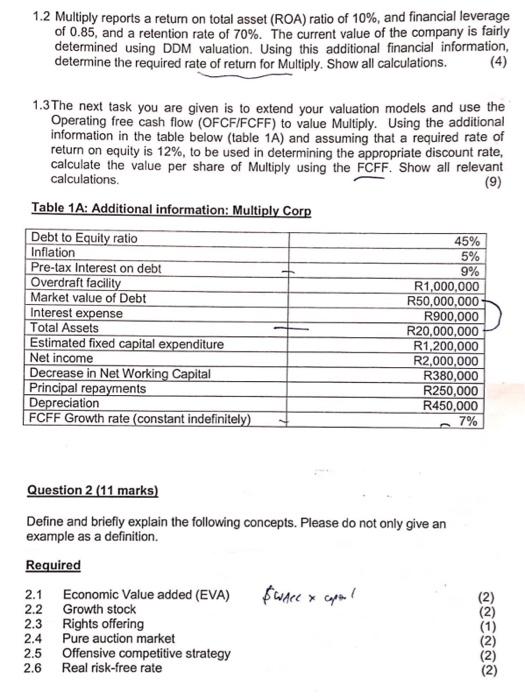
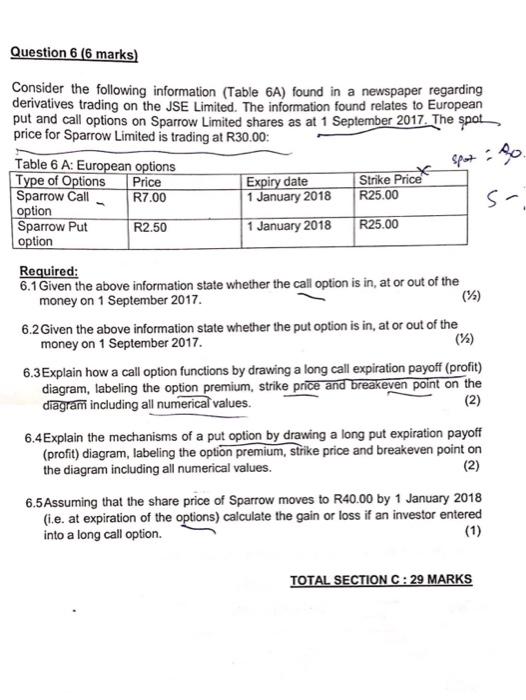
TOTAL SECTION A: 18 MARKS SECTION B (33 marks) PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION B IN THE 4 PAGE BOOK AVAILABLE Question 1 (16 marks) You have been recently employed as a junior analyst at Ultra Invest Inc. Your new role at Ultra Invest entails both share valuation and providing research assistance. Your first company analysis is of a large cap company, Multiply Corporation, which is a leading recreational and sports equipment supplier. The company has recently undergone a major management reshuffle in an effort to roll out a new sales strategy to tap into the gym market. Multiply Corp. currently pays dividends and intends to continue doing so when the company is profitable. The market value of its capital is R21,250,000 with no preference shares in issue. The company is subject to a 30% tax rate and a share currently trades at R85. The projected expected dividends for the next three years respectively are as follows: 212s R1.25, R1.45, R1.60 Required 1.1 It is expected that in three years' time, Multiply will trade at a price multiple of 23 times, a discount rate of 11% and the expected earnings per share for the fourth year is R5. Using the dividend discount model for the three year holding period determine the value of a Multiply Corp share. Keep to 4 decimal place and round off final answer to 2 decimals. (3) 21 250 #slang OS ? 150 o share 5 5 1.2 Multiply reports a return on total asset (ROA) ratio of 10%, and financial leverage of 0.85, and a retention rate of 70%. The current value of the company is fairly determined using DDM valuation. Using this additional financial information, determine the required rate of return for Multiply. Show all calculations, 1.3 The next task you are given is to extend your valuation models and use the Operating free cash flow (OFCF/FCFF) to value Multiply. Using the additional information in the table below (table 1A) and assuming that a required rate of return on equity is 12%, to be used in determining the appropriate discount rate, calculate the value per share of Multiply using the FCFF Show all relevant calculations. (9) Table 1A: Additional information: Multiply Corp Debt to Equity ratio 45% Inflation 5% Pre-tax Interest on debt 9% Overdraft facility R1,000,000 Market value of Debt R50,000,000 Interest expense R900,000 Total Assets R20,000,000 Estimated fixed capital expenditure R1,200,000 Net income R2,000,000 Decrease in Net Working Capital R380,000 Principal repayments R250,000 Depreciation R450,000 FCFF Growth rate (constant indefinitely) 7% Question 2 (11 marks) Define and briefly explain the following concepts. Please do not only give an example as a definition. Required 2.1 Economic Value added (EVA) $ware & capel 2.2 Growth stock 2.3 Rights offering 2.4 Pure auction market Offensive competitive strategy 2.6 Real risk-free rate Qaedas 2.5 Question 3 (6 marks) An investor decided to sell short 100 shares of Ubuntu Company when it is selling at its annual high price of $60 per share. The broker informs him that the margin requirement is 45% and that the commission on the short sale is $150. While the investor is short the stock, Ubuntu pays $3.00 per share dividend. At the end of one year, he purchases the Ubuntu shares to close out his position and is charged a $145 commission and 7% percent interest on the loan. The end of the year quotation from a dealer is as follows: BID: $42.00 ASK: $45.00 Required 3.1 Calculate the rate of return on your initial investment? TOTAL SECTION B: 33 MARKS SECTION C ( 29 marks) PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION C AND D INTHE 8 PAGE BOOK AVAILABLE KEEP ALL INTERIM CALCULATIONS TO 4 DECIMAL PLACES AND ROUND FINAL ANSWERS TO TWO DECIMAL PLACES UNLESS INDICATED OTHERWISE Question 4 (8 marks) You are given the