Question
To cyclically permute the values we can just repeat multiple times this process of enqueueing the value at the head and then dequeueing. When we
To cyclically permute the values we can just repeat multiple times this process of enqueueing the value at the head and then dequeueing. When we are finished with this process we then just copy (and overwrite) the values stored in the queue to our original vector and return this vector.
Task 2: Complete the following function template:
function PermuteVector(row, p) if p = 0 then return row end if new Queue q ... end function
This function should take a four-element vector called row as an input parameter and return that vector but with its values cyclically permuted by p elements to the left: p should be a number between 0 and 3 (inclusive). To be able to get full marks you need to use the queue abstract data structure appropriately as outlined above.
ANSWER SHOULD BE IN PSEUDOCODE ONLY. NO EXTRA CODING IS NEEDED. (ONLY PSEUDOCODE PLEASE)
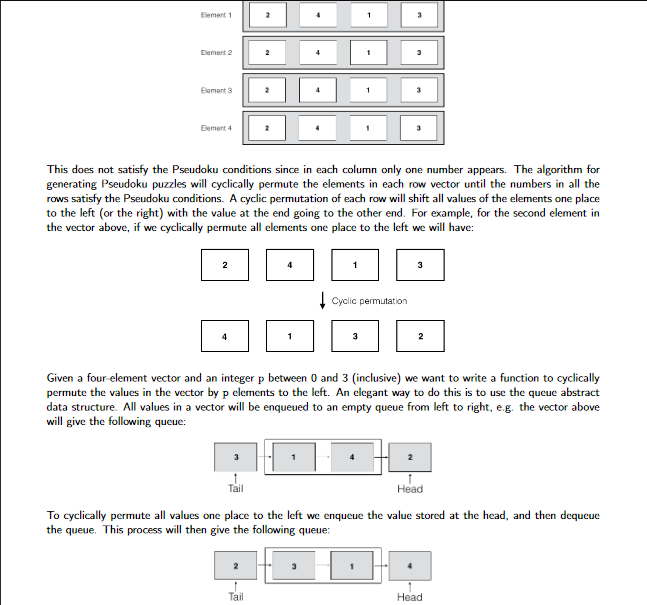
Element1 2 2 Element 2 Element 3 Element 4 This does not satisfy the Pseudoku conditions since in each column only one number appears. The algorithm for generating Pseudoku puzzles will cyclically permute the elements in each row vector until the numbers in all the rows satisfy the Pseudoku conditions. A cyclic permutation of each row will shift all values of the elements one place to the left (or the right) with the value at the end going to the other end. For example, for the second element in the vector above, if we cyclically permute all elements one place to the left we will have: 2 3 Cyclic permutation 3 2 Given a four-element vector and an integer p between 0 and 3 (inclusive) we want to write a function to cyclically permute the values in the vector by p elements to the left. An elegant way to do this is to use the queue abstract data structure. All values in a vector will be enqueued to an empty queue from left to right, eg the vector above will give the following queue: 3 Tail Head To cyclically permute all values one place to the left we enqueue the value stored at the head, and then dequeue the queue. This process will then give the following queue: Tail HeadStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


