Question
To prepare for this case, you should watch Getting Started with Calculations and Calculation Syntax videos listed under Calculations. Future cases will build off of
To prepare for this case, you should watch "Getting Started with Calculations" and "Calculation Syntax" videos listed under "Calculations." Future cases will build off of your knowledge gained from these videos, and additional videos will be suggested. All of Tableaus short training videos can be found here.
In the Chapter 1 and Chapter 2 Applying Tableaus, you compared two (hypothetical) companies: Discount Goods and Big Store. In this case, you continue in your role as an analyst conducting research into the relative merits of investing in one or both of these companies. In this case, you will assess the companies liquidity: i.e., their ability to pay short-term debts as they come due. You should do so by comparing liquidity ratios via the creation of a line chart in Tableau.
Tableau Instructions:
For this case, you will use Tableau to create several calculations and produce a line chart of liquidity ratios which allows you to compare and contrast the two companies. You will need to know how to tell Tableau to change data from continuous to discrete. Continuous data are identified as a range of numeric values, and a bar chart uses continuous data. Measure Names are usually identified by Tableau as continuous data and produce a range of data when dragged to the row shelf. If you want only one number, you must change the data to be discrete data. The pill that represents the data on the shelves in Tableau will be blue if it is set to discrete and green if it is set to continuous.
After you view the training videos, use the following steps to create the charts you will need for the case:
Download the Excel file Discount_Goods_Big_Store_Financials.
Open Tableau and connect to the Excel file.
To begin creating your first visualization, click on the "Sheet 1" tab at the bottom of the canvas. Drag "Company" and Year from the Data tab to the Columns shelf.
If the "Year" pill is green, Tableau has identified it as continuous data. Select the drop-down menu box on the "Year" pill and click "Discrete" instead of "Continuous." Note the pill changes to blue.
Drag "Total current assets" under Measure Names to the Rows shelf. Change it to "Discrete." Note: You must drag accounts into the Rows shelf if you are going to use them in calculated fields and need an aggregated sum. If this is not done first, your answer will not match the solutions.
Drag "Total current liabilities" to the Rows shelf. If necessary, change it to Discrete.
Create a calculated field by clicking the "Analysis" tab from the Toolbar at the top and selecting "Create Calculated field." A calculation box will open up. Name the calculation "Quick Assets." Drag "Cash and cash equivalents" under Measure Names into the calculation box (this is the blank area below the title). Add a plus sign and drag "Receivables, net" into the calculation box. Make sure the box says that the calculation is valid and click OK. The new field "Quick Assets" will now appear under Measure Names.
Create another calculated field named "Current Ratio" by dragging "Total current assets" into the calculation box, typing a division sign, then dragging "Total current liabilities" beside it. Make sure the box says that the calculation is valid and click OK. The new field "Current Ratio" will now appear under Measure Names. Drag "Current Ratio" to the Rows shelf. Click on the dropdown from the "Current Ratio" pill, click Format", and set the following formatting options: Font = Bold and Black, Numbers = Number(custom) "3" decimal places.
Create a calculated field "Quick Ratio" following the same process. Drag the newly created "Quick Assets" under Measure Names into the calculation box. Type a division sign, then drag Total current liabilities" under Measure Names beside it. Make sure the box says that the calculation is valid and click OK. Drag "Quick Ratio" to the Rows shelf. Click on the dropdown from the "Quick Ratio" pill and set the Formats as noted above.
Drag "Sum: Total current assets" and "Sum: Total current liabilities" from the Rows shelf back under Measure Names. This will remove them from the canvas.
In the Marks card select the drop-down menu for presentation type and select Line (it defaults to Automatic). In the Label box, select Show mark labels.
Right click on Sheet 1 at the bottom of the canvas. Rename it to "Liquidity.
Save your work.
Required:
Based on the visualization you created, answer the following questions:
Analyzing the liquidity ratios over the ten-year period, is Discount Goods current ratio (a) generally increasing, (b) roughly the same, or (c) generally decreasing from year to year?
