Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Topic 1 Introduction to Operations Management What is Operations Management? Operations management (OM) is concerned with managing the resources that directly produce the organization's
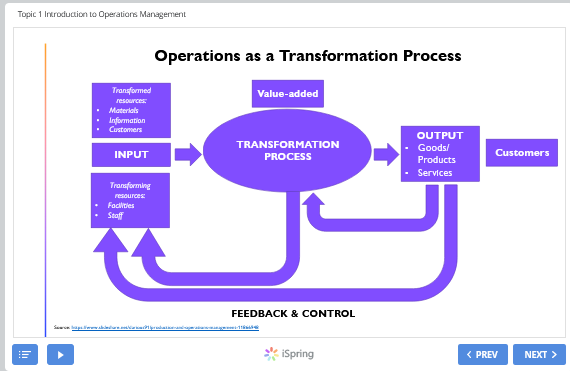




Topic 1 Introduction to Operations Management What is Operations Management? Operations management (OM) is concerned with managing the resources that directly produce the organization's service or product. The resources will usually consist of people, materials, technology and information but may go wider than this. These resources are brought together by a series of processes so that they are utilized to deliver the primary service or product of the organization. Thus, operations is concerned with managing inputs (resources) through transformation processes to deliver outputs (service or products). ze iSpring < PREV NEXT > Topic 1 Introduction to Operations Management Transformed resources: Materials Information Customers Operations as a Transformation Process Value-added OUTPUT INPUT TRANSFORMATION PROCESS Goods/ Products Services Customers Transforming resources: Facilities Staff FEEDBACK & CONTROL 2 iSpring < PREV NEXT > Topic 1 Introduction to Operations Management Operations as a Transformation Function Inputs can come in conventional forms as direct labor, direct materials, and other direct costs. Inputs can also be capital items that are not consumed in the operation. The idea of capital as cash wealth invested for a specific purpose (such as technology, equipment, and land) has broadened to include human capital (labor), intellectual capital (knowledge), and social capital (reputation, brand equity, customer loyalty, and so on). Topic 1 Introduction to Operations Management Inputs to the process One set of inputs to any operation's processes are transformed resources. These are the resources that are treated, transformed or converted in the process. They are usually a mixture of the following: Materials - operations which process materials could do so to transform their physical properties (shape or composition, for example). Most manufacturing operations are like this. Other operations process materials to change their location (parcel delivery companies, for example). Some, like retail operations, do so to change the possession of the materials. Finally, some operations store materials, such as warehouses. Information - operations which process information could do so to transform their informational properties (that is, the purpose or form of the information); accountants do this. Some change the possession of the information, for example market research companies sell information. Some store the information, for example archives and libraries. Finally, some operations, such as telecommunication companies, change the location of the information. Customers - operations which process customers might change their physical properties in a similar way to materials processors, for example hairdressers or cosmetic surgeons. Some store (or more politely accommodate) customers: hotels, for example. Airlines, mass rapid transport systems and bus companies transform the location of their customers, while hospitals transform their physiological state. Some are concerned with transforming their psychological state, for example most entertainment services such as music, theatre, television, radio and theme parks. Topic 1 Introduction to Operations Management Operations processes have different characteristics Although all operations are similar in that they all transform input resources into output products and services, they do differ in a number of ways, four of which are particularly important: 1. the volume of their output; 2. the variety of their output; 3. the variation in the demand for their output; 4. the degree of visibility which customers have of the production of the product or service. Operations management (OM) is the business function that plans, organizes, coordinates, and controls the resources needed to produce a company's goods and services. Operations management is a management function. It involves managing people, equipment, technology, information, and many other resources. Operations management is the central core function of every company. This is true whether the company is large or small, provides a physical good or a service, is for-profit or not-for-profit.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