following information with respect to three money market instruments: 1. Reserve Bank Debenture (RBD) issued at a yield of 6.5% per annum on 1 June 2017 for 90 days. 2. Treasury Bill (TB) issued at a discount rate of 6.5% per annum on 1June 2017 for 90 days. 3. Negotiable Certificate of Deposit issued at a yield of 7% per annum on 1 June for 182 days. r You have a client that invested a R1 000 000 in all these instruments respectively on 1 June 2017. Your client however sold the NCD after 90 days (30 August 2017) at a yield of 5,5% per annum and asked you to do an analysis of his money market portfolio Required: 4.1 Calculate the consideration at maturity that the client will receive on the RBD. (1) 4.2 Calculate the yield that the client earned on the TB instrument. (2) 4.3 Calculate client's proceeds from selling the NCD after 90 days. (2) 4.4 Calculate the client's rate of return for the NCD over the 90 day holding period. 4.5For the 90 day holding period, rank all three money market instruments from the highest return to the lowest return. (1) (2) Question 5 (15 marks) The following corporate bonds are actively traded on the fixed income securities market listed on the JSE Limited. Table 5A provides the market data as at 1 August 2017 Table 5A: Corporate bond market data Bond Years to maturity Coupon interest Yield to maturity A001 0.5 9.3% 7.74% -B001 1 9.1% 7.87% C001 1.5 9.6% 8.14% D001 12% 8.13% E001 2.5 0% 8.14% F001 12.5% 8.15% Additional information: All bonds pay semi-annual coupon interest All bonds have a par value of R1 Million 2 3 Required: Use the information contained in the above table to answer the following questions: 5.1 After purchasing the F001 bond on the 1st August 2017, a bond trader expects the yield-to-maturity to decrease to 8% per annum one year from today. Assume all future coupons are reinvested at this rate. Calculate the realised (horizon) yield on the F001 bond if the trader sells the bond in one years' time. (5) Pr113 783.62 : 1081677.663 cy: 5.2 Calculate the Macaulay duration of the D001 and the E001. Keep your calculations to 5 decimal places. (5) 5.3 Assume that the B001 has a Macaulay duration of 0.9 years and a convexity of 0.70. Calculate the total price change in Rands if interest rates increase with 30 basis points (5) Question 6 (6 marks) Strike Price Consider the following information (Table 6A) found in a newspaper regarding derivatives trading on the JSE Limited. The information found relates to European put and call options on Sparrow Limited shares as at 1 September 2017. The spot price for Sparrow Limited is trading at R30.00: Table 6 A: European options Type of Options Price Expiry date Sparrow Call R7.00 1 January 2018 R25.00 s- option Sparrow Put R2.50 1 January 2018 R25.00 option Required: 6.1 Given the above information state whether the call option is in, at or out of the money on 1 September 2017 (1) 6.2 Given the above information state whether the put option is in, at or out of the money on 1 September 2017. 6.3 Explain how a call option functions by drawing a long call expiration payoff (profit) diagram, labeling the option premium, strike price and breakeven point on the diagram including all numerical values. (2) 6.4 Explain the mechanisms of a put option by drawing a long put expiration payoff (profit) diagram, labeling the option premium, strike price and breakeven point on the diagram including all numerical values. (2) 6.5Assuming that the share price of Sparrow moves to R40.00 by 1 January 2018 (i.e. at expiration of the options) calculate the gain or loss if an investor entered into a long call option TOTAL SECTION C: 29 MARKS SECTION D (10 marks) PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION C AND D INTHE 8 PAGE BOOK AVAILABLE Question 7 (10 marks) Samantha Ngomane, an engineer who has no children or spouse is a client of the advisory