Toying With Nature wants to take advantage of children's current fascination with dinosaurs by adding several scale-model dinosaurs to its existing product line. Annual sales of the dinosaurs are estimated at 80,000 units at a price of $6 per unit. Variable manufacturing costs are estimated at $2.50 per unit, incremental fixed manufacturing costs (excluding depreciation) at $41,000 annually, and additional selling and general expenses related to the dinosaurs at $57,000 annually.
To manufacture the dinosaurs, the company must invest $350,000 in design molds and special equipment. Since toy fads wane in popularity rather quickly, Toying With Nature anticipates the special equipment will have a three-year service life with only a $20,000 salvage value. Depreciation will be computed on a straight-line basis. All revenue and expenses other than depreciation will be received or paid in cash. The company's combined federal and state income tax rate is 40 percent.
Required:
a. Prepare a schedule showing the estimated increase in annual net income from the planned manufacture and sale of dinosaur toys.
b. Compute the annual net cash flows expected from this project.
c. Compute the following. Assume discounted at an annual rate of 15 percent. Use Exhibits 26-3 and 26-4 where necessary.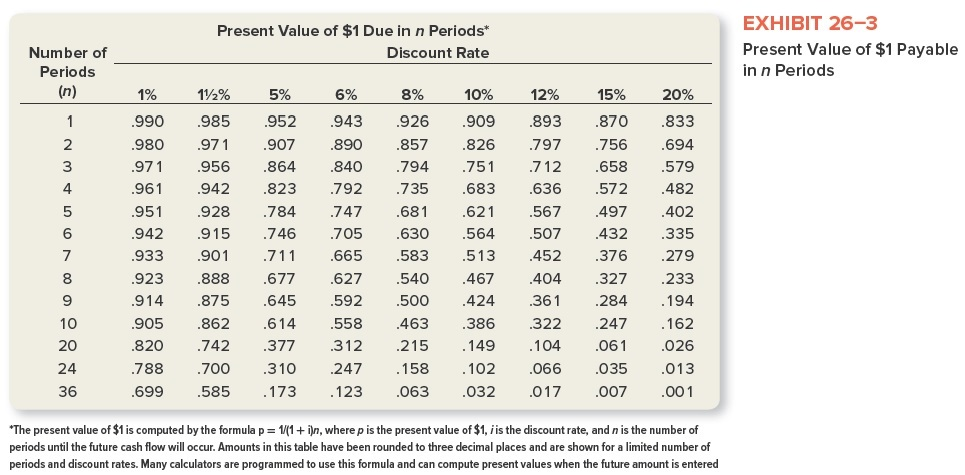
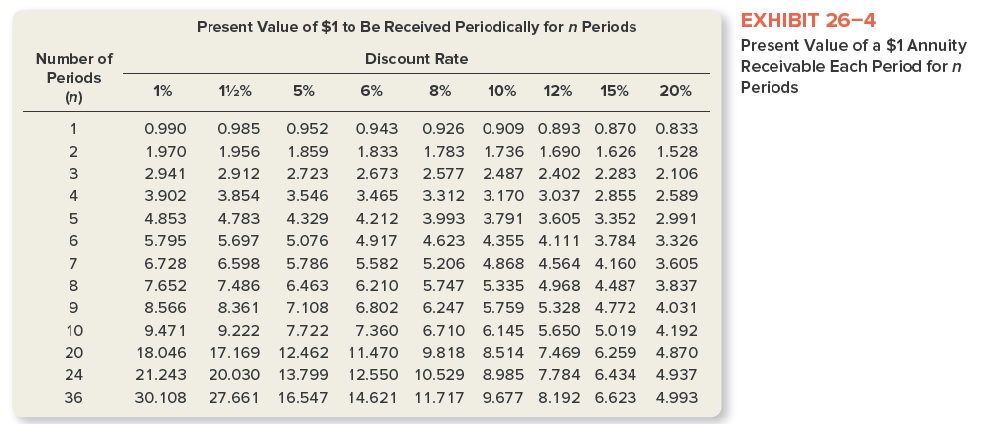
Present Value of $1 Due in n Periods* Discount Rate Number of Periods (n) EXHIBIT 26-3 Present Value of $1 Payable in n Periods 1% 112% 5% 6% 8% 12% 15% 20% 833 1 2 3 .990 .980 .971 .961 985 .971 .956 .942 .926 .857 .794 .735 .694 579 .952 .907 .864 .823 .784 .746 .711 4 5 .951 .942 6 .928 .915 .901 .888 .875 10% .909 .826 .751 .683 .621 .564 .513 .467 .424 .386 .149 .102 .032 943 .890 .840 .792 .747 .705 .665 .627 .592 .558 .312 .247 .123 7 .870 .756 .658 .572 .497 .432 .376 .327 .284 .482 .402 .335 .279 .933 .893 .797 .712 .636 .567 .507 .452 .404 .361 .322 .104 .066 .017 .681 .630 .583 .540 .500 .463 .215 8 .923 .914 9 .233 .194 .162 10 .677 .645 .614 .377 .310 20 .905 .820 .788 .699 .026 .862 .742 .700 .585 .247 .061 .035 .007 .158 24 36 .013 .001 .173 .063 *The present value of $1 is computed by the formula p= 1/(1+i)n, where p is the present value of $1, jis the discount rate, and n is the number of periods until the future cash flow will occur. Amounts in this table have been rounded to three decimal places and are shown for a limited number of periods and discount rates. Many calculators are programmed to use this formula and can compute present values when the future amount is entered Present Value of $1 to Be Received Periodically for n Periods Discount Rate Number of Periods (n) EXHIBIT 26-4 Present Value of a $1 Annuity Receivable Each Period for n Periods 1% 112% 5% 6% 8% 10% 12% 15% 20% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.990 1.970 2.941 3.902 4.853 5.795 6.728 7.652 