
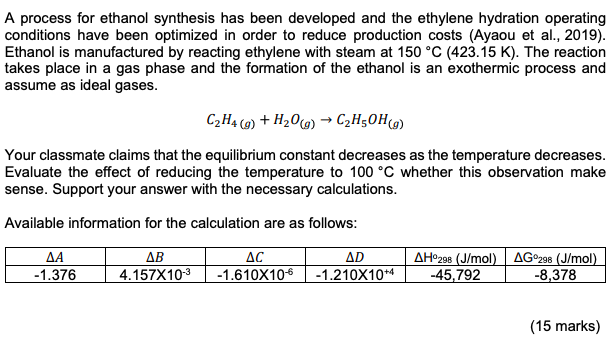
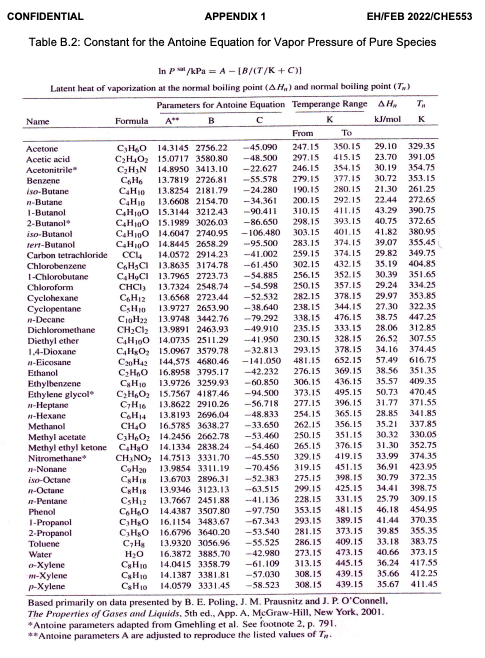

Topic: Vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE), Solution Thermodynamics & Chemical Reaction Equilibria A process for ethanol synthesis has been developed and the ethylene hydration operating conditions have been optimized in order to reduce production costs (Ayaou et al., 2019). Ethanol is manufactured by reacting ethylene with steam at 150 C (423.15 K). The reaction takes place in a gas phase and the formation of the ethanol is an exothermic process and assume as ideal gases. C2H4 (g) +H206) C2H50Hg) Your classmate claims that the equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature decreases. Evaluate the effect of reducing the temperature to 100 C whether this observation make sense. Support your answer with the necessary calculations. Available information for the calculation are as follows: -1.376 AB 4.157X10-3 AC -1.610X106 AD -1.210X104 AH298 (J/mol) AG298 (J/mol) -45,792 -8,378 (15 marks) A CONFIDENTIAL APPENDIX 1 EH/FEB 2022/CHE553 Table B.2: Constant for the Antoine Equation for Vapor Pressure of Pure Species In p/kPa = A - (B/CT/K+C) Latent heat of vaporization at the normal boiling point (AH.) and normal boiling point (T.) Parameters for Antoine Equation Temperange Range AHA T. Name Formula B kJ/mol K From Acetone CHO 14.3145 2756.22 -45.090 247.15 350.15 29.10 329.35 Acetic acid C2H4O15.0717 3580.80 -48.500 297.15 415.15 23.70 391.05 Acetonitrile CHIN 14,890 343.10 -22.627 246.15 354.15 30.19 354.75 Benzene CHE 13.7819 2726.81 -55.578 279.15 377.15 30.72 353.15 iso-Butane C4H10 13.8254 2181.79 -24.280 190.15 280.15 21.30 261.25 n-Butane 13.6608 2154.70 - 34.361 200.15 292.15 22.44 272.65 1-Butanol C4H100 15.3144 3212.43 90.411 310.15 411.15 43.29 390.75 2-Butanol C4H10O 15.1989 3026.03 -86.650 298.15 393.15 40.75 372.65 iso-Butanol C4H10O 14.6047 2740.95 -106.480 303.15 40115 41.82 380.95 Terr-Butanol CHO 14,8445 658 59 95.500 283.15 374.15 39.07 355.45 Carbon tetrachloride CCL 14.0572 2914.23 -41.002 259.15 374.15 29.82 349.75 Chlorobenzene CHCI 13.8635 3174.78 -61.450 302.15 432.15 35.19 404.85 1-Chlorobutane CHCI 13.7965 2723.73 -54.885 256.15 352.15 30.39 351.65 Chloroform CHCI 13.7324 2548.74 -54.598 250.15 357.15 29.24 334.25 Cyclohexane C6H12 13.6568 2723.44 -52.532 282.15 378.15 29.97 353.85 Cyclopentane CHIO 13.9727 2653.90 - 38.640 238.15 344.15 27.30 322.35 -Decane CoH 13.9748 3442.76 - 79.292 338.15 476.15 