firm that you work for. She has a current asset portfolio of R6 000 000 that she has built up over her accumulation phase. She is age 60 and is planning to retire in one years time, her health is extremely good and according to actuarial predictions, her life expectancy is placed at age 85. She rented homes during her life and she plans on buying a small townhouse as she plans to travel extensively during her retirement. The house that she is going to buy amounts to R1 500 000, including transfer fees and taxes, and she plans to pay cash using the funds from her current asset portfolio Samantha supports a local community center and donates an amount of R5000 per month for less fortunate senior citizens. Samantha will continue with this donation during her retirement. Samantha has given an estimate of her living expenses which amounts to R300 000 per year after tax) to maintain her current lifestyle, this expense is expected to increase with inflation Samantha's will state that all of her assets and belongings will be left to her niece. The inflation expectation forecast over her retirement horizon is expected at 5% per annum. The risk questionnaire she completed shows her risk profile has changed from moderate risk to low risk. We assume no tax requirement after retirement for this client. Table 7A shows her current asset allocation Asset Class Current allocation Money Market 2.5% Government bonds 15% Equities (Large Cap) 60% Equities (Small Cap) 22.5% Property 0% Required: 7.1 Formulate the following elements of investment policy statement: 7.1.1 Return Requirement (include calculations) (3) 7.1.2 Risk Tolerance (1) 7.1.3 Liquidity 7.2 Discuss how her current asset allocation (Table 7A) is not suitable for retirement and how this asset allocation should be changed to prepare for retirement Recommend a new asset allocation for Samantha consistent with her investment policy statement (5) TOTAL SECTION D: 10 MARKS GRAND TOTAL= 90 MARKS END OF PAPER TOTAL SECTION A: 18 MARKS SECTION B (33 marks) PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION B IN THE 4 PAGE BOOK AVAILABLE Question 1 (16 marks) You have been recently employed as a junior analyst at Ultra Invest Inc. Your new role at Ultra Invest entails both share valuation and providing research assistance. Your first company analysis is of a large cap company, Multiply Corporation, which is a leading recreational and sports equipment supplier. The company has recently undergone a major management reshuffle in an effort to roll out a new sales strategy to tap into the gym market. Multiply Corp. currently pays dividends and intends to continue doing so when the company is profitable. The market value of its capital is R21,250,000 with no preference shares in issue. The company is subject to a 30% tax rate and a share currently trades at R85. The projected expected dividends for the next three years respectively are as follows: 212s R1.25, R1.45, R1.60 Required 1.1 It is expected that in three years' time, Multiply will trade at a price multiple of 23 times, a discount rate of 11% and the expected earnings per share for the fourth year is R5. Using the dividend discount model for the three year holding period determine the value of a Multiply Corp share. Keep to 4 decimal place and round off final answer to 2 decimals. (3) 21 250 #slang OS ? 