Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
To determine the acceleration of a ball due to gravity, that has been dropped from a window. Givens: Windowsills are 3.15 m apart from

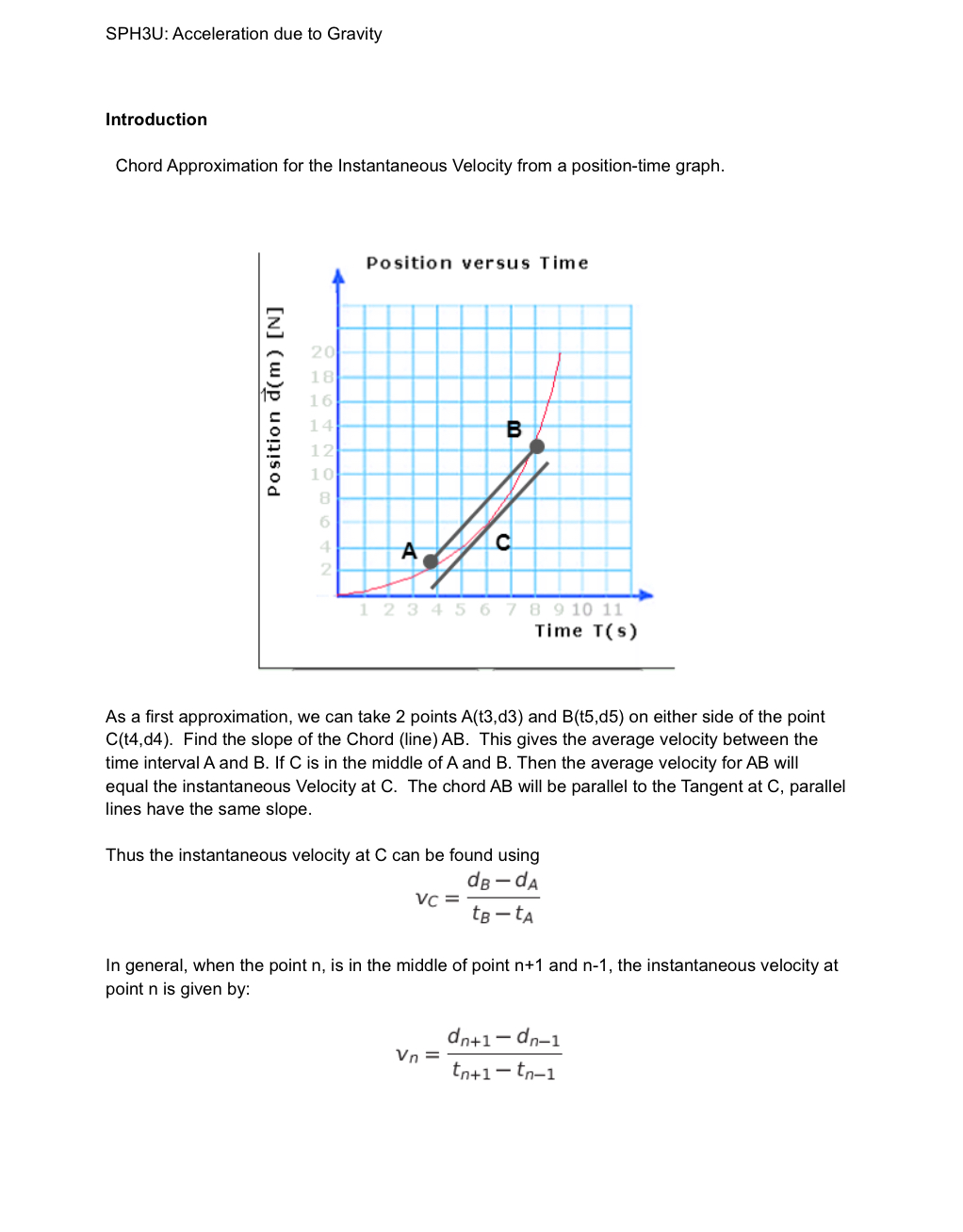

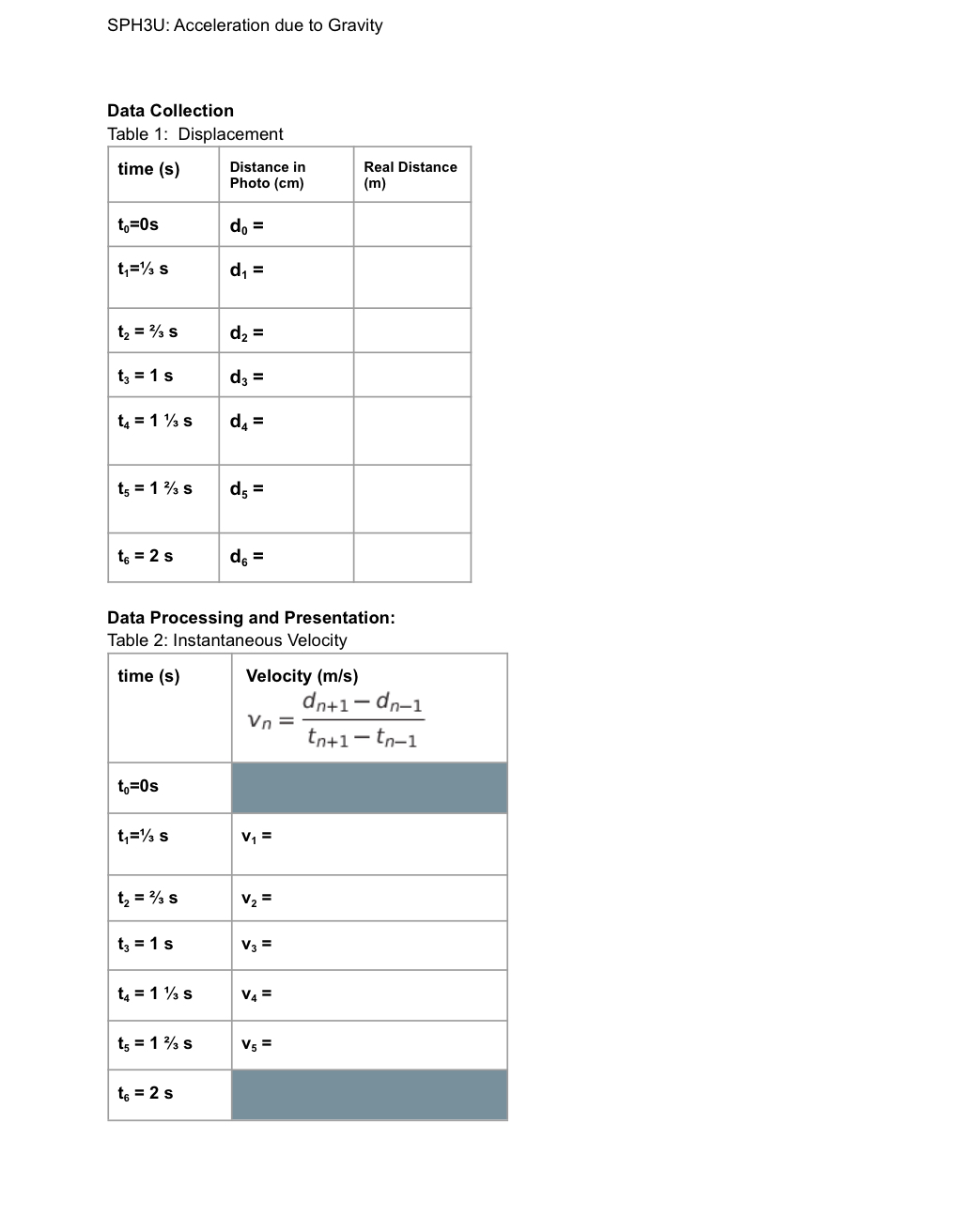

To determine the acceleration of a ball due to gravity, that has been dropped from a window. Givens: Windowsills are 3.15 m apart from each other, 3 photographs were taken in 1 second and a two-second stroboscopic photo of a ball dropping is provided below. AN SPH3U: Acceleration due to Gravity Introduction Chord Approximation for the Instantaneous Velocity from a position-time graph. Position d(m) [N] 20 Position versus Time 18 16 14 B 12 10 8 6 4 A C 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Time T(s) As a first approximation, we can take 2 points A(t3,d3) and B(t5,d5) on either side of the point C(t4,d4). Find the slope of the Chord (line) AB. This gives the average velocity between the time interval A and B. If C is in the middle of A and B. Then the average velocity for AB will equal the instantaneous Velocity at C. The chord AB will be parallel to the Tangent at C, parallel lines have the same slope. Thus the instantaneous velocity at C can be found using VC de-dA te-ta In general, when the point n, is in the middle of point n+1 and n-1, the instantaneous velocity at point n is given by: dn+1-dn-1 Vn= tn+1-to-1 SPH3U: Acceleration due to Gravity Procedure 1. Examine the strobe photo provided. 2. Measure and record the distances (in centimeters) of each falling ball position from the original starting position in Data Table 1. 3. Measure the distance between two adjacent window sills in centimeters. Using the given distance between the window cells. Determine the scale for the strobe photo. 1 cm is the equivalent distance of meters. 