barrels demanded (in millions) $100.00 $50.00 104 $60.00 110 $70.00 105 109 $80.00 $80.00 106 108 $90.00 107 107 $100.00 108 $60.00 $110.00 109 106 105 110 104 $40.00 $ 20.00 103 104 109 110 111 Daily quantity of barrels Daily quantity of Daily quantity of $120. 00 Price per barrel supplied (in millions) barrels barrels demanded demanded (in (in millions) $100.00 millions) $50.00 104 110 112 $ 80.00 $60.00 105 109 $70.00 111 106 108 110 $80.00 $60.00 107 107 109 $90.00 108 106 108 $100.00 109 105 107 $40.00 $110.00 110 104 106 $ 20.00 SO.DOProfit Maximization Cal Overhaut operates an ExxonMobil gas station franchise in Fitzhugh, MD. The price of gasoline is volatile and $2.008 varies greatly from day to day. The price per gallon varies based on the seasonal blend of gasoline, which is Base price of unleaded regular delivered in New York harbor (April 8, 2019) determined by clean-air requirements. Cal's pricing options are based on the desired profit margin. Added cost to Cal: $0.353 Conventional Gasoline Regular Spot Prices can be found at Maryland state gasoline tax (Effective July 1, 2018) Federal gasoline tax $0.184 https://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/EER_EPMRU_PF4_Y35NY_DPGD.htm. Distribution & Delivery $0.042 Cal recently raised the price of regular gas by 1 cent per gallon from $2.749 to $2.759, and his profit declined. Cal Advertising and Marketing to Exxon Mobil $0.042 would like you to explain why that happened. Additives $0.020 Total additions $0.641 Cal competes with another gas station accross the street that typically sells regular gas for 2 to 3 cents per gallon less than his station. They are currently selling gasoline for $2.729 per gallon. Recently, regular gasoline for delivery in Total cost per gallon $2.649 New York harbor sold for $2.008 per gallon. Cal tells you that his gas station has fixed operating costs of about $250 per day. To the right are the components that determine the cost of a gallon of regular gasoline to Cal's business. Answer the seven questions below. You are required to use Excel for all calculations. Answer question 1 below. 1. Last week, Cal sold an average of 4,000 gallons per day at an average price of $2.749 per gallon. This week, he Quantity Price raised the average price by 1 cent to $2.759 per gallon, and both revenues and profits dropped. His station is now 4000 selling an average of 3,600 gallons per day. Fixed costs of operating the gas station are $250 per day. 3600 What is the price elasticity of demand? Average Average Can the demand be characterized as price elastic, price inelastic, or neither? 3800 0 By how much did revenues increase or decrease as a result of the change in price? % change % change Elasticity of Demand By how much did profits increase or decline? (Profits are revenue minus all costs.) Elasticity: By how much did revenues increase or decrease as a result of the change in price? By how much did profits increase or decline? Gallons sold Variable Cost Daily Profit per day Price Revenue (price x gallons) Cost per Gallon [cost per unit |Fixed cost per day Total Cost (Fixed + Variable) [revenue - all x volume) costs 1000 2.749 5 10.996.00 5 2.649 5 10.596.00 $ 3600 250.00 5 10.846.00 | $ 150.00 Answer question 2 below. 2. After seeing your analysis, Cal decides to lower the price of gas to $2.739 per gallon. After this change, the volume Price sold increased to 4,400 gallons per day. He asks you to measure his business gains or losses as a result of this price Quantity 3600 change. Fixed costs are $250 per day. 4400 What is the price elasticity of demand? Average Average 4000 Supply and Demand Graph Profit Maximization4 Cal's son is studying in the MBA program at UMUC. He tells his father that profit maximization occurs when Profit Maximization marginal cost (MC) = marginal revenue [MR). Cal understands that his marginal cost is the same as his variable cost, or $2.649 per gallon. Technically, marginal cost is the added cost from selling one more gallon. Gallons sold Variable Cost Daily Profit per day Price Revenue (price x gallons) Cost per Gallon (cost per unit| Fixed cost per day Total Cost (Fixed + (revenue - all Cal asks you for a chart to show how profits vary with sales volume, assuming that he sells an additional 400 x volume) Variable) costs) losing money. gallons for each 1 cent decrease in price. Also, he wants to know by how much he can lower his price without 3600 $ 2.759 4000 2.749 Given that you know the price and quantity of gallons sold so far, and that Cal's cost per gallon is $2.649 per gallon 4400 2.739 and his fixed cost is $250 per day, complete the table to the right. 4800 2.729 5200 2.719 5600 2.709 6000 2.699 6400 2.689 6800 2.679 7200 2.669 7600 2.659 8000 2.649 8400 2.639 8800 2.629 9200 2.619 5. Once you calculate total profit, what is the profit maximizing price? Answer question 5 below. 6. Next calculate marginal revenue, knowing that it is the difference between the revenue at the price shown and Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost the revenue at 1/400 of a cent less. Calculate 1/400 of a cent as well as the new price. Gallons sold Price Revenue (price x gallons) | Marginal revenue Cost per Calculate the marginal cost of selling one more gallon at each price. Prove that MC = $2.649 per day gallon Variable Cost Fixed Cost Total Cost Marginal Cost 3,600 $2.759000 Prove to Cal that MR = MC at the maximum profit. $2.649 3,601 $2.758975 $2.649 Complete the table to the right. 1000 $2.749000 4,001 4,400 $2.739000 4,401 4,800 $2.729000 4,801 5,200 $2.719000 5,2016. Next calculate marginal revenue, knowing that it is the difference between the revenue at the price shown and Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost the revenue at 1/400 of a cent less. Calculate 1/400 of a cent as well as the new price. Gallons sold per day Price Revenue (price x gallons) | Marginal revenue Cost per gallon Variable Cost Fixed Cost Total Cost Marginal Cost Calculate the marginal cost of selling one more gallon at each price. Prove that MC = $2.649 3,600 $2.759000 Prove to Cal that MR = MC at the maximum profit. $2.649 3,601 $2.758975 $2.649 Complete the table to the right. 4,000 $2.749000 4,001 4,400 $2.739000 4,401 4,800 $2.729000 4,801 5,200 $2.719000 5,201 7. Does MC = MR at the maximum profit point