150 o share 5 5 1.2 Multiply reports a return on total asset (ROA) ratio of 10%, and financial leverage of 0.85, and a retention rate of 70%. The current value of the company is fairly determined using DDM valuation. Using this additional financial information, determine the required rate of return for Multiply. Show all calculations, 1.3 The next task you are given is to extend your valuation models and use the Operating free cash flow (OFCF/FCFF) to value Multiply. Using the additional information in the table below (table 1A) and assuming that a required rate of return on equity is 12%, to be used in determining the appropriate discount rate, calculate the value per share of Multiply using the FCFF Show all relevant calculations. (9) Table 1A: Additional information: Multiply Corp Debt to Equity ratio 45% Inflation 5% Pre-tax Interest on debt 9% Overdraft facility R1,000,000 Market value of Debt R50,000,000 Interest expense R900,000 Total Assets R20,000,000 Estimated fixed capital expenditure R1,200,000 Net income R2,000,000 Decrease in Net Working Capital R380,000 Principal repayments R250,000 Depreciation R450,000 FCFF Growth rate (constant indefinitely) 7% Question 2 (11 marks) Define and briefly explain the following concepts. Please do not only give an example as a definition. Required 2.1 Economic Value added (EVA) $ware & capel 2.2 Growth stock 2.3 Rights offering 2.4 Pure auction market Offensive competitive strategy 2.6 Real risk-free rate Qaedas 2.5 Question 3 (6 marks) An investor decided to sell short 100 shares of Ubuntu Company when it is selling at its annual high price of $60 per share. The broker informs him that the margin requirement is 45% and that the commission on the short sale is $150. While the investor is short the stock, Ubuntu pays $3.00 per share dividend. At the end of one year, he purchases the Ubuntu shares to close out his position and is charged a $145 commission and 7% percent interest on the loan. The end of the year quotation from a dealer is as follows: BID: $42.00 ASK: $45.00 Required 3.1 Calculate the rate of return on your initial investment? TOTAL SECTION B: 33 MARKS SECTION C ( 29 marks) PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION C AND D INTHE 8 PAGE BOOK AVAILABLE KEEP ALL INTERIM CALCULATIONS TO 4 DECIMAL PLACES AND ROUND FINAL ANSWERS TO TWO DECIMAL PLACES UNLESS INDICATED OTHERWISE Question 4 (8 marks) You are given the following information with respect to three money market instruments: 1. Reserve Bank Debenture (RBD) issued at a yield of 6.5% per annum on 1 June 2017 for 90 days. 2. Treasury Bill (TB) issued at a discount rate of 6.5% per annum on 1June 2017 for 90 days. 3. Negotiable Certificate of Deposit issued at a yield of 7% per annum on 1 June for 182 days. r You have a client that invested a R1 000 000 in all these instruments respectively on 1 June 2017. Your client however sold the NCD after 90 days (30 August 2017) at a yield of 5,5% per annum and asked you to do an analysis of his money market portfolio Required: 4.1 Calculate the consideration at maturity that the client will receive on the RBD. (1) 4.2 Calculate the yield that the client earned on the TB instrument. (2) 4.3 Calculate client's proceeds from selling the NCD after 90 days. (2) 4.4 Calculate the client's rate of return for the NCD over the 90 day holding period. 4.5For the 90 day holding period, rank all three money market instruments from the highest return to the lowest return. (1) (2) Question 5 (15 marks) The following corporate bonds are actively traded on the fixed income securities market listed on the JSE Limited. Table 5A provides the market data as at 1 August 2017 Table 5A: Corporate bond market data Bond Years to maturity Coupon interest Yield to maturity A001 0.5 9.3% 7.74% -B001 1 9.1% 7.87% C001 1.5 9.6% 8.14% D001 12% 8.13% E001 2.5 0% 8.14% F001 12.5% 8.15% Additional information: All bonds pay semi-annual coupon interest All bonds have a par value of R1 Million 2 3 Required: Use the information contained in the above table to answer the following questions: 5.1 After purchasing the F001 bond on the 1st August 2017, a bond trader expects the yield-to-maturity to decrease to 8% per annum one year from today. Assume all future coupons are reinvested at this rate. Calculate the realised (horizon) yield on the F001 bond if the trader sells the bond in one years' time. (5) Pr113 