4. Calculate the real distance of the balls using your scale, enter the calculated values in your data table 5. Graph the ball's displacement versus time. 6. Using the Chord Method and your displacement-time graph complete the Data Table for Instantaneous velocities. 7. Construct a second graph of these instantaneous velocities. 8. Determine the acceleration due to gravity of the ball. SPH3U: Acceleration due to Gravity Data Collection Table 1: Displacement time (s) Distance in Photo (cm) to-Os d = t = 13 S d = t = 23 S d = t=15 d = t = 1 s d = t=1% s d5 = t6 = 2 s d = Real Distance (m) Data Processing and Presentation: Table 2: Instantaneous Velocity time (s) Velocity (m/s) dn+1-dn-1 Vn tn+1-to-1 to=0s t=%s V = t=%s V = t3 = 1 s V3 = t = 113 S V4= ts=1% s V5= t6 = 2 s SPH3U: Acceleration due to Gravity SPH3U: Acceleration due to Gravity Error Analysis: The accepted value for the acceleration due to gravity near the Earth's Surface is 9.8 m/s [Down]. Calculate the % error for your acceleration due to gravity. %error = Experimental-Accepted Accepted x100 Conclusion: Interpretation: Answer the question, "What is the relationship between my results and theory?" Evaluation: There are potential systematic errors in every experiment. These are errors, which determine the accuracy of your result, and cannot be reduced by repeating your measurements..You must carefully assess the apparatus and measurement technique, and decide if there are any factors present which could bias your result. Random errors, on the other hand, determine the precision of the experiment. Discuss how these errors affect your result and assess whether they are a result of experimental technique or a function of the equipment. Note: "Human error" is not an acceptable reason: if you made a mistake you should correct it. Improvements: If you were to repeat this experiment what could you have done differently to improve your findings? What changes could/should be made to improve the procedure, results, and/or apparatus?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