38.75 447 25 Dichloromethane CH2Cl213.9891 2463.93 -49.910 235.15 333.15 28.06 312.85 Diethyl ether CAH,00 14.0735 2511.29 -41.950 230.15 328.15 26.52 307.55 1.4-Dioxane CH0 15,0967 3579.78 -32.813 293.15 378.15 34.16 374.45 -Eicosane C20H42 144,575 4680.46 -141.050 481.15 652.15 57.49 616.75 Ethanol CH40 6,898 3795.17 -42.232 276.15 369.15 38.56 351.35 Ethylbenzene CyH10 13.9726 3259.93 -60.850 306.15 436.15 35.57 409.35 Ethylene glycol CH. 15.7567 4187.46 -94.500 373.15 495.15 50.73 470.45 n-Heplane C,H16 13.8622 2910.26 -56.718 277.15 396,15 31.77 371.55 1-Hexane CH14 13.8193 2696.04 -48.833 254.15 365.15 28.85 341.85 Methanol CH4O 16.5785 3638.27 --33.650 262.15 356.15 35.21 337.85 Methyl acetate C3HO) 14.2456 2662.78 -53.460 250.15 351.15 30.32 330.05 Methyl ethyl ketone CH40 141334 2838.244 --54.460 265.15 376.15 31.30 352.75 Nitromethane CHNO 14.7513 3331.70 -45.550 329.15 419.15 33.99 374.35 -Nonane C9H20 13.9854 3311.19 -70.456 319.15 451.15 36.91 423.95 isc-Octane 13.6703 2896,31 -52.383 275.15 398.15 30.79 372.35 -Octane CHI 13.9346 3123.13 -63.515 299.15 425.15 34.41 398.75 -Pentane CsHz 13.7667 2451.88 -41.136 228.15 331.15 25.79 309.15 Phenol C6H40 14.4.387 3507.80 -97.750 353.15 481.15 46.18 454.95 1-Propanol CHg 16.1154 3483.67 -67.343 293.15 389.15 41.44 370.35 2-Propanol CHgo 16.6796 3640.20 -53.540 281.15 373.15 39.85 355.35 Toluene CH 13.9320 3056.96 --55.525 286.15 409.15 33.18 383.75 Water H2O 16.3872 3885.70 -42.980 273.15 473.15 40.66 373.15 0-Xylene CHIO 14.0415 3358.79 -61.109 313.15 445.15 36.24 417.55 -Xylene CH10 14.1387 3381.81 -57.000 308.15 439.15 35.66 412.25 p-Xylene CsHio 14.0579 3331.45 -58.523 308.15 439.15 35.67 411.45 Based primarily on data presented by B. E. Poling. J. M. Prausnitz and J. P. O'Connell, The Properties of Gases and Liquids. 5th ed., App. A. McGraw-Hill, New York, 2001. * Antoine parameters adapted from Gmehling et al. See footnote 2. p. 791, **Antoine parameters A are adjusted to reproduce the listed values of T. CHIN Raoult's Law, YIP- pat modified Raoult's Law, y:P = XY Prat Flash calculation: {1+ 2iK = 1 1+V(K-1) AG998 AH 98 AG" RT - . 298 RT + Sie eine -MT - RT R RT The first integral, AB dT = (84)(CT T.) + (7273) + (79 -13) 10 ( {80 - =) AC + = R The 2nd integral, AC, dT = RT AC en sain () + 4 ) + ABCT TO) + (12 - 13 - 2014 AD1 1 T2 T3 ) Excess Gibbs Energy GE RT = x Iny+ x2inya Activity coefficient for Van laar, Iny. = A12 (1+ A12x1 Az A22 Iny2 = A (1+ A12x1/ -2 (