783.62 : 1081677.663 cy: 5.2 Calculate the Macaulay duration of the D001 and the E001. Keep your calculations to 5 decimal places. (5) 5.3 Assume that the B001 has a Macaulay duration of 0.9 years and a convexity of 0.70. Calculate the total price change in Rands if interest rates increase with 30 basis points (5) Question 6 (6 marks) Strike Price Consider the following information (Table 6A) found in a newspaper regarding derivatives trading on the JSE Limited. The information found relates to European put and call options on Sparrow Limited shares as at 1 September 2017. The spot price for Sparrow Limited is trading at R30.00: Table 6 A: European options Type of Options Price Expiry date Sparrow Call R7.00 1 January 2018 R25.00 s- option Sparrow Put R2.50 1 January 2018 R25.00 option Required: 6.1 Given the above information state whether the call option is in, at or out of the money on 1 September 2017 (1) 6.2 Given the above information state whether the put option is in, at or out of the money on 1 September 2017. 6.3 Explain how a call option functions by drawing a long call expiration payoff (profit) diagram, labeling the option premium, strike price and breakeven point on the diagram including all numerical values. (2) 6.4 Explain the mechanisms of a put option by drawing a long put expiration payoff (profit) diagram, labeling the option premium, strike price and breakeven point on the diagram including all numerical values. (2) 6.5Assuming that the share price of Sparrow moves to R40.00 by 1 January 2018 (i.e. at expiration of the options) calculate the gain or loss if an investor entered into a long call option TOTAL SECTION C: 29 MARKS SECTION D (10 marks) PLEASE ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION C AND D INTHE 8 PAGE BOOK AVAILABLE Question 7 (10 marks) Samantha Ngomane, an engineer who has no children or spouse is a client of the advisory firm that you work for. She has a current asset portfolio of R6 000 000 that she has built up over her accumulation phase. She is age 60 and is planning to retire in one years time, her health is extremely good and according to actuarial predictions, her life expectancy is placed at age 85. She rented homes during her life and she plans on buying a small townhouse as she plans to travel extensively during her retirement. The house that she is going to buy amounts to R1 500 000, including transfer fees and taxes, and she plans to pay cash using the funds from her current asset portfolio Samantha supports a local community center and donates an amount of R5000 per month for less fortunate senior citizens. Samantha will continue with this donation during her retirement. Samantha has given an estimate of her living expenses which amounts to R300 000 per year after tax) to maintain her current lifestyle, this expense is expected to increase with inflation Samantha's will state that all of her assets and belongings will be left to her niece. The inflation expectation forecast over her retirement horizon is expected at 5% per annum. The risk questionnaire she completed shows her risk profile has changed from moderate risk to low risk. We assume no tax requirement after retirement for this client. Table 7A shows her current asset allocation Asset Class Current allocation Money Market 2.5% Government bonds 15% Equities (Large Cap) 60% Equities (Small Cap) 22.5% Property 0% Required: 7.1 Formulate the following elements of investment policy statement: 7.1.1 Return Requirement (include calculations) (3) 7.1.2 Risk Tolerance (1) 7.1.3 Liquidity 7.2 Discuss how her current asset allocation (Table 7A) is not suitable for retirement and how this asset allocation should be changed to prepare for retirement Recommend a new asset allocation for Samantha consistent with her investment policy statement (5) TOTAL SECTION D: 10 MARKS GRAND TOTAL= 90 MARKS END OF PAPER