8.566 9.471 18.046 21.243 30.108 0.985 1.956 2.912 3.854 4.783 5.697 6.598 7.486 8.361 9.222 17.169 20.030 27.661 0.952 1.859 2.723 3.546 4.329 5.076 5.786 6.463 7.108 7.722 12.462 13.799 16.547 0.943 1.833 2.673 3.465 4.212 4.917 5.582 6.210 6.802 7.360 11.470 12.550 14.621 0.926 0.909 0.893 0.870 0.833 1.783 1.736 1.690 1.626 1.528 2.577 2.487 2.402 2.283 2.106 3.312 3.170 3.037 2.855 2.589 3.993 3.791 3.605 3.352 2.991 4.623 4.355 4.111 3.784 3.326 5.206 4.868 4.564 4.160 3.605 5.747 5.335 4.968 4.487 3.837 6.247 5.759 5.328 4.772 4.031 6.710 6.145 5.650 5.0 19 4.192 9.818 8.514 7.469 6.259 4.870 10.529 8.985 7.784 6.434 4.937 11.717 9.677 8.192 6.623 4.993 8 9 10 20 24 36 Present Value of $1 Due in n Periods* Discount Rate Number of Periods (n) EXHIBIT 26-3 Present Value of $1 Payable in n Periods 1% 112% 5% 6% 8% 12% 15% 20% 833 1 2 3 .990 .980 .971 .961 985 .971 .956 .942 .926 .857 .794 .735 .694 579 .952 .907 .864 .823 .784 .746 .711 4 5 .951 .942 6 .928 .915 .901 .888 .875 10% .909 .826 .751 .683 .621 .564 .513 .467 .424 .386 .149 .102 .032 943 .890 .840 .792 .747 .705 .665 .627 .592 .558 .312 .247 .123 7 .870 .756 .658 .572 .497 .432 .376 .327 .284 .482 .402 .335 .279 .933 .893 .797 .712 .636 .567 .507 .452 .404 .361 .322 .104 .066 .017 .681 .630 .583 .540 .500 .463 .215 8 .923 .914 9 .233 .194 .162 10 .677 .645 .614 .377 .310 20 .905 .820 .788 .699 .026 .862 .742 .700 .585 .247 .061 .035 .007 .158 24 36 .013 .001 .173 .063 *The present value of $1 is computed by the formula p= 1/(1+i)n, where p is the present value of $1, jis the discount rate, and n is the number of periods until the future cash flow will occur. Amounts in this table have been rounded to three decimal places and are shown for a limited number of periods and discount rates. Many calculators are programmed to use this formula and can compute present values when the future amount is entered Present Value of $1 to Be Received Periodically for n Periods Discount Rate Number of Periods (n) EXHIBIT 26-4 Present Value of a $1 Annuity Receivable Each Period for n Periods 1% 112% 5% 6% 8% 10% 12% 15% 20% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0.990 1.970 2.941 3.902 4.853 5.795 6.728 7.652 8.566 9.471 18.046 21.243 30.108 0.985 1.956 2.912 3.854 4.783 5.697 6.598 7.486 8.361 9.222 17.169 20.030 27.661 0.952 1.859 2.723 3.546 4.329 5.076 5.786 6.463 7.108 7.722 12.462 13.799 16.547 0.943 1.833 2.673 3.465 4.212 4.917 5.582 6.210 6.802 7.360 11.470 12.550 14.621 0.926 0.909 0.893 0.870 0.833 1.783 1.736 1.690 1.626 1.528 2.577 2.487 2.402 2.283 2.106 3.312 3.170 3.037 2.855 2.589 3.993 3.791 3.605 3.352 2.991 4.623 4.355 4.111 3.784 3.326 5.206 4.868 4.564 4.160 3.605 5.747 5.335 4.968 4.487 3.837 6.247 5.759 5.328 4.772 4.031 6.710 6.145 5.650 5.0 19 4.192 9.818 8.514 7.469 6.259 4.870 10.529 8.985 7.784 6.434 4.937 11.717 9.677 8.192 6.623 4.993 8 9 10 20 24 36