Analyzing the liquidity ratios over the ten-year period, is Big Stores current ratio (a) generally increasing, (b) roughly the same, or (c) generally decreasing from year to year?
What is the current ratio in 2021 for Discount Goods? For Big Store?
Note: Round your answers to 3 decimal places.
What is the acid-test (or quick) ratio in 2021 for Discount Goods? For Big Store?
Note: Round your answers to 3 decimal places.)
Which company has more favorable liquidity ratios in 2021?
Note: As you assess the liquidity aspect of the companies, keep in mind that liquidity ratios should be evaluated in the context of both profitability and efficiency of managing assets.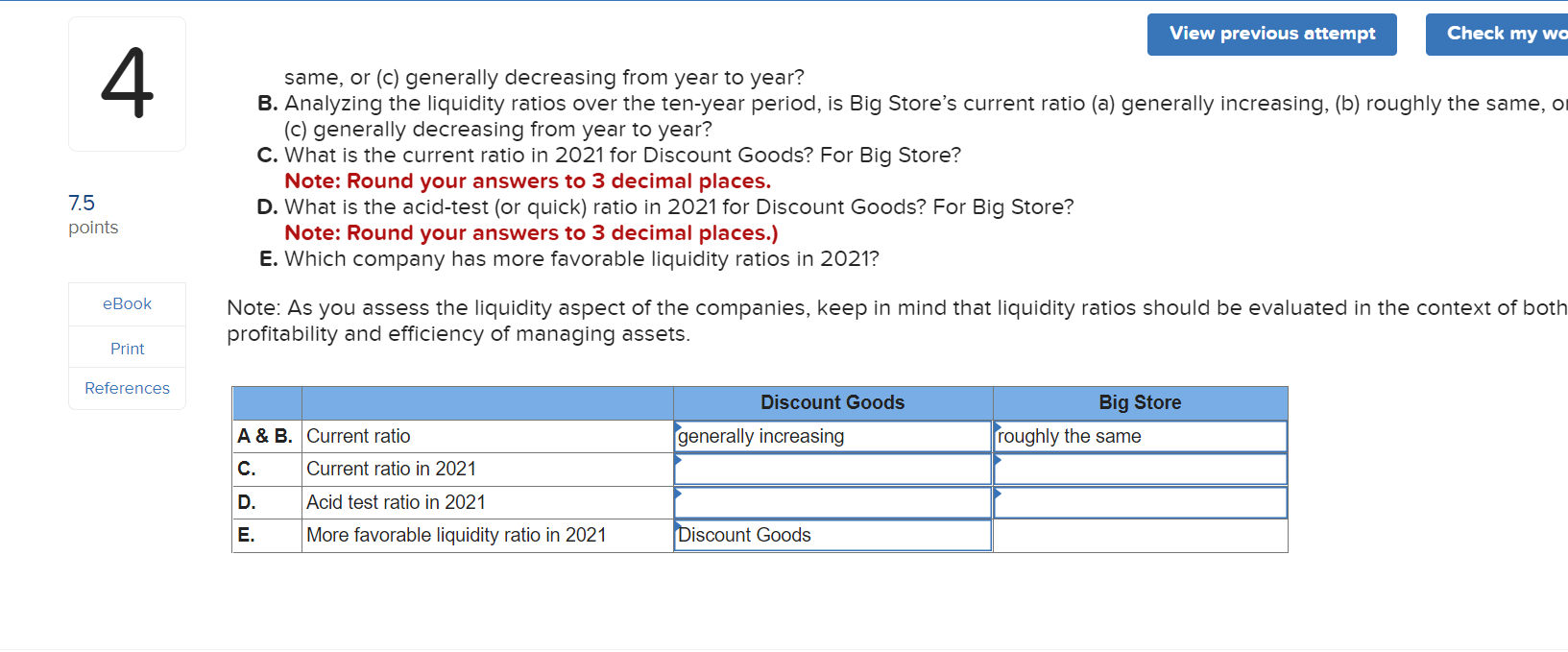
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


